东方博宜OJ 2191:树的重心(2)← 链式前向星 or 邻接表
【题目来源】
【题目描述】
给定一棵树,树中有 n 个结点(编号 1~n)。请求出,删除该重心后,剩余子树的最多结点数?
重心定义:重心是指树中的一个结点,如果将这个点删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值最小,那么这个结点被称为树的重心。
【输入格式】
第 1 行读入一个整数 n,代表树的结点的数量(1≤n≤10^5)。
接下来 n-1 行,每行读入两个整数 x 和 y,表示结点 x 和 y 之间有一条边。(注意:不确定 x 和 y 的父子关系)
【输出格式】
输出一个整数,代表删除重心后,剩余子树的最多结点。
【输入样例】
9
1 2
1 7
2 8
2 5
4 3
1 4
3 9
4 6
【输出样例】
4
【数据范围】
1≤n≤10^5
【算法分析】
若树的示意图如下所示,则依据定义分析“树的重心”求解过程如下。
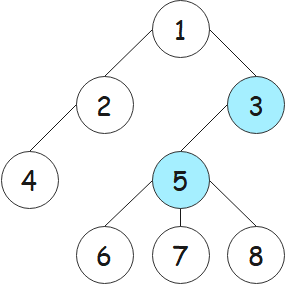
删除结点 1,产生的两个连通块中结点数分别为 2、5,最大值为 5;
删除结点 2,产生的两个连通块中结点数分别为 1、6,最大值为 6;
删除结点 3,产生的两个连通块中结点数分别为 3、4,最大值为 4;
删除结点 4,产生的一个连通块中结点数分别为 7,最大值为 7;
删除结点 5,产生的四个连通块中结点数分别为 1、1、1、4,最大值为 4;
删除结点 6,产生的一个连通块中结点数分别为 7,最大值为 7;
删除结点 7,产生的一个连通块中结点数分别为 7,最大值为 7;
删除结点 8,产生的一个连通块中结点数分别为 7,最大值为 7。
综上,可知 8 个最大值中的最小值为 4,但有两个。也就是说,给出的树有两个重心,分别为结点 3、结点 5。
【算法代码一:链式前向星】
本题代码与“AcWing 846:树的重心”相同。详见:
【算法代码二:邻接表】
【参考文献】




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号