Spring 系列生态-Spring AOP,Spring Data JPA, Spring Batch,Spring Cloud, Spring Security
Spring框架,Java领域流行的轻量级开源框架,以其模块化、松耦合的设计和强大的依赖注入、面向切面编程能力著称。在.Net 中 也提供了这些开源框架,但是没有形成统一的体系框架
1. Spring框架概述与核心依赖注入(DI)
Spring框架的诞生与发展
Spring框架自2003年问世以来,一直是Java开发者首选的轻量级企业级应用开发框架。其最初由Rod Johnson创立并发表于《Expert One-to-One J2EE Design and Development》一书中,旨在解决传统企业应用开发中的复杂性问题。经过多年的发展,Spring逐渐演变成了一个全面的编程和配置模型,不仅支持众多的Java功能,还支持云计算、大数据等现代软件开发的需求。
Spring框架的核心价值与优势
Spring框架的核心价值在于其非侵入式编程模型和依赖注入(DI)机制,降低了对象间的耦合度,提高了系统的可测试性和模块化。Spring的一个主要优势是通过IoC容器管理对象的生命周期和配置,它允许开发者专注于业务逻辑,而非繁琐的配置和初始化代码。此外,Spring提供了丰富的编程和配置模型,支持多种数据访问技术,强化了事务管理,并提供了对RESTful Web Services的全面支持。
依赖注入(DI)的设计理念
依赖注入(Dependency Injection, DI)是一种设计模式,它允许创建对象的外部资源的控制权传递给对象。这种模式的出现是对传统的“new”操作符创建对象方法的改进,它鼓励松耦合和更好的代码组织。在Spring中,依赖注入的核心是通过IoC(控制反转)容器来实现的,容器会根据配置,将被依赖对象注入到需要它们的对象中。
依赖注入的实现方式与应用场景
依赖注入主要有两种方式:构造器注入和设值注入。构造器注入是在创建对象时通过构造函数强制提供依赖项,而设值注入是通过对象的setter方法注入依赖项。选择哪种方式取决于具体的应用场景和开发者的偏好。通常,构造器注入用于必需的依赖,而设值注入用于可选的依赖。依赖注入可以应用于许多场景,比如服务层组件的构造、测试时替换依赖以实现mock对象,或者在Spring MVC中注入控制器层的依赖。
2. Spring AOP(面向切面编程)
Spring AOP 可以通过在方法执行前后插入额外的功能来增强业务逻辑,常用于日志记录、性能监控、安全控制等场景。
基本概念
- 切面(Aspect):切面是一个关注点的模块化,包含了横切关注点的功能代码,比如日志、安全等。
- 连接点(JoinPoint):程序执行的某个点,比如方法调用。
- 通知(Advice):定义在切面中,指定在连接点处执行的操作。通知有多种类型,包括
@Before、@After、@Around等。 - 切入点(Pointcut):指示在什么地方应用通知。通常是通过表达式定义的。
- 织入(Weaving):将通知应用到目标对象的过程
Spring AOP 示例
1. 使用 Maven 构建,首先要在 pom.xml 中添加 AOP 相关的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 创建目标接口
@RestController @RequestMapping("/aop") public class AOPController { @GetMapping("/test") public String test() { System.out.println("Hello, AOP!"); return "Hello, AOP!"; } }
3. 创建切面(Aspect)
package com.example.springbootdemo.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class LoggingAspect { // 定义一个切入点,匹配 AOPController 中所有的方法 @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController.*(..))") public void myServiceMethods() {} // 在方法执行前执行 @Before("myServiceMethods()") public void logBefore() { System.out.println("Before method execution"); /* // 假设有一个方法来获取当前用户信息 User currentUser = getCurrentUser(); // 检查是否有足够的权限 if (!hasPermission(currentUser, "TRANSFER_MONEY")) { throw new UnauthorizedException("User does not have permission to transfer money."); }*/ } // 在方法执行后执行 @After("myServiceMethods()") public void logAfter() { System.out.println("After method execution"); } // 在方法正常返回后执行 @AfterReturning("myServiceMethods()") public void logAfterReturning() { System.out.println("AfterReturning method execution"); } // 在方法抛出异常后执行 @AfterThrowing("myServiceMethods()") public void logAfterThrowing() { System.out.println("AfterThrowing method execution"); } // 环绕通知(既可以在方法前后执行,也可以控制方法是否执行) @Around("myServiceMethods()") public Object logAround(org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 执行目标方法 Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Execution time: " + (end - start) + " ms"); return result; } }
Pointcut:定义了一个切入点,表示我们要拦截 com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController 包中的所有方法。
Before:在目标方法执行之前执行, 比如权限检查、参数校验等。
After:在目标方法执行之后执行,例如更新审计日志。
AfterReturning: 在方法正常返回后执行.
Around:环绕通知,方法执行前后都可以增强,并且能够控制是否执行目标方法, 灵活性较强。
AfterThrowing: 在方法抛出异常后执行
表达式解析: 切点表达式execution(* com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController.*(..)) 用来标记目标方法的执行点,基于 AspectJ 的表达式语言,它用来匹配符合特定条件的方法。这里的表达式含义可以分解为以下几个部分: 1. execution(...):表示匹配方法执行的连接点(JoinPoint)。execution 是 AspectJ 的一个关键字,用于描述方法执行的切点。 2. *:星号(*)表示 任意返回类型。也就是说,这个切点可以匹配任何返回类型的方法,不论它是 void、int 还是其他类型。例如: execution(void com.example.service.MyService.*(..)):只匹配返回类型是 void 的方法。 execution(String com.example.service.MyService.*(..)):只匹配返回类型是 String 的方法。 3. com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController:这是 目标类的完全限定名,表示这个切点只会匹配 com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController 类中的方法。 4. *:第二个星号表示 方法名。这意味着匹配 AOPController类中的 任意方法,不管方法名是什么。也可以指定具体的名称来限制只匹配某些方法。例如: execution(* com.example.service.MyService.process(..)):只匹配 process 方法。 execution(* com.example.service.MyService.*(..)):匹配该类中所有方法。 5. (..):这是 参数列表的匹配,(..) 表示 任意数量和类型的参数,包括零个参数。它可以匹配任意方法的参数列表。 execution(* com.example.service.MyService.*(String)):只匹配接收一个 String 类型参数的方法。 execution(* com.example.service.MyService.*(..)):匹配接收任意参数数量和类型的方法。
所以这里表达式 execution(* com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController.*(..)) 表示匹配 com.example.springbootdemo.controller.AOPController 类中,方法名任意、返回类型任意、参数类型任意的方法。
3. Spring Data JPA
基础概念
jpa 的全称是 Java Persistence API ,ORM 框架中的一种,相当于提供了Dao 层的 持久层API ,不需要我们自己去写持久层,简化了与数据库交互的过程。会根据接口定义的名称自动生成代码,具体接口定义的方式参考这里。
和Mybatis plus 一样都属于ORM框架,JPA可以减少持久层代码开发,开发效率高,但是更适用简单项目快速开发。Mybatis plus 可以更灵活直接操作SQL,对复杂性和较性能要求比较高的系统比较适用
JPA示例
1. 首先要在 pom.xml 中添加 JPA相关的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- (可选)我这里可能是spring boot版本和jpa不兼容,需要添加hibernate-core依赖,并且版本号也要兼容,否则就会报错 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>6.1.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
2. 添加测试类,需要@Entity标识,和无参构造函数。这里可以指定映射的数据库表名和列信息等
@Getter @Setter @Entity //@Table(name = "tb_animal") public class Animal { public Animal() {} @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; //@Column(name = "animalName", nullable = false, length = 50) private String name; private int age; // 构造函数、getter和setter方法省略 // 其他方法... }
3. 创建Repository仓储,继承 JpaRepository ,我这里需要动态查询,所以还继承了 JpaSpecificationExecutor 。JPA会根据方法名称关键字自动生成相应sql实现,不需要我们自己去创建,具体可以参考官方。继承 JpaRepository 之后已经提供了基础的CRUD操作方法,这里可以写一些自定义的方法,并且也可以自定义SQL。
public interface AnimalRepository extends JpaRepository<Animal, Long> ,JpaSpecificationExecutor<Animal>{ //根据名字查找动物 @Lock(LockModeType.READ) Animal findByName(String name); //根据年龄查找动物 List<Animal> findByAge(Integer age); //根据年龄和名字查找动物 @Query("SELECT a FROM Animal a WHERE a.age = :age AND a.name = :name") List<Animal> findListByCustomQuery(Integer age, String name); //根据年龄大于某个值查找动物 List<Animal> findByAgeGreaterThan(int age); @Transactional(timeout = 30) @Query("Update Animal set age = ?1 where name = ?2") Boolean UpdateAnimal(Integer age, String name); }
4. 添加application.yaml 配置
spring: application: name: SpringBootDemo datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false username: root password: hua3182486 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jpa: show-sql: true #控制台打印最终的sql语句,方便开发时查看生成的sql语句是否正确 #generate-ddl: true hibernate: ddl-auto: update #update:该配置比较常用,当服务首次启动会在数据库中生成相应表,后续启动服务时如果实体类有增加属性会在数据中添加相应字段,原来数据仍在保留 #create :该值慎用,每次重启项目的时候都会删除表结构,重新生成,原来数据会丢失不见。 #create-drop :慎用,当项目关闭,数据库中的表会被删掉。 #validate : 验证数据库和实体类的属性是否匹配,不匹配将会报错。 properties: hibernate.format_sql: true #格式化sql语句 hibernate.dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect #数据库方言,要和数据库匹配
5. 到这里就弄好了,接下来添加自己的测试服务类,api接口
@Service public class AnimalService { @Autowired private AnimalRepository animalRepository; //根据名字查询 public Animal getAnimalByName(String name) { return animalRepository.findByName(name); } //根据id查询 public Animal getAnimalById(Long id) { return animalRepository.findById(id).orElse(null); } //新增 or 更新 public Animal saveAnimal(Animal animal) { return animalRepository.save(animal); } //删除 public void deleteAnimal(Long id) { animalRepository.deleteById(id); } //动态查询 public List<Animal> getAllUsers(Integer age) { //使用Specification 进行动态查询 Specification<Animal> spec = Specification.where(null); if (age!= null) { //root 代表查询的根实体对象,在这里它是 Animal 实体的映射 //query 是 CriteriaQuery 的实例,表示实际的查询对象。通常不需要在简单的条件构造中使用它,但是它在处理复杂查询时是非常重要的。例如,在某些情况下,可能需要访问查询的排序、分组或其他信息。 //criteriaBuilder 是 CriteriaBuilder 对象,它用于构造查询的条件,可以使用类似于 SQL 的方法来构造各种条件、表达式和运算符。 spec = spec.and((root, query, criteriaBuilder) -> criteriaBuilder.equal(root.get("age"), age) ); } return animalRepository.findAll(spec); } //自定义查询 public List<Animal> findListByCustomQuery(Integer age, String name) { return animalRepository.findListByCustomQuery( age, name); } //自定义查询 public List<Animal> findByAgeGreaterThan(Integer age) { return animalRepository.findByAgeGreaterThan( age); } //分页查询 public Page<Animal> findListPageable(Integer age, String name) { //root 代表查询的根实体对象,在这里它是 Animal 实体的映射 //query 是 CriteriaQuery 的实例,表示实际的查询对象。通常不需要在简单的条件构造中使用它,但是它在处理复杂查询时是非常重要的。例如,在某些情况下,可能需要访问查询的排序、分组或其他信息。 //criteriaBuilder 是 CriteriaBuilder 对象,它用于构造查询的条件,可以使用类似于 SQL 的方法来构造各种条件、表达式和运算符。 Specification<Animal> spec = (root, query, criteriaBuilder) -> { Predicate predicate = criteriaBuilder.conjunction(); // 没有条件时返回总是为 true 的条件 if (age!= null) { predicate = criteriaBuilder.and(predicate, criteriaBuilder.greaterThan(root.get("age"), age)); } // 如果 name 不为 null,则添加 name 过滤条件 if (name != null && !name.isEmpty()) { predicate = criteriaBuilder.and(predicate, criteriaBuilder.like(root.get("name"), "%" + name + "%")); } return predicate; }; Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "age") .and(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC, "name")); Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, 3).withSort(sort); return animalRepository.findAll(spec,pageable); } }
@RestController @RequestMapping("/data") public class DataController { @Autowired private AnimalService animalService; @GetMapping(value="/getAnimalByName",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public Animal getAnimalByName(String name) { return animalService.getAnimalByName(name); } @GetMapping(value="/getAllUsers",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public List<Animal> getAllUsers(Integer age) { return animalService.getAllUsers(age); } @GetMapping(value="/findByAge",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public List<Animal> findByAge(Integer age) { return animalService.findByAgeGreaterThan(age); } @GetMapping(value="/findListByCustomQuery",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public List<Animal> findListByCustomQuery(Integer age, String name) { return animalService.findListByCustomQuery(age,name); } @GetMapping(value="/getAnimalById",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public Animal getAnimalById(Long id) { return animalService.getAnimalById(id); } @PostMapping(value="/saveAnimal",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public Animal saveAnimal(@RequestBody Animal animal) { return animalService.saveAnimal(animal); } @GetMapping(value="/deleteAnimal",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public Boolean deleteAnimal(Long id) { animalService.deleteAnimal(id); return true; } @GetMapping(value="/PageList",produces="application/json;charset=utf-8") public Page<Animal> PageList(@RequestParam(value = "age", required = false) Integer age,@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false) String name) { return animalService.findListPageable(age,name); } }
4. Spring Batch
Spring Batch是一个开源的批处理框架,旨在帮助企业建立健壮、高效的批处理应用
功能特点:
提供了大量可重用的组件,包括日志、追踪、事务、任务作业统计、任务重启、跳过、重复、资源管理等。
支持大数据量和高性能的批处理任务,提供了高级功能和特性来支持,比如分区功能、远程功能。
可以与Spring的其他组件无缝集成,如Spring Boot、Spring Data等。
核心概念:
Job:批处理任务的最高级别的抽象,包含了多个Step,每个Step执行一个具体的任务。
Step:具体的任务,包含了一个ItemReader、一个ItemProcessor(可选)和一个ItemWriter。
ItemReader:用于读取数据。
ItemWriter:用于写入数据。
ItemProcessor:用于处理数据,将ItemReader读取的数据转换为需要的形式,然后传递给ItemWriter写入。
JobRepository:负责维护作业的状态、各种处理指标,如开始时间、结束时间、状态、读写次数等。
JobLauncher:负责作业的执行,调用execute方法,验证重启作业是否有效,决定如何执行作业(当前线程、线程池),验证参数等。
使用示例
实现一个读取csv文件,并将读取到的内容写入数据库中
1. 首先要在 pom.xml 中添加 batch相关的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 添加批处理配置类
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class BatchConfig {
@Autowired
private JobRepository jobRepository;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
// 定义 Job
@Bean
public Job importUserJob(Step step1) {
return new JobBuilder("importUserJob", jobRepository)
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer()) // 允许任务重复执行
.start(step1)
.build();
}
// 定义 Step
@Bean
public Step step1() {
return new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository)
.<BUser, BUserEntity>chunk(100, transactionManager) // 每处理100条数据后提交事务
.reader(new MyItemReader())
.processor(processor())
.writer(uwriter(dataSource))
.allowStartIfComplete(true) // 确保允许步骤重启
.build();
}
// 1. Reader:从 CSV 读取数据
//业务分离在MyItemRearder中,也可以写在这里
/* @Bean
public FlatFileItemReader<BUser> reader() {
return new FlatFileItemReaderBuilder<BUser>()
.name("userReader")
.resource(new ClassPathResource("users.csv")) // CSV 文件路径,注意这里文件一定要放在/src/main/resource路径下
.delimited()
.names("name", "age", "email") // CSV 列名
.targetType(BUser.class) // 映射到 User 对象
.linesToSkip(1) // 跳过第一行(表头)
.build();
}*/
// 2. 定义 Processor,处理reader读取的数据
@Bean
public ItemProcessor<BUser, BUserEntity> processor() {
return new MyItemProcessor(); // 注入 UserProcessor 实例
}
// 3. 定义 Writer,将处理后的数据写入数据库
@Bean
public JdbcBatchItemWriter<BUserEntity> uwriter(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcBatchItemWriterBuilder<BUserEntity>()
.itemSqlParameterSourceProvider(new BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<>())
.sql("INSERT INTO user (name, age, email) VALUES (:name, :age, :email)")
.dataSource(dataSource)
.build();
}
}
3. 添加 MyItemReader (读取文件), MyItemProcessor(处理数据),MyItemWriter (写入数据,这里没有创建,换了一种方式写在了上面BatchConfig 中)
// 自定义 ItemReader 类 public class MyItemReader implements ItemReader<BUser> { private FlatFileItemReader<BUser> reader; public MyItemReader() { reader = new FlatFileItemReader<>(); reader.setResource(new ClassPathResource("users.csv")); final String[] columnNames; try { columnNames = readHeader(new ClassPathResource("users.csv")); } catch (IOException e) { // 可以根据实际情况进行日志记录或者其他处理 System.err.println("读取 CSV 文件表头时发生错误: " + e.getMessage()); // 这里也可以考虑抛出一个自定义异常,以便上层调用者处理 throw new RuntimeException("读取 CSV 文件表头失败", e); } // 设置行映射器 reader.setLineMapper(new DefaultLineMapper<BUser>() {{ // 使用 DelimitedLineTokenizer 并设置从表头获取列名 DelimitedLineTokenizer tokenizer = new DelimitedLineTokenizer(); tokenizer.setNames(columnNames); // 不手动设置列名,自动从表头读取 tokenizer.setStrict(false); // 设置映射器,将字段映射到 BUser 类的属性 BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<BUser> fieldSetMapper = new BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<>(); fieldSetMapper.setTargetType(BUser.class); setLineTokenizer(tokenizer); setFieldSetMapper(fieldSetMapper); }}); reader.setLinesToSkip(1); // 跳过第一行(表头) try { reader.open(new org.springframework.batch.item.ExecutionContext()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("初始化 ItemReader 失败", e); } } private String[] readHeader(ClassPathResource resource) throws IOException { try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resource.getInputStream()))) { String headerLine = reader.readLine(); return headerLine.split(","); } } @Override public BUser read() throws Exception { return reader.read(); } }
public class MyItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<BUser, BUserEntity> { @Override public BUserEntity process(BUser user) { BUserEntity entity = new BUserEntity(); entity.setName(user.getName().toUpperCase()); entity.setAge(user.getAge()); entity.setEmail(user.getEmail()); return entity; } }
4. 添加测试项

age,name,email 30,John,[email protected] 25,Jane,[email protected] 28,Bob,[email protected]

@lombok.Data public class BUser { private String name; private Integer age; private String email; } @lombok.Data public class BUserEntity { private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }
@RestController @RequestMapping("/BatchJob") public class BatchJobExecutorController { @Autowired private JobLauncher jobLauncher; @Autowired private Job importUserJob; @GetMapping("/executeJob") public void executeJob() { try { JobExecution execution = jobLauncher.run(importUserJob, new JobParameters()); System.out.println("Job Status: " + execution.getStatus()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
注意:spring batch 会自动生成数据库表,可以自动生成
自动生成:在 application.properties 或 application.yml 中添加:
spring.batch.jdbc.initialize-schema=alwaysy
手动生成:再引用的包里面,找到对应的schema-*.sql 文件,我这里数据库是mysql ,所以直接找到schema-mysql.sql ,
5. Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud 是一个用于构建分布式系统的工具集,它基于 Spring Boot 提供了微服务架构的支持。Spring Cloud 提供了诸如服务发现、配置管理、负载均衡、断路器等微服务相关的功能。
完整的 Spring Cloud 示例,包含以下组件:
-
Eureka Server:服务注册与发现中心。
-
Config Server:集中化的配置管理。
-
Service A:一个简单的微服务,注册到 Eureka Server。
-
Service B:另一个微服务,调用 Service A 并通过 Config Server 获取配置。
- Service C:一个简单的微服务,注册到 Eureka Server.
-
Gateway:API 网关,统一处理外部请求。
1. 创建 Eureka Server
1.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,添加 Eureka Server 依赖。(使用Spring Initializr 创建项目的时候,可以直接选择依赖进行初始化项目,不需要手动引用以下包)

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.2 配置文件 application.yml
spring: application: name: SpringCloudService server: port: 9000 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: registerWithEureka: false fetchRegistry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
1.3 设置启动类 SpringCloudServiceApplication.java
package com.example.springcloudservice; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @EnableEurekaServer @SpringBootApplication public class SpringCloudServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudServiceApplication.class, args); } }
2. 创建 Config Server
2.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,添加 Config Server 依赖。

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2.2 配置文件 application.yml
server: port: 9001 spring: cloud: config: server: git: force-pull: true #每次启动就会拉取最新的配置 timeout: 10 uri: http://192.168.0.208/fanchenbin/test.git #github,gitlab 存储的仓库地址,需要先把仓库手动建立好,把配置文件传上去 username: x-access-token #如果是使用token就是固定值x-access-token,否则是账号 password: github_pat_xxxx #生成的Token 或者是密码 default-label: master # 仓库的分支,注意新版本可能是main clone-on-start: true
2.3 启动类 SpringCloudConfigServerApplication.java
package com.example.springcloudconfigserver; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigServer public class SpringCloudConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudConfigServerApplication.class, args); } }
3. 创建 Service A
3.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,添加 Eureka Discovery Client 和 Web 依赖。

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2 配置文件 application.yml
spring:
application:
name: service-a #服务名称
server:
port: 9002
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:9000/eureka/ #服务发现服务端的地址
3.3 启动类 SpringCloudClientApplication.java
package com.example.springcloudclient; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class SpringCloudClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudClientApplication.class, args); } }
3.4 创建一个简单的 REST 控制器 HelloController.java
package com.example.springcloudclient.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @RestController public class HelloController { //restTemplate 是 Spring 提供的用于访问 HTTP 服务的客户端 private final RestTemplate restTemplate; public HelloController(RestTemplate restTemplate) { this.restTemplate = restTemplate; } @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "Hello from Service A!"; } @GetMapping("/one") public String one() { // 使用 restTemplate 访问 Service B 这里服务名称为 service-b 是 服务发现中的服务名称,只要该服务注册到注册中心,就可以通过服务名称访问到该服务 // 这里的 restTemplate 就是 Spring 提供的用于访问 HTTP 服务的客户端 return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-b/hello", String.class); } @GetMapping("/two") public String two() { return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-c/hello", String.class); } }
@Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } }
4. 创建 Service B
4.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,添加 Eureka Discovery Client、Web 和 Config Client 依赖。

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
4.2 配置文件 application.yml
spring: application: name: service-b config: import: configserver:http://localhost:9001/ #这里指定configserver的地址 cloud: config: uri: http://localhost:9001 # 这里指定configserver地址,如果指定了上面的地址这里可以不用指定了 profile: dev #这里可以指定环境,default 表示默认环境,dev表示开发环境,test表示测试环境,prod表示生产环境。通过指定的环境会在configserver上读取相应的配置。 #例如指定dev 就会读取service-b-dev.yml文件。 logging: level: root: INFO com.netflix.discovery: DEBUG # 只开启eureka的debug日志 server: port: 9003 eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:9000/eureka/ # register-with-eureka: true # fetch-registry: true
4.3 启动类 SpringCloudClient2Application.java
package com.example.springcloudclient2; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class SpringCloudClient2Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudClient2Application.class, args); } }
4.4 创建一个 REST 控制器 HelloController.java
package com.example.springcloudclient2.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @RestController public class HelloController { @Value("${message}") //这里是通过配置中心直接读取配置中心的yaml文件的配置 private String message; private final RestTemplate restTemplate; public HelloController(RestTemplate restTemplate) { this.restTemplate = restTemplate; } @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "Hello from Service B!"; } @GetMapping("/one") public String one() { String serviceAResponse = restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-a/hello", String.class); return message + " " + serviceAResponse; } @GetMapping("/two") public String three() { String serviceAResponse = restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-c/hello", String.class); return message + " " + serviceAResponse; } }
@Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } }
service-b-dev.yml 配置
{ "message": "aaa" }
5. 创建 Service C
和Service A 一样,只是端口不一样,用的9004
6. 创建 Gateway
6.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目 , 引入 Gateway 和 Eureka Discovery Client
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
6.2 配置文件 application.yml
spring: application: name: gateway-service #指定网关服务的应用名称 cloud: gateway: routes: - id: service-a-route #路由的唯一标识符,每个路由规则需要一个唯一的 id,用于区分不同的路由 uri: lb://SERVICE-A #指定路由的目标地址,表示使用负载均衡(lb)将请求转发到名为 service-a 的服务 predicates: - Path=/service-a/** #定义路由的匹配条件。Path=/service-a/**:表示当请求路径以 /service-a/ 开头时,匹配该路由. ** 是通配符,表示匹配任意子路径。 filters: - StripPrefix=1 #定义路由的过滤器. StripPrefix=1:表示去掉请求路径中的第一个前缀(即 /service-a)。例如,请求路径为 /service-a/hello,经过 StripPrefix=1 处理后,转发到 service-a 的路径变为 /hello。 - id: service-b-route uri: lb://SERVICE-B predicates: - Path=/service-b/** filters: - RewritePath=/service-b/(?<segment>.*), /$\{segment} #这个配置主要用于在网关接收到请求后,利用正则表达式将请求路径中特定的前缀部分去除,然后将处理后的路径转发到实际的服务。效果和上面 StripPrefix=1 一样 server: port: 9005 #当前网关的端口号 eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:9000/eureka/ #表示 Eureka Server 的注册中心地址。
测试效果
先运行 SpringCloudService 服务, 再运行SpringCloudConfigServer配置中心 服务,其他服务可以不按照顺序依次运行起来
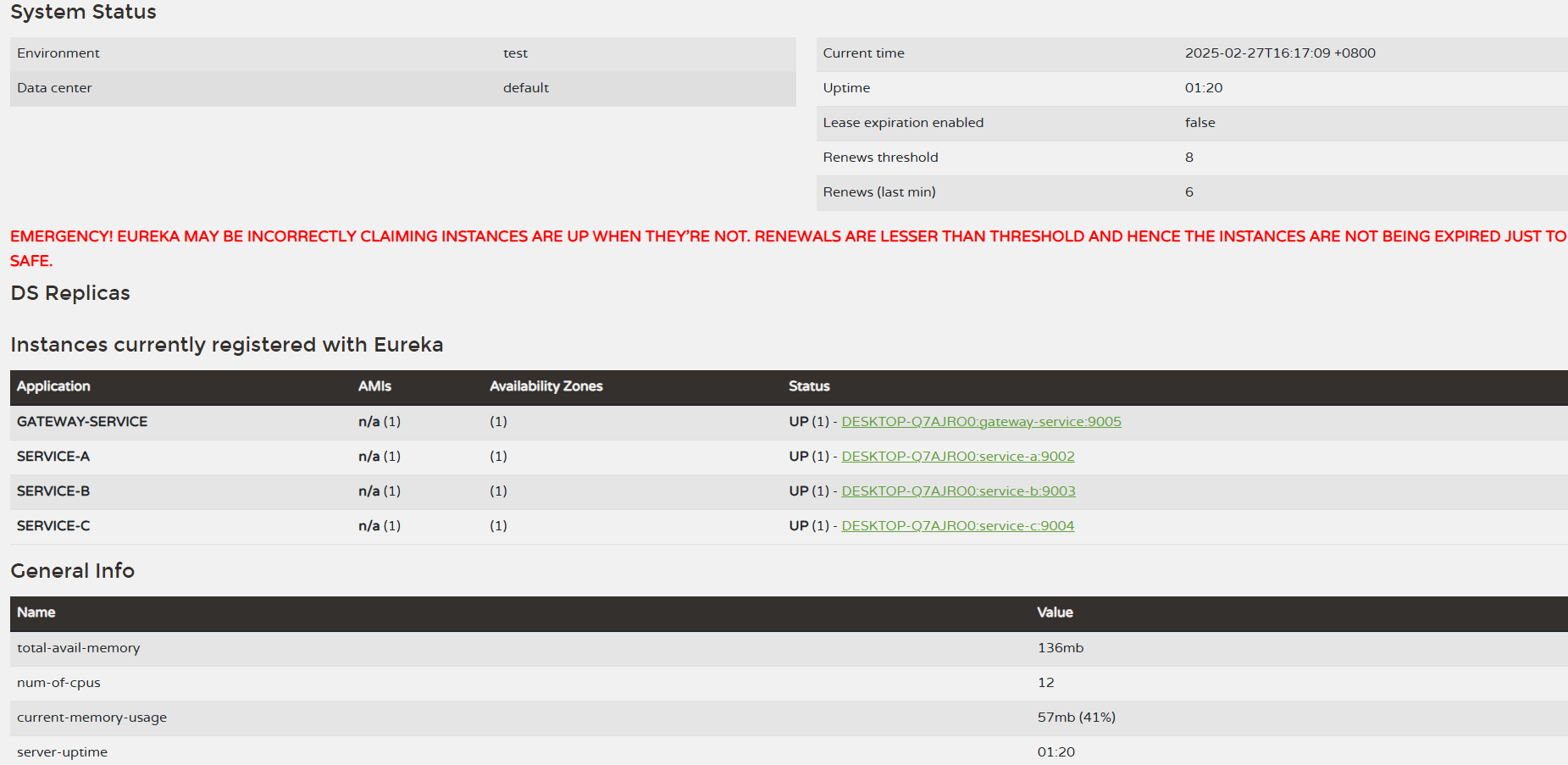
测试 服务注册与发现
访问 Eureka Server端 http://localhost:9000/ ,可以看到几个客户端服务都注册成功了
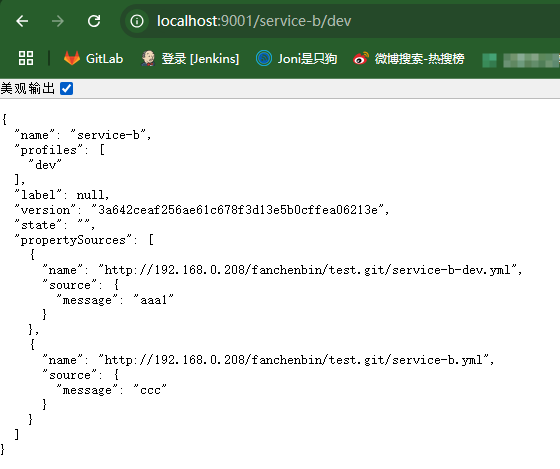
测试 服务注册与发现 和配置中心
访问配置中心+对应的服务名+环境可以得到配置信息。例如 http://localhost:9001/service-b/dev
访问 Service-b 服务 接口 http://localhost:9003/one 会 输出 aaa1 Hello from Service A 。 说明服务调用也正确,配置中心读取也正确了(这里aaa1是读取的配置中心配置的字段)

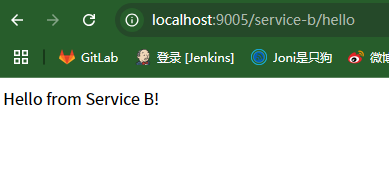
测试 网关
访问网关的服务+对应服务名+接口名称。例如这里访问 http://localhost:9005/service-a/hello 和 http://localhost:9005/service-b/hello 。可以自动转发到对应的服务接口地址上

测试 网关负载均衡
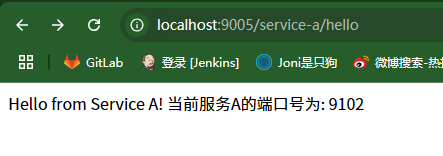
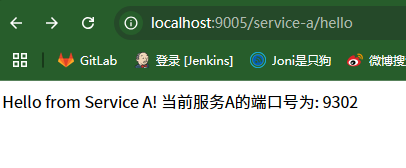
这里只测试service-a 服务的负载均衡,修改hello接口,用于获取当前运行实例的端口
package com.example.springcloudclient.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { // 获取当前实例的端口号 String port = env.getProperty("local.server.port"); return "Hello from Service A! 当前服务A的端口号为: " + port; } }
打包文件,运行不同端口的实例
java -jar SpringCloudClient-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=9102 java -jar SpringCloudClient-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=9202 java -jar SpringCloudClient-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=9302
Eureka 服务端 也可以看到各个实例都已经注册成功

运行网关对应的 service-a 服务的hello接口,不停地刷新,可以看到每次访问的服务A的端口号是依次切换的,说明负载均衡已经成功

6. Spring Security
基本定义
Spring Security 是基于 Spring 框架构建的身份验证与访问控制框架,为 Java 应用提供全面的安全防护. 通过 Spring 的 AOP 思想和 Servlet 过滤器链实现安全控制,依赖 IoC(控制反转)和 DI(依赖注入)简化配置
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter:负责在请求开始时从会话中获取安全上下文,并在请求结束时将安全上下文保存到会话中。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter:处理表单登录请求,验证用户名和密码。
FilterSecurityInterceptor:根据配置的访问规则,对请求进行访问控制检查。
简单示例
1. 创建项目依赖。这里通过内存存储的账号密码,没有通过数据库校验
-
Spring Web
-
Spring Security
-
Thymeleaf (用于演示页面)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 基础安全配置
package com.example.springsecurity.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager; import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain; @Configuration // 标记为配置类 @EnableWebSecurity // 启用Spring Security的Web安全支持 public class SecurityConfig { /** * 配置安全过滤器链(核心安全配置) * @param http HTTP安全配置对象 * @return 构建的安全过滤器链 */ @Bean public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http // 授权配置:定义哪些请求需要认证/授权。这里过滤器通过匹配路由对配置的路由进行拦截 .authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth .requestMatchers("/", "/home", "/login").permitAll() // 允许匿名访问 .requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") // 需要ADMIN角色 .anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他请求需要认证 ) // 表单登录配置 .formLogin(form -> form .loginPage("/login") // 自定义登录页路径 .permitAll() // 允许所有用户访问登录页 .defaultSuccessUrl("/dashboard") // 登录成功后的默认跳转地址 .failureUrl("/login?error=true") // 登录失败跳转地址 ) // 退出登录配置 .logout(logout -> logout .logoutSuccessUrl("/login?logout=true") // 退出成功后的跳转地址 .permitAll() // 允许所有用户访问退出功能 ); return http.build(); } /** * 密码编码器(必须配置) * 使用BCrypt强哈希算法加密密码 */ @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } /** * 内存用户存储(演示用,生产环境请使用数据库) * 创建两个测试用户: * - 普通用户(user/1) * - 管理员(admin/1) */ @Bean public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() { // 创建普通用户(注意使用passwordEncoder加密密码) UserDetails user = User.builder() .username("user") .password(passwordEncoder().encode("1")) // 必须加密 .roles("USER") // 自动添加ROLE_前缀 .build(); // 创建管理员用户 UserDetails admin = User.builder() .username("admin") .password(passwordEncoder().encode("1")) .roles("ADMIN") // 可以添加多个角色,例如:.roles("ADMIN", "USER") .build(); return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user, admin); } }
3. 创建控制器和相应页面
package com.example.springsecurity.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; @Controller // 声明为控制器 public class HomeController { /** * 首页(允许匿名访问) */ @GetMapping("/") public String home() { return "home"; // 返回home.html模板。这里和html命名一致,就会跳转到对应页面 } /** * 用户仪表盘(需要登录) */ @GetMapping("/dashboard") public String dashboard() { return "dashboard"; // 返回dashboard.html模板 } // 添加登录页面的GET请求处理 @GetMapping("/login") public String loginPage() { return "login"; // 返回 login.html 模板 } /** * 管理员页面(需要ADMIN角色) */ @GetMapping("/admin") public String admin() { return "admin"; // 返回admin.html模板 } }
创建home.html. 这个页面不需要授权可以直接访问
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Home Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to our website!</p>
</body>
</html>
创建login.html。 注意:
Spring Security 框架内部已经实现了一套完整的登录认证逻辑,当你在配置类中配置了表单登录(如 formLogin() 方法),Spring Security 会自动创建一个过滤器来处理 /login 的 POST 请求。具体而言,当用户在前端表单输入用户名和密码并提交表单时,Spring Security 会拦截这个 POST /login 请求,并进行以下操作: 获取用户名和密码:从请求中提取 username 和 password 参数。 用户认证:使用配置好的 UserDetailsService 从存储(如内存、数据库)中查找用户信息,并与输入的用户名和密码进行比对。 认证结果处理: 认证成功:根据配置的 defaultSuccessUrl 或其他逻辑将用户重定向到相应的页面。 认证失败:根据配置的 failureUrl 将用户重定向到登录页面,并附带错误参数(如 error=true)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 错误提示 -->
<div th:if="${param.error}">用户名或密码错误</div>
<!-- 退出提示 -->
<div th:if="${param.logout}">您已退出登录</div>
<!-- Spring Security的登录表单必须:
1. action指向/login
2. 使用post方法
3. 用户名字段名为username
4. 密码字段名为password -->
<!-- login.html -->
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<!-- 自动添加 CSRF 令牌(Thymeleaf 模板) -->
<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}"/>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username">
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password">
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
创建dashboard.html。 只有授权的账号才能访问
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Dashboard</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户控制台</h1>
<!-- 管理员链接(对没有权限的用户会显示404) -->
<a th:href="@{/admin}">管理员区域</a>
<!-- Spring Security的退出表单必须:
1. action指向/logout
2. 使用post方法
3. 需要CSRF令牌(默认启用) -->
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="退出登录"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
创建admin.html 。只有管理员账号可以访问
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Admin</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Admin Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to our website!</p>
</body>
</html>
4. 测试
/:公共页面 /dashboard:需要登录 /admin:需要ADMIN角色
基于OAuth2.1 实现 授权码模式(web端登录),授权码+PKCE模式(移动端登录),自定义密码模式(可以用于移动端账号密码登录,短信登录,小程序登录等等)
SecurityConfig完整配置在下面第3点开头
1. pom.xml 引入相关的包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-authorization-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 添加登录页面相关的信息及数据库相应配置
配置application.yaml . 指向登录页面的文件夹
spring:
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
cache: false
创建 login.html 登录界面
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Login</title> </head> <body> <!-- 错误提示 --> <div th:if="${param.error}">用户名或密码错误</div> <!-- 退出提示 --> <div th:if="${param.logout}">您已退出登录</div> <!-- Spring Security的登录表单必须: 1. action指向/login 2. 使用post方法 3. 用户名字段名为username 4. 密码字段名为password --> <!-- login.html --> <form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> <!-- 自动添加 CSRF 令牌(Thymeleaf 模板) --> <input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}"/> <input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username"> <input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password"> <input type="submit" value="Login"> </form> </body> </html>
相关的控制器
@Controller public class TestAuthController { /** * 首页(允许匿名访问) */ @GetMapping("/home") public String home() { return "home"; // 返回home.html模板 } // 添加登录页面的GET请求处理 @GetMapping("/login") public String loginPage() { return "login"; // 返回 login.html 模板 } /** * 生成PKCE 对应的codeVerifier和codeChallenge * @return */ @GetMapping("/login/pkce") public String pkce() { try { //生成code_verifier String codeVerifier = codeVerifierGenerator(); //生成code_challenge String codeChallenge = codeChallengeGenerator(codeVerifier); System.out.println("code_verifier:"+codeVerifier); System.out.println("code_challenge:"+codeChallenge); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "pkce"; // 返回home.html模板 } public static String codeVerifierGenerator(){ return Base64URL.encode(UUID.randomUUID().toString()).toString(); } public static String codeChallengeGenerator(String codeVerifier) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256"); byte[] digestCodeVerifier = messageDigest.digest(codeVerifier.getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII)); return Base64URL.encode(digestCodeVerifier).toString(); } }
如果不用上面简单示例使用内存中的用户,可以用数据库的数据进行校验账号密码,这里用的Spring Data Jpa ,只需要在Service 继承UserDetailsService ,重写对应的loadUserByUsername方法就行了
import com.example.springbootdemo.domain.*; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface AccountRepository extends JpaRepository<Account, Long> { Account findByUsername(String username); }
@Getter @Setter @Entity public class Account implements UserDetails { public Account() {} @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @Column(unique = true) private String username; private String password; // 实现UserDetails接口方法 @Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() { return Collections.emptyList(); } }
import com.example.springbootdemo.domain.Account; import com.example.springbootdemo.service.test.AccountRepository; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Autowired private AccountRepository userService; /** * 根据用户名加载用户详情 * @param username 用户名 * @return UserDetails 对象 * @throws UsernameNotFoundException 用户未找到异常 */ @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { Account user = userService.findByUsername(username); if (user == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found"); } return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User( user.getUsername(), //user.getPassword(), passwordEncoder().encode(user.getPassword()), // 密码加密 //"{noop}" + user.getPassword(), // 让 Spring Security 识别明文密码 user.getAuthorities() ); } public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
添加相应的数据库配置。这里就是上面spring data jpa演示的配置
spring: thymeleaf: prefix: classpath:/templates/ suffix: .html cache: false application: name: SpringBootDemo datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false username: root password: hua3182486 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jpa: show-sql: true #打印sql语句 # generate-ddl: true hibernate: ddl-auto: update #update:该配置比较常用,当服务首次启动会在数据库中生成相应表,后续启动服务时如果实体类有增加属性会在数据中添加相应字段,原来数据仍在保留 #create :该值慎用,每次重启项目的时候都会删除表结构,重新生成,原来数据会丢失不见。 #create-drop :慎用,当项目关闭,数据库中的表会被删掉。 #validate : 验证数据库和实体类的属性是否匹配,不匹配将会报错。 properties: hibernate.format_sql: true #格式化sql语句 hibernate.dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect #数据库方言,要和数据库匹配
3. 添加SecurityConfig配置类
下面示例完整的SecurityConfig配置

package com.example.springbootdemo.config.oauth; import com.example.springbootdemo.authorization.password.PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter; import com.example.springbootdemo.authorization.password.PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider; import com.example.springbootdemo.constant.OAuth2Constant; import com.example.springbootdemo.filters.CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint; import com.example.springbootdemo.filters.MyAuthenticationFailureHandler; import com.nimbusds.jose.jwk.JWKSet; import com.nimbusds.jose.jwk.RSAKey; import com.nimbusds.jose.jwk.source.ImmutableJWKSet; import com.nimbusds.jose.jwk.source.JWKSource; import com.nimbusds.jose.proc.SecurityContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.security.config.Customizer; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.AuthorizationGrantType; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.ClientAuthenticationMethod; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.oidc.OidcScopes; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jose.jws.SignatureAlgorithm; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.NimbusJwtEncoder; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.*; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.JdbcRegisteredClientRepository; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.RegisteredClient; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.RegisteredClientRepository; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.config.annotation.web.configurers.OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.AuthorizationServerSettings; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.ClientSettings; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.OAuth2TokenFormat; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.TokenSettings; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.token.*; import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint; import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.MediaTypeRequestMatcher; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.security.*; import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey; import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey; import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.Base64; import java.util.UUID; @Configuration // 标记为 Spring 配置类 @EnableWebSecurity // 启用 Spring Security public class SecurityConfig { /** * 配置 OAuth2 授权服务器的安全过滤器链 * * @param http Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity 对象 * @return SecurityFilterChain 安全过滤器链 * @throws Exception 配置过程中可能抛出的异常 */ @Bean @Order(1) // 指定过滤器链的优先级,授权服务器的安全配置优先 public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http, OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService, OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator) throws Exception { // 创建 OAuth2 授权服务器的配置 OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer authorizationServerConfigurer = OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.authorizationServer(); http // 只匹配 OAuth2 授权服务器的相关端点 .securityMatcher(authorizationServerConfigurer.getEndpointsMatcher()) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, (authorizationServer) -> authorizationServer //设置自定义密码模式 .tokenEndpoint(tokenEndpoint -> tokenEndpoint .accessTokenRequestConverter( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter()) .authenticationProvider( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider( authorizationService, tokenGenerator)) .errorResponseHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler()) // 自定义认证失败处理器 ) .oidc(Customizer.withDefaults()) // 启用 OpenID Connect 1.0 ) // 任何请求都需要认证 .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .anyRequest().authenticated() ) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, customizer -> customizer.oidc(Customizer.withDefaults())) // 启用 OIDC(可选) // 未认证时,HTML 请求重定向到 /login 页面 .exceptionHandling((exceptions) -> exceptions .defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor( //new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"), new ClientAwareAuthenticationEntryPoint(), //根据客户端id自定义跳转登录界面 new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(MediaType.TEXT_HTML) ) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) ) ; return http.build(); // 构建安全过滤器链 } /** * 配置默认的 Spring Security 过滤器链,处理用户身份认证 * * @param http Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity 对象 * @return SecurityFilterChain 安全过滤器链 * @throws Exception 配置过程中可能抛出的异常 */ @Bean @Order(2) // 低于授权服务器的过滤器链优先级 public SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http //.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable()) // 禁用 CSRF(移动端无 Cookie 场景) // 任何请求都需要认证 .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .requestMatchers("/auth/login", "/api/auth/refresh","/home","/login/**").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() ) // 使用 Spring Security 默认的表单登录 //.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 使用自定义表单登录配置 .formLogin(form -> form .loginPage("/login") // // 默认登录页 .permitAll() // 允许所有用户访问登录页 ) .oauth2ResourceServer((resourceServer) -> resourceServer .jwt(Customizer.withDefaults()) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) // 自定义认证失败处理器 ); return http.build(); } /** * 配置 OAuth2 客户端信息(存储在内存中) * * @return RegisteredClientRepository OAuth2 客户端存储库 */ /* @Bean public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository() { // 配置一个 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 客户端 RegisteredClient oidcClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("OIDC客户端") .clientId("oidc-client") // 客户端 ID //.clientSecret("{noop}secret") // 客户端密钥(未加密) .clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .scope("myResource") // 自定义作用域 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient mobileClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientId("mobile-client") // 客户端 ID .clientName("授权码+PKCE客户端") .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings( ClientSettings.builder() .requireAuthorizationConsent(true) .requireProofKey(true) // 关键配置:强制客户端使用 PKCE 进行授权 .build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient passwordClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("自定义密码模式客户端") .clientId("password-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret2")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(new AuthorizationGrantType(OAuth2Constant.GRANT_TYPE_PASSWORD)) // 密码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); return new InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository(oidcClient,mobileClient,passwordClient); // 使用内存存储客户端信息,如果使用数据库存储,请使用 jpa 存储库继承 RegisteredClientRepository 实现 }*/ /** * 授权信息(存储在内存中) */ /* @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService(RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new InMemoryOAuth2AuthorizationService(); }*/ /** * 客户端信息(存储在数据库中,直接引用数据库数据的版本) * 对应表:oauth2_registered_client */ /* @Bean public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { //System.out.println(passwordEncoder().encode("secret"));//打印加密后的密码 return new JdbcRegisteredClientRepository(jdbcTemplate); }*/ /** * 客户端信息(存储在数据库中,写入初始值的版本) * 对应表:oauth2_registered_client */ @Bean public JdbcRegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository(DataSource dataSource, PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) { JdbcRegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository = new JdbcRegisteredClientRepository(new JdbcTemplate(dataSource)); // 检查数据库是否已存在客户端,若不存在则初始化 if (registeredClientRepository.findByClientId("oidc-client") == null) { // 配置一个 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 客户端 RegisteredClient oidcClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("OIDC客户端") .clientId("oidc-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder.encode("secret")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .scope("myResource") // 自定义作用域 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient mobileClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientId("mobile-client") // 客户端 ID .clientName("授权码+PKCE客户端") .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings( ClientSettings.builder() .requireAuthorizationConsent(true) .requireProofKey(true) // 关键配置:强制客户端使用 PKCE 进行授权 .build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient passwordClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("自定义密码模式客户端") .clientId("password-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder.encode("secret2")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(new AuthorizationGrantType("password")) // 密码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); // 保存到数据库 registeredClientRepository.save(oidcClient); registeredClientRepository.save(mobileClient); registeredClientRepository.save(passwordClient); } return registeredClientRepository; } /** * 授权信息(存储在数据库中) * 对应表:oauth2_authorization */ @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate, RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new JdbcOAuth2AuthorizationService(jdbcTemplate, registeredClientRepository); } /** * 授权确认(存储在数据库中) *对应表:oauth2_authorization_consent */ @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationConsentService authorizationConsentService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate, RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new JdbcOAuth2AuthorizationConsentService(jdbcTemplate, registeredClientRepository); } /** * 配置用户自定义的 JWT 令牌自定义器,自定义 claims 信息 * * @return UserDetailsService 用户信息服务 */ @Bean public OAuth2TokenCustomizer<JwtEncodingContext> jwtTokenCustomizer() { return new CustomTokenCustomizer(); } /** * 配置 JSON Web Key (JWK) 源,用于 JWT 令牌签名和验证 * * @return JWKSource<SecurityContext> JWK 源 */ @Bean public JWKSource<SecurityContext> jwkSource() { // 自动生成 RSA 密钥对 KeyPair keyPair = generateRsaKey(); // 生成 RSA 密钥对 RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); /* // 手动配置 RSA 公钥和私钥 String privateKeyPEM = "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...12s3a1f3as...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----"; String publicKeyPEM = "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\n...eeeeeeeeeqqqqqqqq1123123123...\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"; // 解析公钥和私钥 try { publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) parsePublicKey(publicKeyPEM); privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) parsePrivateKey(privateKeyPEM); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }*/ // 构建 RSA JWK RSAKey rsaKey = new RSAKey.Builder(publicKey) .privateKey(privateKey) .keyID(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .build(); // 将 JWK 存储到 JWKSet JWKSet jwkSet = new JWKSet(rsaKey); return new ImmutableJWKSet<>(jwkSet); } public static PublicKey parsePublicKey(String pem) throws Exception { String publicKeyPEM = pem.replace("-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----", "") .replace("-----END PUBLIC KEY-----", "") .replaceAll("\\s", ""); // 移除换行和空格 byte[] decoded = Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKeyPEM); X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(decoded); KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA"); return keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec); } public static PrivateKey parsePrivateKey(String pem) throws Exception { String privateKeyPEM = pem.replace("-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----", "") .replace("-----END PRIVATE KEY-----", "") .replaceAll("\\s", ""); // 移除换行和空格 byte[] decoded = Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKeyPEM); PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(decoded); KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA"); return keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec); } /** * 配置 OAuth2 授权服务器的基本设置 * * @return AuthorizationServerSettings 授权服务器设置 */ @Bean public AuthorizationServerSettings authorizationServerSettings() { return AuthorizationServerSettings.builder() .issuer("http://localhost:8088/") // 设置令牌签发者(issuer) .tokenEndpoint("/oauth2/token") // 设置令牌端点地址 .authorizationEndpoint("/oauth2/authorize") // 设置授权端点地址 .jwkSetEndpoint("/oauth2/jwks") // 设置 JWK 端点地址 .build(); } private KeyPair generateRsaKey() { try { KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException("无法生成 RSA 密钥对", e); } } /** *配置token生成器,这里用于自定义模式生成JwtToken */ @Bean OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator(JWKSource<SecurityContext> jwkSource) { JwtGenerator jwtGenerator = new JwtGenerator(new NimbusJwtEncoder(jwkSource)); jwtGenerator.setJwtCustomizer(new CustomTokenCustomizer()); // 配置用户自定义的 JWT 令牌自定义器,自定义 claims 信息 OAuth2AccessTokenGenerator accessTokenGenerator = new OAuth2AccessTokenGenerator(); OAuth2RefreshTokenGenerator refreshTokenGenerator = new OAuth2RefreshTokenGenerator(); return new DelegatingOAuth2TokenGenerator( jwtGenerator, accessTokenGenerator, refreshTokenGenerator); } /** * 配置密码模式认证提供者 */ @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
下面是单独挑重点说明
3.1 如果想通过客户端区分登录页,这里就可以直接继承 AuthenticationEntryPoint
public class ClientAwareAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint { @Override public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException { String clientId = request.getParameter("client_id"); // 提取客户端标识 System.out.println("进来了:"+clientId); if (clientId != null) { try { if(clientId.equals("oidc-client")) response.sendRedirect("/login"); // web登录页 else response.sendRedirect("/home"); // 移动端登录页 return; } catch (Exception ignored) { ignored.printStackTrace(); } } response.sendRedirect("/login"); // 默认登录页 } }
@Bean @Order(1) // 指定过滤器链的优先级,授权服务器的安全配置优先 public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http, OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService, OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator) throws Exception { // 创建 OAuth2 授权服务器的配置 OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer authorizationServerConfigurer = OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.authorizationServer(); http /*其他配置*/
// 未认证时,HTML 请求重定向到 /login 页面 .exceptionHandling((exceptions) -> exceptions .defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor( //new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"), new ClientAwareAuthenticationEntryPoint(), //根据客户端id自定义跳转登录界面 new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(MediaType.TEXT_HTML) ) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) ) ; return http.build(); // 构建安全过滤器链 }
3.2 如果在JWT生成token时想自定义Claims声明信息
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.JwtClaimsSet; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.token.JwtEncodingContext; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.token.OAuth2TokenCustomizer; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class CustomTokenCustomizer implements OAuth2TokenCustomizer<JwtEncodingContext> { @Override public void customize(JwtEncodingContext context) { JwtClaimsSet.Builder claims = context.getClaims(); // 获取当前认证的用户信息 // 这里可以根据实际情况从 Authentication 对象中获取更多信息 String username = context.getPrincipal().getName(); // 添加自定义的声明信息 Map<String, Object> customClaims = new HashMap<>(); customClaims.put("custom_claim", "This is a custom claim"); customClaims.put("username", username); // 将自定义声明信息添加到 JWT 声明中 claims.claims(existingClaims -> existingClaims.putAll(customClaims)); } }
在SecurityConfig需要注册进去
/** * 配置用户自定义的 JWT 令牌自定义器,自定义 claims 信息 * * @return UserDetailsService 用户信息服务 */ @Bean public OAuth2TokenCustomizer<JwtEncodingContext> jwtTokenCustomizer() { return new CustomTokenCustomizer(); }
3.3 自定义密码登录
添加自定义密码模式常量
public class OAuth2Constant { /** * 密码模式(自定义) */ public static final String GRANT_TYPE_PASSWORD = "authorization_password"; /** * 构造方法私有化 */ private OAuth2Constant(){ } }
添加 PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter 继承 AuthenticationConverter. 初步校验参数,过滤掉不需要的参数,将参数传递给下面的PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider 进行数据校验和token签发

import com.example.springbootdemo.constant.OAuth2Constant; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.OAuth2AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.endpoint.OAuth2ParameterNames; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationConverter; import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap; import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter implements AuthenticationConverter { @Nullable @Override public Authentication convert(HttpServletRequest request) { // grant_type (REQUIRED) String grantType = request.getParameter(OAuth2ParameterNames.GRANT_TYPE); if (!OAuth2Constant.GRANT_TYPE_PASSWORD.equals(grantType)) { return null; } Authentication clientPrincipal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication(); //从request中提取请求参数,然后存入MultiValueMap<String, String> MultiValueMap<String, String> parameters = getParameters(request); // username (REQUIRED) String username = parameters.getFirst(OAuth2ParameterNames.USERNAME); if (!StringUtils.hasText(username) || parameters.get(OAuth2ParameterNames.USERNAME).size() != 1) { throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException("无效请求,用户名不能为空!"); } String password = parameters.getFirst(OAuth2ParameterNames.PASSWORD); if (!StringUtils.hasText(password) || parameters.get(OAuth2ParameterNames.PASSWORD).size() != 1) { throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException("无效请求,密码不能为空!"); } //收集要传入PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken构造方法的参数, //该参数接下来在PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider中使用 Map<String, Object> additionalParameters = new HashMap<>(); //遍历从request中提取的参数,排除掉grant_type、client_id、code等字段参数,其他参数收集到additionalParameters中 parameters.forEach((key, value) -> { if (!key.equals(OAuth2ParameterNames.GRANT_TYPE) && !key.equals(OAuth2ParameterNames.CLIENT_ID) && !key.equals(OAuth2ParameterNames.CODE)) { additionalParameters.put(key, value.get(0)); } // additionalParameters.put("abc", "123"); }); //返回自定义的PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken对象 return new PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken(clientPrincipal, additionalParameters); } /** *从request中提取请求参数,然后存入MultiValueMap<String, String> */ private static MultiValueMap<String, String> getParameters(HttpServletRequest request) { Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap(); MultiValueMap<String, String> parameters = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(parameterMap.size()); parameterMap.forEach((key, values) -> { if (values.length > 0) { for (String value : values) { parameters.add(key, value); } } }); return parameters; } }
添加 PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken 继承 OAuth2AuthorizationGrantAuthenticationToken.注册自定义密码模式

public class PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken extends OAuth2AuthorizationGrantAuthenticationToken { public PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken(Authentication clientPrincipal, @Nullable Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) { super(new AuthorizationGrantType(OAuth2Constant.GRANT_TYPE_PASSWORD), clientPrincipal, additionalParameters); } }
添加PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider 继承 AuthenticationProvider 。这个是核心部分,用于校验账号密码,jwt签发access token,refresh token, 还可以自定义返回给调用端参数(比如添加业务信息,移除传递上来的密码明文等等)。注意这里返回给前端密码不正确的提示信息可以用我注释掉的 OAuth2AuthenticationException 直接返回,想要自定义属性返回需要看下面3.4

import com.example.springbootdemo.filters.MyAuthenticationException; import jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider; import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.*; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.endpoint.OAuth2ParameterNames; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.*; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.OAuth2Authorization; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationService; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.OAuth2TokenType; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.authentication.OAuth2AccessTokenAuthenticationToken; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.authentication.OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.RegisteredClient; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.context.AuthorizationServerContextHolder; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.token.*; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import java.security.Principal; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider { private static final String ERROR_URI = "https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6749#section-5.2"; @Resource private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Resource private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; private final OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService; private final OAuth2TokenGenerator<? extends OAuth2Token> tokenGenerator; private JwtGenerator jwtGenerator; private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); public PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider(OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService ,OAuth2TokenGenerator<? extends OAuth2Token> tokenGenerator ){ Assert.notNull(authorizationService, "authorizationService cannot be null"); Assert.notNull(tokenGenerator, "tokenGenerator cannot be null"); this.authorizationService = authorizationService; this.tokenGenerator = tokenGenerator; } @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken passwordGrantAuthenticationToken = (PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken) authentication; Map<String, Object> additionalParameters = passwordGrantAuthenticationToken.getAdditionalParameters(); //授权类型 AuthorizationGrantType authorizationGrantType = passwordGrantAuthenticationToken.getGrantType(); //用户名 String username = (String)additionalParameters.get(OAuth2ParameterNames.USERNAME); //密码 String password = (String)additionalParameters.get(OAuth2ParameterNames.PASSWORD); //请求参数权限范围 String requestScopesStr = (String)additionalParameters.get(OAuth2ParameterNames.SCOPE); //请求参数权限范围专场集合 Set<String> requestScopeSet = Stream.of(requestScopesStr.split(" ")).collect(Collectors.toSet()); // Ensure the client is authenticated OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken clientPrincipal = getAuthenticatedClientElseThrowInvalidClient(passwordGrantAuthenticationToken); RegisteredClient registeredClient = clientPrincipal.getRegisteredClient(); // Ensure the client is configured to use this authorization grant type if (!registeredClient.getAuthorizationGrantTypes().contains(authorizationGrantType)) { throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(OAuth2ErrorCodes.UNAUTHORIZED_CLIENT); } //校验用户名信息 UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username); //if(!password.equals(userDetails.getPassword().replace("{noop}",""))) if(!passwordEncoder.matches(password,userDetails.getPassword())) { /* OAuth2Error error = new OAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.INVALID_GRANT, "密码不正确", ERROR_URI); throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(error);*/ throw new MyAuthenticationException("密码不正确!"); } //由于在上面已验证过用户名、密码,现在构建一个已认证的对象UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.authenticated(userDetails,clientPrincipal,userDetails.getAuthorities()); // Initialize the DefaultOAuth2TokenContext DefaultOAuth2TokenContext.Builder tokenContextBuilder = DefaultOAuth2TokenContext.builder() .registeredClient(registeredClient) .principal(usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) .authorizationServerContext(AuthorizationServerContextHolder.getContext()) .authorizationGrantType(authorizationGrantType) .authorizedScopes(requestScopeSet) .authorizationGrant(passwordGrantAuthenticationToken); // Initialize the OAuth2Authorization OAuth2Authorization.Builder authorizationBuilder = OAuth2Authorization.withRegisteredClient(registeredClient) .principalName(clientPrincipal.getName()) .authorizedScopes(requestScopeSet) .attribute(Principal.class.getName(), usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) .authorizationGrantType(authorizationGrantType); // ✅ 添加自定义 Claims Map<String, Object> customClaims = new HashMap<>(); customClaims.put("custom_claim_1", "value_1"); customClaims.put("custom_claim_2", "value_2"); authorizationBuilder.attribute("custom_claims", customClaims); // ----- 生成 Access Token ----- OAuth2TokenContext tokenContext = tokenContextBuilder .tokenType(OAuth2TokenType.ACCESS_TOKEN) .build(); /* OAuth2Token generatedAccessToken = this.tokenGenerator.generate(tokenContext);*/ OAuth2Token generatedAccessToken= tokenGenerator.generate(tokenContext); if (generatedAccessToken == null) { OAuth2Error error = new OAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.SERVER_ERROR, "The token generator failed to generate the access token.", ERROR_URI); throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(error); } if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Generated access token"); } OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = new OAuth2AccessToken(OAuth2AccessToken.TokenType.BEARER, generatedAccessToken.getTokenValue(), generatedAccessToken.getIssuedAt(), generatedAccessToken.getExpiresAt(), tokenContext.getAuthorizedScopes()); if (generatedAccessToken instanceof ClaimAccessor) { authorizationBuilder.token(accessToken, (metadata) -> { metadata.put(OAuth2Authorization.Token.CLAIMS_METADATA_NAME,((ClaimAccessor) generatedAccessToken).getClaims() ); }); } else { authorizationBuilder.accessToken(accessToken); } // ----- Refresh token ----- OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = null; if (registeredClient.getAuthorizationGrantTypes().contains(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) && // Do not issue refresh token to public client !clientPrincipal.getClientAuthenticationMethod().equals(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE)) { tokenContext = tokenContextBuilder.tokenType(OAuth2TokenType.REFRESH_TOKEN).build(); OAuth2Token generatedRefreshToken = this.tokenGenerator.generate(tokenContext); if (!(generatedRefreshToken instanceof OAuth2RefreshToken)) { OAuth2Error error = new OAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.SERVER_ERROR, "The token generator failed to generate the refresh token.", ERROR_URI); throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(error); } if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Generated refresh token"); } refreshToken = (OAuth2RefreshToken) generatedRefreshToken; authorizationBuilder.refreshToken(refreshToken); } //保存认证信息 OAuth2Authorization authorization = authorizationBuilder.build(); this.authorizationService.save(authorization); if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Saved authorization"); } if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Authenticated token request"); } //控制自定义返回项 创建一个新的可变 Map 并复制原有的参数 Map<String, Object> mutableAdditionalParameters = new HashMap<>(additionalParameters); // 移除密码参数 mutableAdditionalParameters.remove(OAuth2ParameterNames.PASSWORD); mutableAdditionalParameters.put("test","123"); return new OAuth2AccessTokenAuthenticationToken( registeredClient, clientPrincipal, accessToken, refreshToken, mutableAdditionalParameters); } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) { return PasswordGrantAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication); } private static OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken getAuthenticatedClientElseThrowInvalidClient(Authentication authentication) { OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken clientPrincipal = null; if (OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication.getPrincipal().getClass())) { clientPrincipal = (OAuth2ClientAuthenticationToken) authentication.getPrincipal(); } if (clientPrincipal != null && clientPrincipal.isAuthenticated()) { return clientPrincipal; } throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(OAuth2ErrorCodes.INVALID_CLIENT); } }
SecurityConfig 注册自定义密码模式和相应的Bean
/** * 配置 OAuth2 授权服务器的安全过滤器链 * * @param http Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity 对象 * @return SecurityFilterChain 安全过滤器链 * @throws Exception 配置过程中可能抛出的异常 */ @Bean @Order(1) // 指定过滤器链的优先级,授权服务器的安全配置优先 public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http, OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService, OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator) throws Exception { // 创建 OAuth2 授权服务器的配置 OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer authorizationServerConfigurer = OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.authorizationServer(); http // 只匹配 OAuth2 授权服务器的相关端点 .securityMatcher(authorizationServerConfigurer.getEndpointsMatcher()) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, (authorizationServer) -> authorizationServer //设置自定义密码模式 .tokenEndpoint(tokenEndpoint -> tokenEndpoint .accessTokenRequestConverter( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter()) .authenticationProvider( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider( authorizationService, tokenGenerator)) .errorResponseHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler()) // 自定义认证失败处理器 ) .oidc(Customizer.withDefaults()) // 启用 OpenID Connect 1.0 ) // 任何请求都需要认证 .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .anyRequest().authenticated() ) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, customizer -> customizer.oidc(Customizer.withDefaults())) // 启用 OIDC(可选) // 未认证时,HTML 请求重定向到 /login 页面 .exceptionHandling((exceptions) -> exceptions .defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor( //new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"), new ClientAwareAuthenticationEntryPoint(), //根据客户端id自定义跳转登录界面 new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(MediaType.TEXT_HTML) ) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) ) ; return http.build(); // 构建安全过滤器链 }
/** *配置token生成器,这里用于自定义模式生成JwtToken */ @Bean OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator(JWKSource<SecurityContext> jwkSource) { JwtGenerator jwtGenerator = new JwtGenerator(new NimbusJwtEncoder(jwkSource)); jwtGenerator.setJwtCustomizer(new CustomTokenCustomizer()); // 配置用户自定义的 JWT 令牌自定义器,自定义 claims 信息 OAuth2AccessTokenGenerator accessTokenGenerator = new OAuth2AccessTokenGenerator(); OAuth2RefreshTokenGenerator refreshTokenGenerator = new OAuth2RefreshTokenGenerator(); return new DelegatingOAuth2TokenGenerator( jwtGenerator, accessTokenGenerator, refreshTokenGenerator); } /** * 配置密码模式认证提供者 */ @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); }
3.4 一般参数不对就会跳转到登录界面,或者密码错误会返回OAuth固定的格式给前端,如果想返回自定义格式给前端,还需要配置一下过滤器进行拦截重写(如果不需要自定义格式,用上面3.3注释掉的OAuth2AuthenticationException 返回一样的)

public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint { private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); @Override public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException { if(authException instanceof InsufficientAuthenticationException){ String accept = request.getHeader("accept"); if(accept.contains(MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)){ //如果是html请求类型,则返回登录页 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint loginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint = new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"); loginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint.commence(request,response,authException); }else { //如果是api请求类型,则返回json ResponseResult.exceptionResponse(response,"需要带上令牌进行访问"); } }else if(authException instanceof InvalidBearerTokenException){ ResponseResult.exceptionResponse(response,"令牌无效或已过期"); }else{ ResponseResult.exceptionResponse(response,authException); } } }

public class MyAuthenticationException extends AuthenticationException { public MyAuthenticationException(String msg) { super(msg); } }

public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler { @Override public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException { ResponseResult.exceptionResponse(response,exception); } }

import lombok.Getter; @Getter public enum ResultCodeEnum { SUCCESS(200,"成功"), FAIL(201, "失败"); private Integer code; private String message; private ResultCodeEnum(Integer code, String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } }

import com.nimbusds.jose.shaded.gson.Gson; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.OAuth2AuthenticationException; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; @Data public class ResponseResult<T> { /** * 状态码 */ private Integer code; /** * 返回信息 */ private String message; /** * 数据 */ private T data; private ResponseResult() { } public static <T> ResponseResult<T> build(T body, ResultCodeEnum resultCodeEnum) { ResponseResult<T> result = new ResponseResult<>(); //封装数据 if (body != null) { result.setData(body); } //状态码 result.setCode(resultCodeEnum.getCode()); //返回信息 result.setMessage(resultCodeEnum.getMessage()); return result; } public static <T> ResponseResult<T> ok() { return build(null, ResultCodeEnum.SUCCESS); } public static <T> ResponseResult<T> ok(T data) { return build(data, ResultCodeEnum.SUCCESS); } public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail() { return build(null, ResultCodeEnum.FAIL); } public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail(T data) { return build(data, ResultCodeEnum.FAIL); } public ResponseResult<T> message(String msg) { this.setMessage(msg); return this; } public ResponseResult<T> code(Integer code) { this.setCode(code); return this; } public static void exceptionResponse(HttpServletResponse response, Exception e) throws AccessDeniedException, AuthenticationException, IOException { String message = null; if (e instanceof OAuth2AuthenticationException o) { message = o.getError().getDescription(); } else { message = e.getMessage(); } exceptionResponse(response, message); } public static void exceptionResponse(HttpServletResponse response, String message) throws AccessDeniedException, AuthenticationException, IOException { ResponseResult responseResult = ResponseResult.fail(message); Gson gson = new Gson(); String jsonResult = gson.toJson(responseResult); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE); //response.setCharacterEncoding(Charsets.UTF_8.name()); response.setCharacterEncoding(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); response.getWriter().print(jsonResult); } }
最后在SecurityConfig 中authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain 和defaultSecurityFilterChain进行配置

/** * 配置 OAuth2 授权服务器的安全过滤器链 * * @param http Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity 对象 * @return SecurityFilterChain 安全过滤器链 * @throws Exception 配置过程中可能抛出的异常 */ @Bean @Order(1) // 指定过滤器链的优先级,授权服务器的安全配置优先 public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http, OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService, OAuth2TokenGenerator<?> tokenGenerator) throws Exception { // 创建 OAuth2 授权服务器的配置 OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer authorizationServerConfigurer = OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.authorizationServer(); http // 只匹配 OAuth2 授权服务器的相关端点 .securityMatcher(authorizationServerConfigurer.getEndpointsMatcher()) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, (authorizationServer) -> authorizationServer //设置自定义密码模式 .tokenEndpoint(tokenEndpoint -> tokenEndpoint .accessTokenRequestConverter( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationConverter()) .authenticationProvider( new PasswordGrantAuthenticationProvider( authorizationService, tokenGenerator)) .errorResponseHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler()) // 自定义认证失败处理器 ) .oidc(Customizer.withDefaults()) // 启用 OpenID Connect 1.0 ) // 任何请求都需要认证 .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .anyRequest().authenticated() ) .with(authorizationServerConfigurer, customizer -> customizer.oidc(Customizer.withDefaults())) // 启用 OIDC(可选) // 未认证时,HTML 请求重定向到 /login 页面 .exceptionHandling((exceptions) -> exceptions .defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor( //new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"), new ClientAwareAuthenticationEntryPoint(), //根据客户端id自定义跳转登录界面 new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(MediaType.TEXT_HTML) ) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) ) ; return http.build(); // 构建安全过滤器链 } /** * 配置默认的 Spring Security 过滤器链,处理用户身份认证 * * @param http Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity 对象 * @return SecurityFilterChain 安全过滤器链 * @throws Exception 配置过程中可能抛出的异常 */ @Bean @Order(2) // 低于授权服务器的过滤器链优先级 public SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http //.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable()) // 禁用 CSRF(移动端无 Cookie 场景) // 任何请求都需要认证 .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .requestMatchers("/auth/login", "/api/auth/refresh","/home","/login/**").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() ) // 使用 Spring Security 默认的表单登录 //.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 使用自定义表单登录配置 .formLogin(form -> form .loginPage("/login") // // 默认登录页 .permitAll() // 允许所有用户访问登录页 ) .oauth2ResourceServer((resourceServer) -> resourceServer .jwt(Customizer.withDefaults()) .authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()) // 自定义认证失败处理器 ); return http.build(); }
4. 最后测试
1. 测试授权码模式。web端登录授权
先获取code授权码,将这一串放在浏览器跳转至登录界面授权


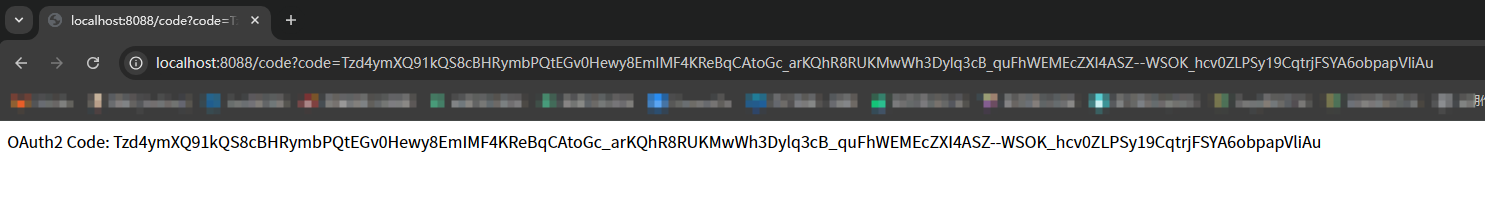
这里将拿到的code用来换取token.注意如果后端配置了 CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC 就需要在请求头通过clientid 和secret进行加密。postman 可以直接输入账号进行加密,前端调用需要自己进行base64编码{clientid}:{secret} ,然后放入到请求头中
.clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式
Authorization:Basic {编码后字符串}"


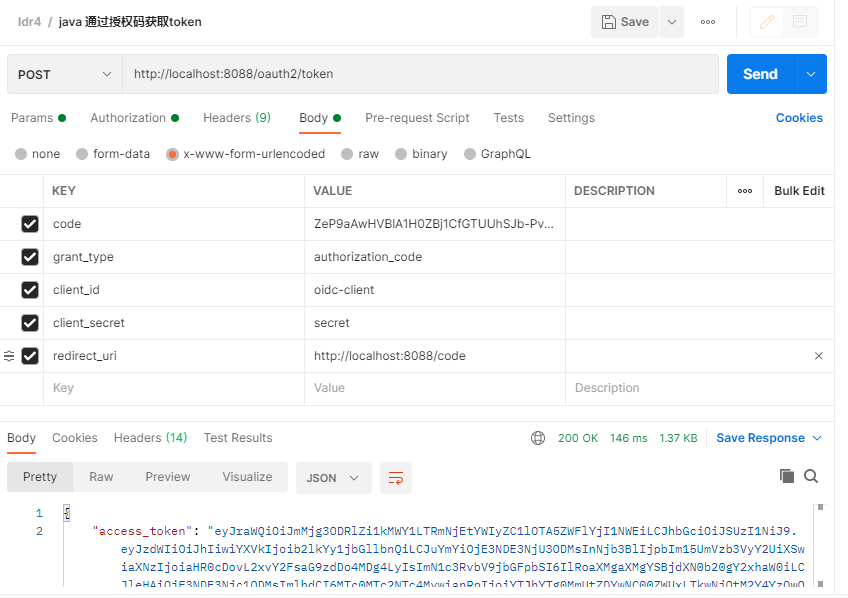
2. 测试授权码+pkce模式。移动端登录授权
需要在上面客户端配置中开启pkce,也不需要配置 clientSecret,认证方式也不需要了

RegisteredClient mobileClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientId("mobile-client") // 客户端 ID .clientName("授权码+PKCE客户端") .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings( ClientSettings.builder() .requireAuthorizationConsent(true) .requireProofKey(true) // 关键配置:强制客户端使用 PKCE 进行授权 .build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build();
这里和授权码模式很像,上面授权码后面拿token需要传递clientSecret,但是在移动端配置clientSecret是很容易泄露的(第一种web端可以存储在服务端进行交互),返回的code也容易被拦截,所以就需要 换一种安全的方式进行授权,每次跳转到登录页面之前把 通过code_verifier加密后的code_challenge传递给认证服务器

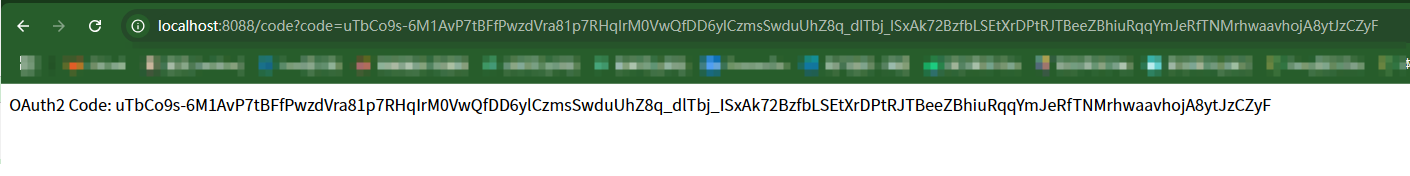
最后换取token的时候需要带上code_verifier,授权服务器就会将当前code_verifier进行加密和开始跳转登录之前传递的code_challenge进行对比,就算code泄露了,只要这里对不上也会认证失败

如果不知道怎么生成code_verifier和code_challenge,可以通过这段代码生成

/** * 生成PKCE 对应的codeVerifier和codeChallenge * @return */ @GetMapping("/login/pkce") public String pkce() { try { //生成code_verifier String codeVerifier = codeVerifierGenerator(); //生成code_challenge String codeChallenge = codeChallengeGenerator(codeVerifier); System.out.println("code_verifier:"+codeVerifier); System.out.println("code_challenge:"+codeChallenge); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "pkce"; // 返回home.html模板 } public static String codeVerifierGenerator(){ return Base64URL.encode(UUID.randomUUID().toString()).toString(); } public static String codeChallengeGenerator(String codeVerifier) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256"); byte[] digestCodeVerifier = messageDigest.digest(codeVerifier.getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII)); return Base64URL.encode(digestCodeVerifier).toString(); }
3. 自定义密码模式。适用于手机号验证码登录,小程序登录等等。
有些程序不会让用户输入账号密码,可以直接通过短信进行校验,如果是新用户直接先执行添加注册逻辑(这里省略了),再返回token,如果是注册过的用户就只需要校验验证码直接颁发token

5. 将客户端信息存储在数据库中
上面的例子都是基于内存存储的,如果重启服务器,那么都会重置客户端信息,也会清空用户的确认授权信息。这里将客户端及相关信息存储在数据库中
创建数据库表,我这里测试就放在上面用户一个表中了
/**
* 客户端信息表
*/
CREATE TABLE oauth2_registered_client (
id varchar(100) NOT NULL,
client_id varchar(100) NOT NULL,
client_id_issued_at datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
client_secret varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
client_secret_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
client_name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
client_authentication_methods varchar(1000) NOT NULL,
authorization_grant_types varchar(1000) NOT NULL,
redirect_uris varchar(1000) DEFAULT NULL,
post_logout_redirect_uris varchar(1000) DEFAULT NULL,
scopes varchar(1000) NOT NULL,
client_settings varchar(2000) NOT NULL,
token_settings varchar(2000) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
/**
* 授权确认表
*/
CREATE TABLE oauth2_authorization_consent (
registered_client_id varchar(100) NOT NULL,
principal_name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
authorities varchar(1000) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (registered_client_id, principal_name)
);
/**
* 授权信息表
*/
CREATE TABLE oauth2_authorization (
id varchar(100) NOT NULL,
registered_client_id varchar(100) NOT NULL,
principal_name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
authorization_grant_type varchar(100) NOT NULL,
authorized_scopes varchar(1000) DEFAULT NULL,
attributes blob DEFAULT NULL,
state varchar(500) DEFAULT NULL,
authorization_code_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
authorization_code_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
authorization_code_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
authorization_code_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_type varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
access_token_scopes varchar(1000) DEFAULT NULL,
oidc_id_token_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
oidc_id_token_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
oidc_id_token_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
oidc_id_token_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
refresh_token_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
refresh_token_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
refresh_token_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
refresh_token_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
user_code_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
user_code_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
user_code_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
user_code_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
device_code_value blob DEFAULT NULL,
device_code_issued_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
device_code_expires_at datetime DEFAULT NULL,
device_code_metadata blob DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
新增客户端语句
INSERT INTO oauth2_registered_client (`id`, `client_id`, `client_id_issued_at`, `client_secret`, `client_secret_expires_at`, `client_name`, `client_authentication_methods`, `authorization_grant_types`, `redirect_uris`, `post_logout_redirect_uris`, `scopes`, `client_settings`, `token_settings`) VALUES ('3eacac0e-0de9-4727-9a64-6bdd4be2ee1f', 'oidc-client', '2023-07-12 07:33:42', '{noop}secret', NULL, '3eacac0e-0de9-4727-9a64-6bdd4be2ee1f', 'client_secret_basic', 'refresh_token,authorization_code', 'http://localhost:8088/code', 'http://localhost:8088/', 'openid,profile,myResource', '{\"@class\":\"java.util.Collections$UnmodifiableMap\",\"settings.client.require-proof-key\":false,\"settings.client.require-authorization-consent\":true}', '{\"@class\":\"java.util.Collections$UnmodifiableMap\",\"settings.token.reuse-refresh-tokens\":true,\"settings.token.id-token-signature-algorithm\":[\"org.springframework.security.oauth2.jose.jws.SignatureAlgorithm\",\"RS256\"],\"settings.token.access-token-time-to-live\":[\"java.time.Duration\",300.000000000],\"settings.token.access-token-format\":{\"@class\":\"org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.OAuth2TokenFormat\",\"value\":\"self-contained\"},\"settings.token.refresh-token-time-to-live\":[\"java.time.Duration\",3600.000000000],\"settings.token.authorization-code-time-to-live\":[\"java.time.Duration\",300.000000000],\"settings.token.device-code-time-to-live\":[\"java.time.Duration\",300.000000000]}');
注意:这里{noop}secret 要改成密文,如果不知道密文是多少,可以直接通过代码生成打印出来。然后替换掉上面的{noop}secret
System.out.println(passwordEncoder().encode("明文"));
pom.xml添加配置,不添加运行会报错
<!-- 添加spring security cas支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-cas</artifactId>
</dependency>
这里改一下SecurityConfig就行了,这里只贴了更改的部分,把之前的写在内存的代码注释了

/** * 配置 OAuth2 客户端信息(存储在内存中) * * @return RegisteredClientRepository OAuth2 客户端存储库 */ /* @Bean public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository() { // 配置一个 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 客户端 RegisteredClient oidcClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("OIDC客户端") .clientId("oidc-client") // 客户端 ID //.clientSecret("{noop}secret") // 客户端密钥(未加密) .clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .scope("myResource") // 自定义作用域 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient mobileClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientId("mobile-client") // 客户端 ID .clientName("授权码+PKCE客户端") .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings( ClientSettings.builder() .requireAuthorizationConsent(true) .requireProofKey(true) // 关键配置:强制客户端使用 PKCE 进行授权 .build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient passwordClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("自定义密码模式客户端") .clientId("password-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret2")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(new AuthorizationGrantType(OAuth2Constant.GRANT_TYPE_PASSWORD)) // 密码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); return new InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository(oidcClient,mobileClient,passwordClient); // 使用内存存储客户端信息,如果使用数据库存储,请使用 jpa 存储库继承 RegisteredClientRepository 实现 }*/ /** * 授权信息(存储在内存中) */ /* @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService(RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new InMemoryOAuth2AuthorizationService(); }*/ /** * 客户端信息(存储在数据库中) * 对应表:oauth2_registered_client */ @Bean public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { System.out.println(passwordEncoder().encode("secret")); return new JdbcRegisteredClientRepository(jdbcTemplate); } /** * 授权信息(存储在数据库中) * 对应表:oauth2_authorization */ @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationService authorizationService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate, RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new JdbcOAuth2AuthorizationService(jdbcTemplate, registeredClientRepository); } /** * 授权确认(存储在数据库中) *对应表:oauth2_authorization_consent */ @Bean public OAuth2AuthorizationConsentService authorizationConsentService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate, RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository) { return new JdbcOAuth2AuthorizationConsentService(jdbcTemplate, registeredClientRepository); }
重新执行上面授权码模式的代码,可以在数据库生成数据就说明成功了


当然,每次去手动添加客户端确实不好操作,所以可以优化一下,可以通过现有的客户端配置进行数据库初始化数据,每次运行判断数据库如果不存在客户端则进行初始化。注意,如果生产环境在已经生成数据后想改客户端配置,只能在数据库里面进行更改
/** * 客户端信息(存储在数据库中,写入初始值的版本) * 对应表:oauth2_registered_client */ @Bean public JdbcRegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository(DataSource dataSource, PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) { JdbcRegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository = new JdbcRegisteredClientRepository(new JdbcTemplate(dataSource)); // 检查数据库是否已存在客户端,若不存在则初始化 if (registeredClientRepository.findByClientId("oidc-client") == null) { // 配置一个 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 客户端 RegisteredClient oidcClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("OIDC客户端") .clientId("oidc-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder.encode("secret")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .scope("myResource") // 自定义作用域 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient mobileClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientId("mobile-client") // 客户端 ID .clientName("授权码+PKCE客户端") .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings( ClientSettings.builder() .requireAuthorizationConsent(true) .requireProofKey(true) // 关键配置:强制客户端使用 PKCE 进行授权 .build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); RegisteredClient passwordClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("自定义密码模式客户端") .clientId("password-client") // 客户端 ID .clientSecret(passwordEncoder.encode("secret2")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(new AuthorizationGrantType("password")) // 密码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .reuseRefreshTokens(true) .idTokenSignatureAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256) // 设置 ID 令牌签名算法为 RS256 .accessTokenFormat(OAuth2TokenFormat.SELF_CONTAINED) // 设置访问令牌格式为 JWT .build()) .build(); // 保存到数据库 registeredClientRepository.save(oidcClient); registeredClientRepository.save(mobileClient); registeredClientRepository.save(passwordClient); } return registeredClientRepository; }
添加资源服务
上面有了认证服务,客户端(postman代替的),这里添加一个资源服务
1. pom.xml 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2. 配置application.properties 的issue地址(上面的认证服务的地址)
spring.application.name=ResourceServer spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.jwt.issuer-uri=http://localhost:8088/
3. 配置ResourceServerConfig。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.authentication.JwtAuthenticationConverter; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.authentication.JwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter; import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain; @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class ResourceServerConfig{ @Bean protected SecurityFilterChain configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize .requestMatchers("/userinfo/**").hasAuthority("SCOPE_myResource") // 只有具有该作用域的才能访问 .anyRequest().authenticated() ) .oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> oauth2 .jwt(jwt -> jwt .jwtAuthenticationConverter(jwtAuthenticationConverter()) //自定义解析 scope 声明, 添加 SCOPE_ 前缀 ) ); return http.build(); } // 自定义JWT解析逻辑(可选) private JwtAuthenticationConverter jwtAuthenticationConverter() { JwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter grantedAuthoritiesConverter = new JwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter(); grantedAuthoritiesConverter.setAuthoritiesClaimName("scope"); // 从 scope 声明中获取权限 grantedAuthoritiesConverter.setAuthorityPrefix("SCOPE_"); JwtAuthenticationConverter jwtAuthenticationConverter = new JwtAuthenticationConverter(); jwtAuthenticationConverter.setJwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter(grantedAuthoritiesConverter); return jwtAuthenticationConverter; } }
注意:这里可以配置资源服务的名称 SCOPE_myResource (scope_为jwtAuthenticationConverter 写入的前缀)。 myResource 也就是上面认证服务配置客户端的自定义作用域

// 配置一个 OpenID Connect (OIDC) 客户端 RegisteredClient oidcClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) .clientName("OIDC客户端") .clientId("oidc-client") // 客户端 ID //.clientSecret("{noop}secret") // 客户端密钥(未加密) .clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret")) // 客户端密钥(加密) .clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 认证方式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式 .authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 允许刷新令牌 .redirectUri("http://localhost:8088/code") // 认证成功后的回调地址 .postLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8088/") // 退出后的回调地址 .scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // 启用 OpenID 作用域 .scope(OidcScopes.PROFILE) // 允许访问用户基本信息 .scope("myResource") // 自定义作用域 .clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 需要用户授权 .tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder() .accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 设置访问令牌过期时间为 30 分钟 .refreshTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置刷新令牌过期时间为 1 天 .build()) .build();
4. 添加测试接口
import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal; import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.Jwt; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class UserInfoController { @GetMapping("/userinfo") public String getUserInfo(@AuthenticationPrincipal Jwt jwt) { System.out.println(jwt.getClaims()); String username = jwt.getSubject(); return "Current user: " + username; } }
5. 用上面授权码模式获取到的token测试一下

这里可以授权成功,下面用自定义密码模式拿到的token请求一下
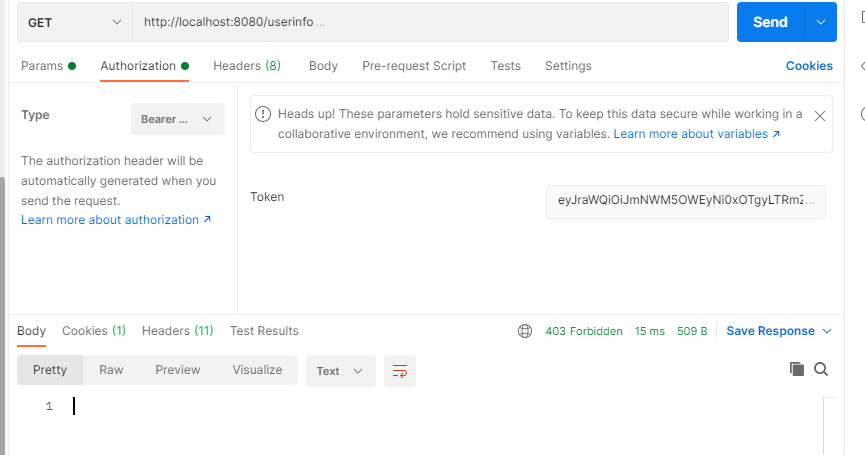
这里可以看到提示403,因为授权码模式的 oidc-client 才包含了 .scope("myResource") 自定义作用域,才能够成功访问。 而自定义密码模式没有包含,所以没有权限访问



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号