java工具类
输入输出
规范输出
//整数输出规范,保证长度
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.format("%04d",4)); //0004(输出规范)
System.out.println(String.format("%04d",11)); //0011
//按照一定精度输出小数
double a = 1.2349;
String a = String.format("%.2f",a);//1.23
//数组输出
int[] nums = {1,1,1,2};
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(nums));
文件读取
String filename = "records.txt";
// 创建BufferedReader读取文件
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
// 逐行读取文件内容
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
//对一行内容处理
}
reader.close(); // 关闭文件读取器
字符、字符串
基础操作
//整数 → 字符串
int m = 123;
String s = m + "";
//基本类型 / 包装类 → String
String s = String.valueOf(num);
//字符串 → 整数
String str = "123";
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
// String → Integer 对象
Integer integerObj = Integer.valueOf(str);
int num = integerObj.intValue(); // 转换为基本类型
//String → int[]
String str = "5 6 8 6 9 1 6 1";
String[] num = str.split(" ");
int[] nums = Arrays.stream(num)
.mapToInt(s -> Integer.parseInt(s)) // mapToInt返回IntStream
.toArray();// 返回int[]
//String → char[]
String s = "456987412dfwerfd";
char[] array = s.toCharArray();
//char[] → String
String str = String.valueOf(array);
//根据字符串获取数据的每一位数字(可能存入列表、map等容器,或者有其他逻辑)
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
String s = "123456";
int a = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){
a = s.charAt(i) - '0';
list.add(a);
//其他逻辑
}
//根据特定字符串对所给字符串进行分割,得到字符串数组
String[] d = s2.split("\n");
//字符串截取
//截取n - m位
String s = str.substring(n-1,m);//获取索引[n-1,m-1]
//截取从索引2开始的所有字符
String s = str.substring(2);
//是否含有子串
s.contains("123");//true or false
//判断数字串中的两个字符的大小
String s = "123450";
if(s.charAt(j) - s.charAt(j-1) < 0){} //当前字符的ASCII值是否小于前一个字符的ASCII值
StringBuilder
导入类:在java.lang包下,默认直接导入
//反转---回文数
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder("123456");
System.out.print(s.reverse());//654321
//反转后转换回字符串,用于判断是否是回文
String str = "12321";
if(new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString().equals(s)){}
位运算
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
System.out.print(a & b);//与 0
System.out.print(a | b);//或 1
System.out.print(a ^ b);//异或 1
数学
进制转换
String num1 = Integer.toBinaryString(15); // 1111 转为二进制
String num2 = Integer.toOctalString(15); // 17 转为八进制
String num3 = Integer.toHexString(15); // f 转为十六进制
String num4 = Integer.toString(5,4); // 11 十转为任意制
通用进制转换 BigInteger
导入类:import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new BigInteger("2022", 9).toString(10);//9进制的2022转十进制
System.out.print(s);//1478
String s = new BigInteger("15", 10).toString(2);//10进制的15转二进制
System.out.print(s);//1111
}
}
double小数位数限制
//字符串
String s = String.format("%.4f", H);
// 使用DecimalFormat
double number = 123.456789;
// 保留2位小数
DecimalFormat df2 = new DecimalFormat("#.##");
System.out.println(df2.format(number)); // 123.46
// 固定2位小数(不足补0)
DecimalFormat dfFixed2 = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
System.out.println(dfFixed2.format(number)); // 123.46
// 整数部分3位,小数部分2位
DecimalFormat dfCombo = new DecimalFormat("000.00");
System.out.println(dfCombo.format(number)); // 123.46
BigDecimal
导入类:import java.math.BigDecimal;
将 double 类型的值四舍五入到4位小数:
//将 double 值 r转换为字符串,再用字符串构造 BigDecimal。因为 new BigDecimal(0.1)可能会有精度误差,new BigDecimal("0.1")没有误差
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(r));
bd = bd.setScale(4, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
double result = bd.doubleValue();
基础计算
当 x和 count都是 int类型,且 x < count时,x / count的结果是 0。
int x = 3;
int count = 10;
double px = x / count; // px = 0.0
double px = x * 1.0 / count; // px != 0.0
高精度计算大数
导入类:import java.math.BigInteger;
使用方法
//输入
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger a = sc.nextBigInteger();
//创建大数的两种方式
BigInteger b = new BigInteger("1000000007"); // 参数为String
BigInteger b = BigInteger.valueOf(1000000007L); //参数为long
//以下五种运算函数的参数都必须是 BigInteger
System.out.println(a.add(b)); //加
System.out.println(a.subtract(b));//减
System.out.println(a.multiply(b)); //乘
System.out.println(a.divide(b)); //除
System.out.println(a.mod(b));//余数。注意:如果b是负数,这里可能报错
Math
导入类:import java.lang.Math;
//使用:Math.方法名()
Math.abs(Object o);//绝对值
Math.min(Object a, Object b);
Math.max(Object a, Object b);
Math.pow(double a, double b);//计算a的b次方
Math.sqrt(double a);//开平方
Math.log(double a);//求对数,以e为底
Math.log(double a) / Math.log(2);//取对数,以2为底
// 四舍五入函数 - 返回最接近参数的整数
// 参数:浮点数
// 返回值:最接近的long或int值
Math.round(float a); // 对float,返回int
Math.round(double a); // 对double,返回long
//平面距离公式:A(x,y)点到原点的距离
double R = Math.sqrt(x*x + y*y);
//计算点 (x, y) 相对于x轴的极角(单位:弧度)
double theta = Math.atan2(y, x);
//用弧度(极角)求弧长
double S = R * theta;
日期类
Date
导入类:import java.util.Date;
//getTime()方法返回的是从1970.1.1 00:00:00 GMT到Date对象表示的时间所经过的毫秒数。
Date date = new Date(); // 当前时间
long timestamp = date.getTime(); // 获取时间戳
LocalDate
导入类:import java.time.LocalDate;
相关用法:
//设置日期
LocalDate begin = LocalDate.of(2000,1,1);//2000.1.1
LocalDate end = LocalDate.of(2024,4,14);//2024.4.14
//下一天
begin = begin.plusDays(1);
//判断是不是在某一天之前
begin.isBefore(end);//返回true or false
//获取时间字段的函数
LocalDate begin = LocalDate.of(2025,6,1);
System.out.print(begin.getYear()); // 2025
System.out.print(begin.getMonthValue()); // 6
System.out.print(begin.getDayOfMonth()); // 1
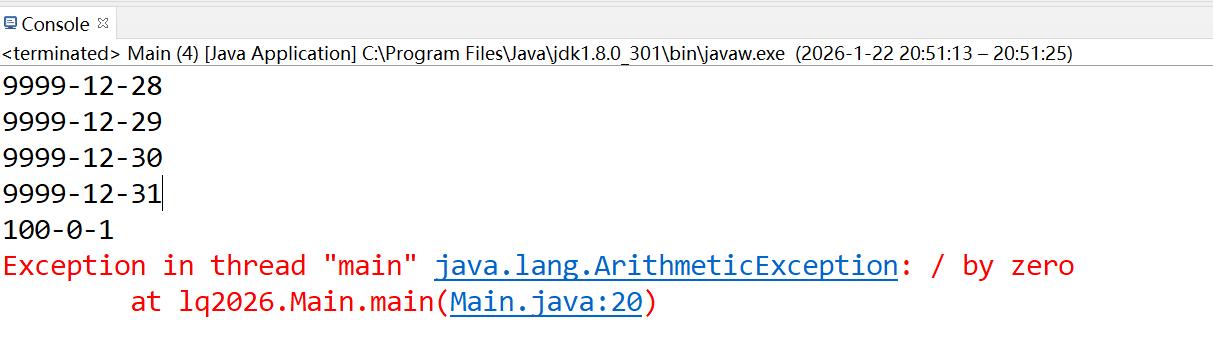
不是所有日期相关问题都能用日期类,因为年份有大小限制,比如题目特殊日期 3495,最大年份2000000,超出限制。超出年份后,日期变成100-0-1,该题目中year % month出现除0的异常ArithmeticException:

LocalDateTime
导入类:import java.time.LocalDateTime;
//获取日期格式化的LoalDateTime对象
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime d = LocalDateTime.parse(line,formatter);
TODO:补全
日期格式化:DateTimeFormatter(主)
导入类:import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter
相关用法:
//设置日期格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd");
//获取该格式的日期
String s = formatter.format(begin);//20000101、2022-12-20 07:17:03
例题:蓝桥题目编号:19937
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate begin = LocalDate.of(2000,1,1);//开始日期
LocalDate end = LocalDate.of(2024,4,14);//结束日期后一天
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd");//日期格式
int[] bihua = {13,1,2,3,5,4,4,2,2,2};//汉字0-9的笔画
int ans = 0;
while(begin.isBefore(end)){
int sum = 0;
String s = formatter.format(begin);//日期格式化
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++){
sum += bihua[s.charAt(i) - '0'];
}
if(sum > 50) ans++;
begin = begin.plusDays(1);//下一天
}
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
DayOfWeek
导入类:import java.time.DayOfWeek;
用法:
//获取今天是星期几
LocalDate begin = LocalDate.of(2025,6,1);
System.out.print(begin.getDayOfWeek()); // SUNDAY
//判断今天是不是星期六
begin.getDayOfWeek().equals(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY) //false
例题:下一次相遇 20153,判断下一个6.1是星期六的时候是哪一年。
两种解法:
- 使用LocalDate、DayOfWeek直接判断
- 计算一年的天数与一周七天之间的数学逻辑
时间差:Duration
用于表示时间间隔或持续时间,它主要用于计算两个时间点之间的时间差。
导入类:import java.time.Duration;
使用方法:
//计算从 start到 end的时间段,然后获取总秒数。
LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2024, 1, 21, 9, 0, 0);
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.of(2024, 1, 21, 17, 30, 0);
Duration duration = Duration.between(start, end);//计算从 start到 end的时间段
System.out.println(duration); // 输出: PT8H30M
totalSeconds += duration.getSeconds();//该事件段的总秒数
// 获取总时间
long seconds = duration.getSeconds(); // 总秒数: 30600
long minutes = duration.toMinutes(); // 总分钟数: 510
long hours = duration.toHours(); // 总小时数: 8
long days = duration.toDays(); // 总天数: 0
long millis = duration.toMillis(); // 总毫秒数: 30600000
long nanos = duration.toNanos(); // 总纳秒数: 30600000000000
// 获取组成部分
long hoursPart = duration.toHoursPart(); // 小时部分: 8
long minutesPart = duration.toMinutesPart(); // 分钟部分: 30
long secondsPart = duration.toSecondsPart(); // 秒部分: 0
日期格式化SimpleDateFormat
注意!!!!
- 可以处理:
java.util.Date(主)、java.sql.Date、java.sql.Time、java.sql.Timestamp - 不能处理:
java.time.LocalDate;、java.time.LocalTime;、java.time.LocalDateTime;
//日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
SimpleDateFormat sdf3 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
//获取格式化日期
Date date = format.parse(String str);
String s = format.format(new Date());//将 Date 格式化为字符串
String s = format.toPattern(new Date());//返回当前格式日期的字符串
Arrays 数组操作类
导入类:import java.util.Arrays
基本用法
//将数组d转换为格式化的字符串表示
String[] d = {"123456"};
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(d));
关于“流”相关用法
//用于将数组转换为流(Stream)
int[] intArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(intArray);
String[] strArray = {"a", "b", "c", "d"};
Stream<String> strStream = Arrays.stream(strArray);
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
//基本操作
int sum = Arrays.stream(numbers).sum();// 求和
double average = Arrays.stream(numbers).average().orElse(0);// 求平均值,使用orElse()提供默认值
int min = Arrays.stream(numbers).min().orElse(0);// 最小值
int max = Arrays.stream(numbers).max().orElse(0);// 最大值
long count = Arrays.stream(numbers).count();// 计数
//过滤和映射
int[] evens = Arrays.stream(numbers).filter(n -> n % 2 == 0).toArray();// 过滤偶数
int[] squares = Arrays.stream(numbers).map(n -> n * n).toArray();// 每个数平方
int[] result = Arrays.stream(numbers).filter(n -> n > 5).map(n -> n * 2).toArray();// 过滤并转换
注意:
map():返回Stream<数据包装类>,比如Stream<Integer>、Stream<String>,取决于返回的数据是什么类型的,但是使用toArray()只能返回Object[]
mapToInt():返回IntStream,toArray()返回int[]
//查找和匹配
boolean hasGreaterThan3 = Arrays.stream(numbers).anyMatch(n -> n > 3);// 是否有大于3的数
boolean allPositive = Arrays.stream(numbers).allMatch(n -> n > 0);// 是否都大于0
int first = Arrays.stream(numbers).filter(n -> n > 3).findFirst().orElse(-1);// 找到第一个大于3的数
实际案例,流的使用(简化操作):蓝桥题目编号:19937
import java.util.Arrays;
int[] bihua = {13, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 4, 2, 2, 2};
String s = "20240121";
int sum = s.chars() // 返回IntStream
.map(c -> bihua[c - '0']) // 将每个字符映射为笔画数
.sum(); // 求和
集合
集合工具类Collecitons
导入类:import java.util.Collections;
sort()可以重写排序方式:
- Comparable<>接口重写compareTo()方法
- Comparator<>接口,传递一个比较规则
dates.sort((date1, date2) -> date1.compareTo(date2));//自定义排序规则
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
//1.将集合按照从小到大排序
Collections.sort(list);
//2.将数据顺序翻转
Collections.reverse(list);
//3.随机打乱里边的数据
Collections.shuffle(list);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号