【AIOPS】AI Agent 专题【左扬精讲】(MCP+A2A+LangChain/LangGraph)—— 纯 Go 实现 AIOPS AI Agent:Function Calling
【AIOPS】AI Agent 专题【左扬精讲】(MCP+A2A+LangChain/LangGraph)—— 纯 Go 实现 AIOPS AI Agent:Function Calling
引言
本次精讲的 AIOPS AI Agent 专题中,MCP、A2A(Agent-to-Agent)与 LangChain/LangGraph 共同构成了复杂 Agent 系统的核心架构,而 Function Calling 则是 Agent 连接外部工具的关键能力。网上大多都是依赖 Python 生态,但对于追求高性能、低延迟的分布式系统场景,Go 语言的并发优势和编译型特性更具吸引力。
本文将聚焦纯 Go 实现 Function Calling,从开发环境搭建到完整 Demo 实战,详解如何在 Go 生态中落地 Agent 的工具调用能力,同时适配 MCP+A2A 架构的扩展需求。
一、Function Calling 基础认知 —— 从“是什么”到“为什么需要”
- 核心本质:LLM 自然语言需求 → 结构化函数调用指令 → 工具结果解析 → 自然语言回答
- 与 Agent 闭环的关系:支撑 “思考 - 行动 - 反馈” 的关键环节(意图转指令、结果转回答)
- 通俗理解:让 LLM 从 “会聊天” 到 “会干活” 的能力升级
-
- 意图转指令:Agent 将用户输入 + 工具元信息传给 LLM,LLM 输出结构化的函数调用指令(如 “调用哪个工具、传什么参数”);
- 结果转回答:Agent 执行工具后,将结果回传给 LLM,LLM 生成自然语言总结。
简单说:Function Calling 让 LLM 从“只会聊天”变成“会干活”—— 通过调用外部工具(API、数据库、脚本等)扩展能力边界,解决纯文本无法处理的问题(如数据分析、信息查询、系统操作)。
二、Function Calling 的核心价值(为什么 Agent 离不开它?3大原因)
- 意图结构化:模糊自然语言 → 机器可执行的标准化指令
- 能力外延化:突破 LLM 边界,对接实时数据 / 系统操作 / 第三方服务
- 闭环自动化:端到端无需人工介入,实现 “需求 - 执行 - 反馈 - 回答” 全流程
-
- 意图结构化:将模糊的自然语言(如 “查一下昨天服务器的 5xx 错误数”)转化为机器可执行的结构化指令(如 { "function": "query_error_count", "params": { "date": "2024-10-01", "error_code": "5xx" } });
- 能力外延化:LLM 本身无法访问实时数据、操作系统、调用第三方服务,通过 Function Calling 可对接任意工具(如 Elasticsearch 查询、K8s 接口、HTTP API);
- 闭环自动化:支持 “用户需求 → 工具调用 → 结果反馈 → 最终回答” 的端到端自动化,无需人工介入解析或执行。
三、Function Calling 的技术原理(Agent 中的工作流程讲解)
3.1、定义工具元信息(Agent 与 LLM 的 “沟通协议”)
Agent 必须先向 LLM 说明“可用工具清单”,即工具元信息(Tool Metadata),通常包含:
-
-
- 工具名称(name):唯一标识(如 elasticsearch_query);
- 工具描述(description):告诉 LLM 该工具的用途(如 “查询 Elasticsearch 中的日志数据”);
- 参数列表(parameters):工具所需的输入参数,含参数名、类型、是否必填、描述(如 index:索引名,字符串,必填;query:查询语句,JSON,必填)。
-
type Tool struct {
Name string `json:"name"` // 工具名称
Description string `json:"description"` // 工具描述
Parameters []ToolParam `json:"parameters"` // 参数列表
}
type ToolParam struct {
Name string `json:"name"` // 参数名
Type string `json:"type"` // 参数类型(string/int/bool/json)
Required bool `json:"required"` // 是否必填
Description string `json:"description"` // 参数描述
}
// 示例:Elasticsearch 查询工具
var ElasticsearchQueryTool = Tool{
Name: "elasticsearch_query",
Description: "用于查询 Elasticsearch 中的日志或数据,支持 Lucene 语法或 DSL 查询",
Parameters: []ToolParam{
{
Name: "index",
Type: "string",
Required: true,
Description: "Elasticsearch 索引名(支持通配符,如 log-2024-10-*)",
},
{
Name: "dsl",
Type: "json",
Required: true,
Description: "Elasticsearch 查询 DSL(JSON 字符串格式)",
},
{
Name: "size",
Type: "int",
Required: false,
Description: "返回结果数量,默认 10",
},
},
}
3.2、构造 Prompt 并调用 LLM
Agent 将“用户输入 + 工具元信息 + 系统指令”组合成 Prompt,发送给支持 Function Calling 的 LLM(如 GPT-3.5/4、Claude 3、通义千问、智谱清言等)。
func buildPrompt(userInput string, tools []Tool) string {
systemPrompt := `你是一个 AIOps 助手,负责通过工具查询和分析服务器日志。
可用工具:%s
如果用户的需求需要查询日志,请调用对应的工具,输出格式为 JSON:{"function": "工具名称", "params": {"参数名": "参数值"}}
如果不需要调用工具,直接返回自然语言回答。`
// 将工具元信息转为 JSON 字符串
toolsJSON, _ := json.MarshalIndent(tools, "", " ")
return fmt.Sprintf(systemPrompt, toolsJSON) + "\n\n用户需求:" + userInput
}
3.3、解析 LLM 响应,判断是否调用工具
LLM 会根据 Prompt 输出两种结果之一:
-
-
- 直接回答:无需调用工具(如用户问 “什么是 5xx 错误”);
- 函数调用指令:需要调用工具(结构化 JSON 格式)。
-
Agent 需要解析 LLM 响应,核心是区分两种结果并校验函数调用的合法性(如工具是否存在、必填参数是否齐全)。
type FunctionCall struct {
Function string `json:"function"`
Params map[string]interface{} `json:"params"`
}
func parseLLMResponse(llmOutput string, tools []Tool) (interface{}, error) {
// 尝试解析为 FunctionCall(JSON 格式)
var funcCall FunctionCall
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(llmOutput), &funcCall); err == nil {
// 校验工具是否存在
toolExists := false
for _, t := range tools {
if t.Name == funcCall.Function {
toolExists = true
break
}
}
if !toolExists {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("工具不存在:%s", funcCall.Function)
}
// 校验必填参数(简化版)
// ...(可根据工具元信息校验 params 中的必填项)
return funcCall, nil
}
// 若解析失败,视为直接回答
return llmOutput, nil
}
3.4、调用工具服务(HTTP/gRPC)
- 工具服务封装原则:标准化输入 / 输出(JSON 格式)
- Go 实现:工具调用函数(以 Elasticsearch 为例)
- 参数类型转换、请求构造、响应读取关键细节
- 常见问题处理(超时重试、异常捕获)
// 假设已有 Elasticsearch 客户端(使用官方 go-elasticsearch 库)
func callElasticsearchTool(params map[string]interface{}) (string, error) {
index, ok := params["index"].(string)
if !ok {
return "", fmt.Errorf("index 参数必须是字符串")
}
dslStr, ok := params["dsl"].(string)
if !ok {
return "", fmt.Errorf("dsl 参数必须是 JSON 字符串")
}
size := 10
if s, ok := params["size"].(float64); ok { // JSON 解析数字默认是 float64
size = int(s)
}
// 构造 Elasticsearch 查询请求
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", fmt.Sprintf("http://es-host:9200/%s/_search", index), strings.NewReader(dslStr))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
// 发送请求(使用 http.Client 或 es 官方客户端)
client := &http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 读取响应结果
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return string(body), nil
}
3.5、结果回传 LLM,生成最终回答
工具调用成功后,Agent 将“用户原始需求 + 工具返回结果”再次发送给 LLM,请求 LLM 生成自然语言格式的总结回答。
func buildFinalPrompt(userInput, toolResult string) string {
prompt := `用户需求:%s
工具返回结果:%s
请根据工具结果,用自然语言总结回答用户的问题,无需调用任何工具。`
return fmt.Sprintf(prompt, userInput, toolResult)
}
// 调用 LLM 生成最终回答
finalLLMOutput, err := callLLM(buildFinalPrompt(userInput, toolResult))
四、Go 语言实现 Function Calling 的关键注意事项
作为 Go 开发者,实现时需重点关注以下 4 点,确保稳定性和可扩展性:
4.1、选择支持 Function Calling 的 LLM SDK
Go 生态中,主流 LLM 都提供了官方或第三方 SDK,支持直接传递工具元信息(无需手动构造 JSON Prompt),推荐使用:
五、核心逻辑梳理(Go 与 MCP+A2A+Function Calling)
在 AIOPS AI Agent 架构中,各组件的职责与 Go 语言的适配逻辑如下:
-
-
- Function Calling:Agent 的 "执行器",负责调用外部工具(API、数据库、脚本等)完成具体任务,Go 语言通过 HTTP/gRPC 服务封装工具逻辑,提供高性能的调用端点。
- A2A(Agent-to-Agent):Agent 间的协作协议,Go 语言的接口化设计和轻量级 RPC 框架(如 gRPC)可实现标准化的 Agent 通信,确保协作流程的高效可靠。
- MCP(Meta-Control Plane):全局调度中心,Go 语言的高并发特性适合处理多 Agent 调度、任务分解与状态监控,可作为 MCP 的核心开发语言。
- 无 Python 依赖的优势:避免 GIL 带来的性能瓶颈,编译后的二进制文件部署更轻便,与 Kubernetes、Prometheus 等云原生组件的生态兼容性更强,适合大规模分布式 AIOPS 场景。
-
简单来说,Go 语言可同时承担 "工具实现"(Function Calling 载体)、"Agent 协作"(A2A 通信层)和 "全局调度"(MCP 核心)的角色,形成全栈式的 Agent 开发体系。
六、开发环境准备
6.1、基础环境准备
6.2、环境搭建准备
# 1. 创建项目目录 mkdir go-ai-agent-function-calling && cd go-ai-agent-function-calling # 2. 初始化Go模块 go mod init github.com/your-username/go-ai-agent # 3. 安装依赖库 go get github.com/sashabaranov/go-openai go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin go get github.com/google/uuid
6.3、前置准备
-
- OpenAI API Key:前往OpenAI Platform获取,用于调用 LLM 的 Function Calling 能力
- 环境变量配置:创建.env文件存储 API Key(使用github.com/joho/godotenv加载,可选)
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-your-api-key-here OPENAI_BASE_URL=https://api.openai.com/v1
七、纯 Go 实战:Function Calling Demo(天气查询 Agent)
7.1、场景定义
7.2、三层架构设计
-
- 工具层:Go 实现天气查询 HTTP 服务(模拟真实工具,可替换为第三方天气 API)
- Agent 层:Go 实现 Agent 核心逻辑(接收用户输入、调用 LLM 判断是否需要工具调用、执行工具请求、整合结果)
- 通信层:基于 HTTP 协议实现 Agent 与工具的交互,遵循 Function Calling 协议规范
7.3、实现 Function 工具(天气查询 HTTP 服务)
-
入参结构体(WeatherRequest)与校验
-
出参结构体(WeatherResponse)设计(含业务预处理字段)
-
模拟数据返回(支持多城市差异化结果)
-
-
服务启动与测试(端口 8081)
首先编写一个独立的天气查询工具,暴露 HTTP 接口供 Agent 调用,工具的入参 / 出参需符合 JSON 格式(便于 Agent 解析)。
tools/weather_server.go:
package main
import (
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// WeatherRequest 工具入参结构(需与Agent的Function Calling定义一致)
type WeatherRequest struct {
City string `json:"city" binding:"required"` // 城市名称(必填)
}
// WeatherResponse 工具出参结构(Agent需基于此结构解析结果)
type WeatherResponse struct {
City string `json:"city"` // 城市
Date string `json:"date"` // 日期(格式:YYYY-MM-DD)
Temperature string `json:"temperature"` // 气温范围
Condition string `json:"condition"` // 天气状况(晴/雨/多云)
UVIndex int `json:"uv_index"` // 紫外线指数
UpdatedAt time.Time `json:"updated_at"` // 数据更新时间
IsValidTrip bool `json:"is_valid_trip"` // 是否适合出游(工具层预处理,减少Agent计算)
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// 天气查询工具接口(POST方法,符合RESTful规范)
r.POST("/api/tool/weather", func(c *gin.Context) {
var req WeatherRequest
// 解析入参(必填字段校验)
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&req); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "参数错误:缺少城市名称", "code": 400})
return
}
// 模拟天气数据(真实场景替换为第三方天气API调用,如高德/百度天气API)
mockResp := WeatherResponse{
City: req.City,
Date: time.Now().AddDate(0, 0, 1).Format("2006-01-02"), // 明天日期
Temperature: "22°C ~ 28°C",
Condition: "晴",
UVIndex: 5,
UpdatedAt: time.Now(),
IsValidTrip: true, // 晴+气温适宜=适合出游
}
// 模拟不同城市的天气差异
switch req.City {
case "上海":
mockResp.Condition = "多云转小雨"
mockResp.Temperature = "18°C ~ 23°C"
mockResp.UVIndex = 3
mockResp.IsValidTrip = false // 有雨=不适合出游
case "广州":
mockResp.Condition = "雷阵雨"
mockResp.Temperature = "25°C ~ 30°C"
mockResp.UVIndex = 6
mockResp.IsValidTrip = false
}
// 返回工具结果(HTTP 200表示成功)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, mockResp)
})
// 启动工具服务(端口:8081,避免与Agent端口冲突)
if err := r.Run(":8081"); err != nil {
panic("天气工具服务启动失败:" + err.Error())
}
}
7.4、实现 Agent 核心逻辑 —— 核心逻辑完整代码
Agent 是整个系统的 “大脑”。它需要具备以下能力:
-
-
-
- 接收用户的自然语言输入。
- 将用户输入和工具的元信息(如描述、参数)发送给 LLM。
- 解析 LLM 的响应,判断是直接返回答案还是需要调用工具。
- 如果需要调用工具,则构造请求并发送给工具服务(HTTP/gRPC)。
- 获取工具返回的结果,并将结果再次发送给 LLM,请求其生成最终的、自然语言格式的回答。
- 将最终回答返回给用户。
-
-
这个过程通常被称为“Function Calling Loop”。
创建 .env:
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=sk-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX -> 马赛克脱敏
创建 agent/main.go:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"github.com/joho/godotenv"
)
// Tool 工具元信息结构体
type Tool struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Description string `json:"description"`
Parameters []ToolParam `json:"parameters"`
}
// ToolParam 工具参数结构体
type ToolParam struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Type string `json:"type"`
Required bool `json:"required"`
Description string `json:"description"`
}
// 定义天气查询工具元信息
var WeatherQueryTool = Tool{
Name: "weather_query",
Description: "用于查询指定城市次日的天气情况,判断是否适合出游",
Parameters: []ToolParam{
{
Name: "city",
Type: "string",
Required: true,
Description: "城市名称(如北京、上海、广州)",
},
},
}
// FunctionCall 工具调用结构体
type FunctionCall struct {
Function string `json:"function"`
Params map[string]interface{} `json:"params"`
}
// Qwen API 相关结构体
type Message struct {
Role string `json:"role"`
Content string `json:"content"`
}
type RequestBody struct {
Model string `json:"model"`
Messages []Message `json:"messages"`
}
func callQwen(apiKey, prompt string) (string, error) {
// 创建 HTTP 客户端
client := &http.Client{}
// 构建请求体
requestBody := RequestBody{
Model: "qwen-plus", // 使用qwen-plus模型
Messages: []Message{
{
Role: "user",
Content: prompt,
},
},
}
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(requestBody)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("序列化请求体失败:%v", err)
}
// 创建 POST 请求
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1/chat/completions", bytes.NewBuffer(jsonData))
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("创建请求失败:%v", err)
}
// 设置请求头
req.Header.Set("Authorization", "Bearer "+apiKey)
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
// 发送请求
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("发送请求失败:%v", err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 读取响应体
bodyText, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("读取响应失败:%v", err)
}
// 检查HTTP状态码
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return "", fmt.Errorf("API返回错误(状态码:%d):%s", resp.StatusCode, string(bodyText))
}
return string(bodyText), nil
}
func buildToolCallPrompt(userInput string, tools []Tool) string {
systemPrompt := `你是一个天气助手,负责处理用户的天气查询需求。
可用工具:
%s
如果用户的需求需要查询天气,请严格按照以下JSON格式输出工具调用指令:
{"function": "工具名称", "params": {"参数名": "参数值"}}
如果不需要调用工具,直接返回自然语言回答。`
// 将工具元信息转为格式化JSON字符串
toolsJSON, err := json.MarshalIndent(tools, "", " ")
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("工具元信息序列化失败:%v", err))
}
return fmt.Sprintf(systemPrompt, toolsJSON) + "\n\n用户需求:" + userInput
}
func parseLLMResponse(llmOutput string) (interface{}, error) {
// 尝试解析为 FunctionCall 结构体(工具调用指令)
var fullResponse map[string]interface{}
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(llmOutput), &fullResponse); err != nil {
// 如果不是JSON格式,视为直接回答
return llmOutput, nil
}
// 提取choices[0].message.content字段
choices, ok := fullResponse["choices"].([]interface{})
if !ok || len(choices) == 0 {
return llmOutput, nil
}
firstChoice, ok := choices[0].(map[string]interface{})
if !ok {
return llmOutput, nil
}
message, ok := firstChoice["message"].(map[string]interface{})
if !ok {
return llmOutput, nil
}
content, ok := message["content"].(string)
if !ok {
return llmOutput, nil
}
// 尝试解析content为FunctionCall
var funcCall FunctionCall
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(content), &funcCall); err == nil {
// 校验工具是否存在
validTools := []string{"weather_query"}
toolExists := false
for _, t := range validTools {
if t == funcCall.Function {
toolExists = true
break
}
}
if !toolExists {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("工具不存在:%s", funcCall.Function)
}
// 校验必填参数(以天气工具为例)
if funcCall.Function == "weather_query" {
if _, ok := funcCall.Params["city"]; !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("天气查询工具缺少必填参数:city")
}
if city, ok := funcCall.Params["city"].(string); !ok || city == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("city参数必须是非空字符串")
}
}
return funcCall, nil
}
// 解析失败,视为直接回答
return content, nil
}
func callWeatherTool(city string) (string, error) {
// 构造工具请求参数
toolReq := map[string]string{
"city": city,
}
reqBody, err := json.Marshal(toolReq)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("构造天气工具请求参数失败:%v", err)
}
// 调用天气工具 HTTP 接口(工具服务运行在 8081 端口)
resp, err := http.Post(
"http://localhost:8081/api/tool/weather",
"application/json",
bytes.NewBuffer(reqBody),
)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("调用天气工具失败:%v", err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 读取工具响应
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("读取天气工具响应失败:%v", err)
}
// 校验 HTTP 状态码
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return "", fmt.Errorf("天气工具返回错误(状态码:%d):%s", resp.StatusCode, body)
}
return string(body), nil
}
func buildFinalPrompt(userInput, toolResult string) string {
prompt := `你是一个天气助手,需要根据天气数据回答用户的问题。
用户需求:%s
天气数据:%s
请根据提供的天气数据,用简洁、易懂的自然语言回答用户的问题。回答中应包含:
1. 城市和日期
2. 天气状况
3. 温度范围
4. 是否适合出游的建议
回答示例:
北京明天的天气为晴,气温22°C ~ 28°C,紫外线指数5,适合出游。`
return fmt.Sprintf(prompt, userInput, toolResult)
}
func main() {
// 加载 .env 环境变量
if err := godotenv.Load("../.env"); err != nil {
log.Printf("加载.env文件失败(非必选):%v\n", err)
}
// 从环境变量获取API Key
apiKey := os.Getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")
if apiKey == "" {
log.Fatal("请在.env文件中设置 DASHSCOPE_API_KEY 环境变量")
}
// 用户输入示例
userInput := "北京明天天气适合出游吗?"
fmt.Printf("用户需求:%s\n\n", userInput)
// 构造 Prompt,调用 Qwen 获取工具调用指令
tools := []Tool{WeatherQueryTool}
prompt := buildToolCallPrompt(userInput, tools)
llmOutput, err := callQwen(apiKey, prompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("调用Qwen生成工具指令失败:%v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Qwen 原始响应:%s\n\n", llmOutput)
// 解析 Qwen 响应
parsedResult, err := parseLLMResponse(llmOutput)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("解析Qwen响应失败:%v", err)
}
// 判断是否需要调用工具
switch result := parsedResult.(type) {
case string:
// 无需调用工具,直接返回回答
fmt.Printf("最终回答:%s\n", result)
case FunctionCall:
// 需要调用工具,执行工具调用逻辑
fmt.Printf("需要调用工具:%s,参数:%v\n\n", result.Function, result.Params)
// 调用天气工具
city := result.Params["city"].(string)
toolResult, err := callWeatherTool(city)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("调用天气工具失败:%v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("天气工具返回结果:%s\n\n", toolResult)
// 构造最终 Prompt,调用 Qwen 生成自然语言回答
finalPrompt := buildFinalPrompt(userInput, toolResult)
finalAnswer, err := callQwen(apiKey, finalPrompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("调用Qwen生成最终回答失败:%v", err)
}
// 输出最终回答
fmt.Printf("最终回答:%s\n", finalAnswer)
default:
log.Fatal("未知的解析结果类型")
}
}
创建 README.md:
# Go AI Agent - 天气查询演示
这是一个使用 Go 语言开发的 AI Agent 示例项目,专门演示如何构建一个能够查询天气的智能代理系统,使用通义千问 API 作为语言模型。
## 项目结构
```
go-ai-agent/
├── agent/ # AI Agent 实现
│ └── main.go # Agent 主程序
├── tools/ # 工具实现
│ └── weather_server.go # 天气查询工具服务
├── .env # 环境变量配置文件
└── README.md # 项目说明文档
```
## 功能特性
1. **Function Calling**: 实现了类似 OpenAI Function Calling 的机制,让 Agent 能够根据用户需求决定是否调用天气查询工具
2. **模块化设计**: 工具和 Agent 分离,便于独立开发和测试
3. **HTTP API 集成**: 工具通过 HTTP API 提供服务,便于独立部署和维护
4. **天气查询**: 查询指定城市次日的天气情况,并判断是否适合出游
5. **通义千问 API 集成**: 使用阿里云通义千问作为语言模型
## 快速开始
### 环境准备
1. 安装 Go 1.16+
### 安装依赖
```bash
go mod tidy
```
### 配置环境变量
在项目根目录创建 `.env` 文件,并添加你的 DashScope API Key:
```env
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=sk-马赛克脱敏,用你自己的。
```
注意:出于安全考虑,不应将敏感信息硬编码在代码中。在生产环境中,请使用更安全的方式来管理密钥。
### 启动工具服务
```bash
cd tools
go run weather_server.go
```
工具服务将在 `localhost:8081` 上启动,提供天气查询 API。
### 运行 Agent
```bash
cd agent
go run main.go
```
## 天气查询工具 API
工具通过 HTTP POST 方法提供服务:
- URL: `http://localhost:8081/api/tool/weather`
- 参数:
```json
{
"city": "北京"
}
```
- 返回:
```json
{
"city": "北京",
"date": "2023-08-20",
"temperature": "22°C ~ 28°C",
"condition": "晴",
"uv_index": 5,
"updated_at": "2023-08-19T10:00:00Z",
"is_valid_trip": true
}
```
## 通义千问 API 配置
项目使用环境变量来管理 API 密钥,确保敏感信息不会被硬编码在代码中。
在 `.env` 文件中配置你的 API Key:
```env
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=your_actual_api_key_here
```
## 核心代码说明
### Agent 部分 ([agent/main.go](file:///d%3A/worker-go/go-ai-agent/agent/main.go))
主要包含以下功能:
1. 从环境变量加载 API 密钥
2. 初始化通义千问客户端
3. 构造 Prompt 并调用通义千问 API
4. 解析通义千问响应,判断是否需要调用工具
5. 调用天气查询工具
6. 根据工具返回结果生成最终回答
特别说明:近期修复了对 DashScope API 响应格式的解析逻辑。原先的实现假设模型直接返回工具调用指令,但实际上 DashScope API 会在响应的 `choices[0].message.content` 字段中包装实际内容。新的实现能够正确解析这种嵌套结构,提取真正的工具调用指令。
### 工具部分 ([tools/weather_server.go](file:///d%3A/worker-go/go-ai-agent/tools/weather_server.go))
主要包含以下功能:
1. 提供 HTTP API 接口
2. 解析城市参数
3. 模拟天气数据(实际项目中可替换为真实天气 API)
4. 返回结构化天气信息
## 扩展建议
如果你想基于这个演示项目进行扩展,可以考虑以下方向:
1. **集成真实天气 API**:替换模拟数据,接入真实的天气服务(如高德、百度天气 API)
2. **增加更多城市支持**:扩展不同城市的天气数据和出游建议
3. **丰富天气信息**:添加风力、湿度、空气质量等更多信息
4. **添加对话历史管理**:支持多轮天气查询对话
5. **实现工具结果缓存**:避免重复查询同一城市的天气
6. **添加错误处理和重试机制**:提高系统稳定性
7. **支持更多工具类型**:扩展 Agent 的能力范围,例如新闻查询、股票信息等
7.5、运行步骤
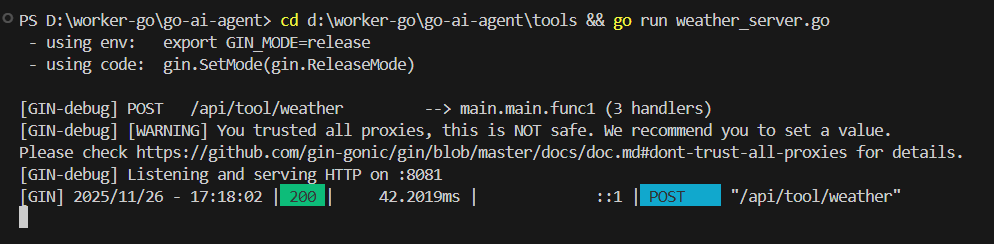
7.5.1、第一步:启动天气工具服务
cd tool go run weather_server.go
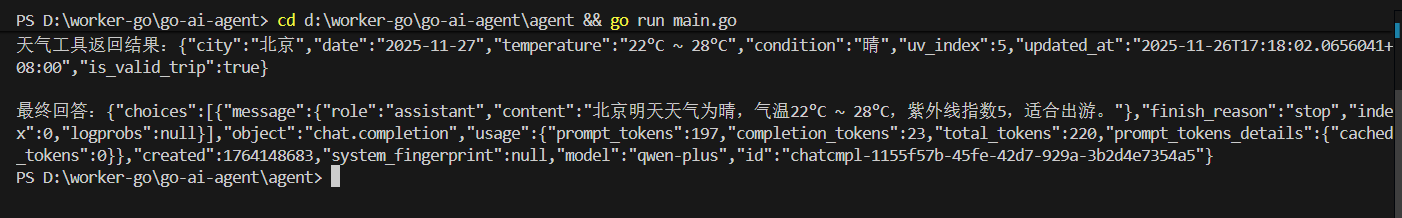
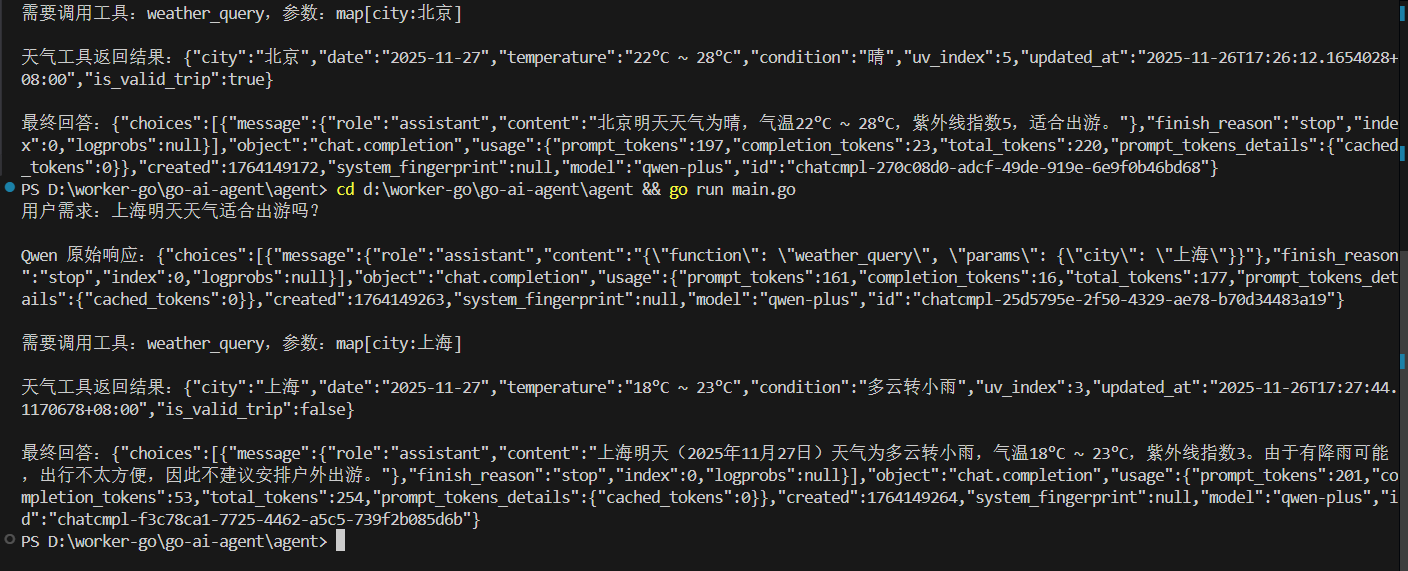
7.5.2、第二步:启动 Agent 程序
cd agent go run main.go





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号