集信达短信平台-2
集信达【短信平台】短信接收服务
1. 短信接收服务介绍
短信接收服务的作用就是为应用提供访问接口,应用需要发送短信时只需要调用短信接收服务,由短信接收服务将信息保存到消息缓冲区(Mysql、Redis)。后续会由短信发送服务从消息缓冲区获取消息并发送短信。
集信达短信平台整体架构:
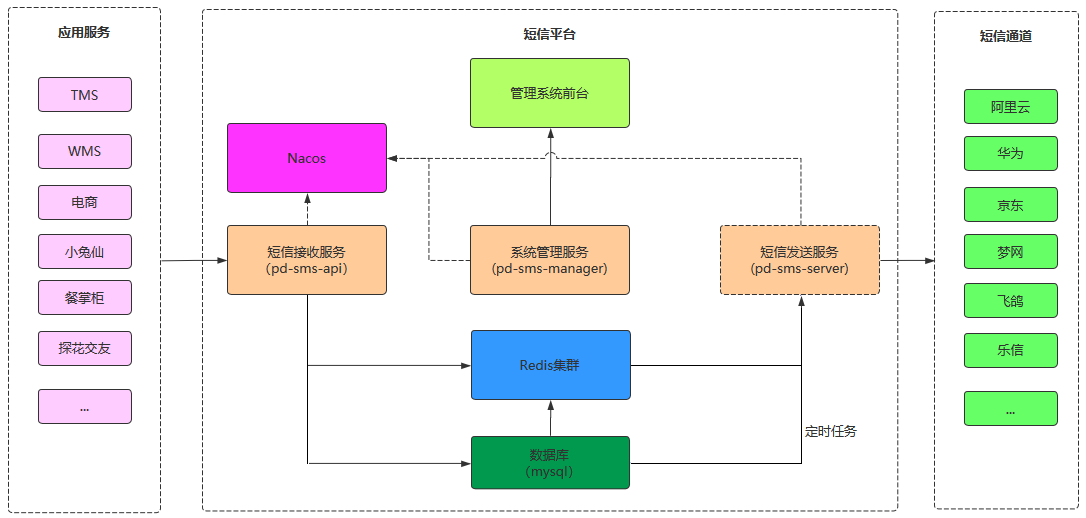
集信达短信平台业务架构:
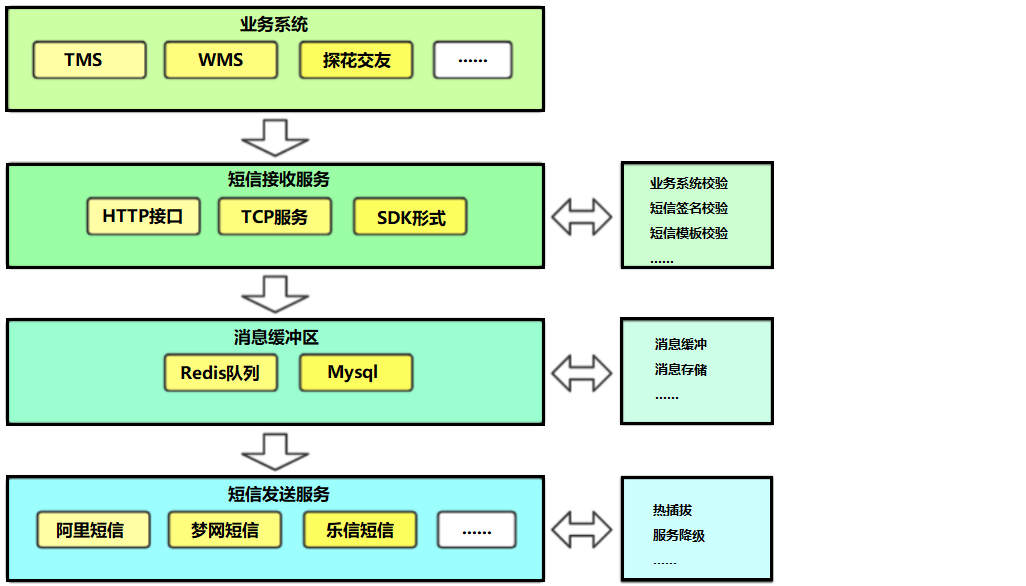
通过上面的业务架构可以看到,短信接收服务(pd-sms-api)提供3种方式供业务系统调用:
- HTTP接口
- TCP
- SDK形式
短信接收服务通过资质验证(可开关)、短信内容校验后将短信信息发送到对应中间件中(Redis、MySQL)。
短信发送方式分为两种类型:
1、定时发送短信:将短信内容存储到MySQL数据库中,由短信发送服务通过定时任务获取并发送
2、普通短信:将短信内容推送到Redis队列中,由短信发送服务异步接收并发送
2. Redis队列
2.1 Redis队列介绍
Redis支持五种数据类型:string(字符串),hash(哈希),list(列表),set(集合)及zset(sorted set:有序集合)。
Redis的list是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)。
使用Redis的list可以模拟消息队列,即使用rpush和lpush命令将数据插入队列(生产消息),使用lpop和rpop命令将数据弹出队列(消费消息)。
队列中的消息可以由不同的生产者写入,也可以由不同的消费者消费,但是一个消息一定是只能被消费一次。
2.2 案例演示
发布消息:
root@77889f10b0c8:/data# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH channel1 msg1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH channel1 msg2
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH channel1 msg3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH channel1 msg4
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH channel1 msg5
(integer) 5
查看消息:
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE channel1 0 -1
1) "msg5"
2) "msg4"
3) "msg3"
4) "msg2"
5) "msg1"
消费消息:
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
"msg1"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
"msg2"
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE channel1 0 -1
1) "msg5"
2) "msg4"
3) "msg3"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
"msg3"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
"msg4"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
"msg5"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP channel1
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE channel1 0 -1
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379>
RPOP命令不具有阻塞功能,如果需要阻塞功能可以使用BRPOP命令。
2.3 代码案例
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.sms.SmsApiApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SmsApiApplication.class)
public class RedisListTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//生产消息
@Test
public void testPush(){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("itcast","msg" + i);
}
}
//消费消息
@Test
public void testPop(){
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
Object itcast = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("itcast");
System.out.println("消费消息:"+itcast);
}
}
}
3. 短信接收服务
3.1 需求分析
功能需求:
- 应用系统调用短信接收服务提供的接口,由短信接收服务将信息保存到消息缓冲区(Mysql、Redis)
- 调用方式:HTTP、TCP、SDK
处理流程:
短信接收服务接收到应用系统请求后,会进行相关的校验处理,校验通过则将信息保存到消息缓存区,具体处理流程如下:

3.2 项目结构

3.3 数据模型与类
| 序号 | 表名 | 类名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | signature | SignatureEntity | 短信签名 |
| 2 | template | TemplateEntity | 短信模板 |
| 3 | config | ConfigEntity | 短信通道配置 |
| 4 | config_signature | ConfigSignatureEntity | 通道与签名关系 |
| 5 | config_template | ConfigTemplateEntity | 通道与模板关系 |
| 6 | platform | PlatformEntity | 接入平台(应用管理) |
| 7 | receive_log | ReceiveLogEntity | 短信接收日志 |
| 8 | black_list | BlackListEntity | 黑名单 |
| 9 | timing_push | TimingPushEntity | 定时发送 |
注意:此处只是列出和短信接收服务有关的数据模型和类。
3.4 消息存储
导入的初始工程中已经实现了大部分代码,主要逻辑为通过Controller提供HTTP接口服务接收应用系统请求,然后调用Service,在Service中进行一系列校验,如果校验通过则需要将消息保存到消息缓冲区。
将消息保存到消息缓冲区的业务逻辑为:
1、进行短信分类,分为实时发送短信和定时发送短信
2、如果是定时发送短信则将消息保存到Mysql数据库
3、如果是实时发送短信则将消息保存到Redis队列,判断短信模板类型,如果是验证码类型则将消息保存到高优先级队列TOPIC_HIGH_SMS,如果是其他类型则将消息保存到普通队列TOPIC_GENERAL_SMS
4、保存短信接收日志到Mysql数据库
具体实现代码如下(SmsSendServiceImpl类的pushSmsMessage方法):
/**
* 将消息保存到消息缓冲区
*
* @param templateEntity
* @param smsSendDTO
* @param platformEntity
*/
private void pushSmsMessage(TemplateEntity templateEntity,
SmsSendDTO smsSendDTO, PlatformEntity platformEntity) {
// TODO 短信发送服务:将短信信息保存到数据库或者Redis队列
ReceiveLogEntity entity = new ReceiveLogEntity();
entity.setApiLogId(UUID.randomUUID().toString().toUpperCase());
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 设置日志id
smsSendDTO.setLogId(entity.getApiLogId());
String smsJson = JSON.toJSONString(smsSendDTO);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(smsSendDTO.getSendTime())) {
// 定时发送,存入mysql数据库
TimingPushEntity timingPushEntity = new TimingPushEntity();
timingPushEntity.setMobile(smsSendDTO.getMobile());
timingPushEntity.setTemplate(smsSendDTO.getTemplate());
timingPushEntity.setSignature(smsSendDTO.getSignature());
timingPushEntity.setTiming(smsSendDTO.getSendTime());
timingPushEntity.setRequest(JSON.toJSONString(smsSendDTO));
timingPushService.save(timingPushEntity);
} else {
// 实时发送,存入redis队列
if (templateEntity.getType() == TemplateType.VERIFICATION.getCode()) {
// 验证码类型 单独队列 优先级高
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("TOPIC_HIGH_SMS", smsJson);
log.info("TOPIC_HIGH_SMS:{}", smsJson);
} else {
// 营销类 单独队列 优先级不高
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("TOPIC_GENERAL_SMS", smsJson);
log.info("TOPIC_GENERAL_SMS:{}", smsJson);
}
}
entity.setStatus(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("发送短息异常", e);
entity.setStatus(0);
entity.setError(ExceptionUtils.getErrorStackTrace(e));
} finally {
entity.setPlatformId(platformEntity.getId());
entity.setPlatformName(platformEntity.getName());
entity.setConfigIds(StringUtils.join(smsSendDTO.getConfigIds(), ","));
entity.setTemplate(smsSendDTO.getTemplate());
entity.setSignature(smsSendDTO.getSignature());
entity.setMobile(smsSendDTO.getMobile());
entity.setRequest(JSON.toJSONString(smsSendDTO.getParams()));
entity.setUseTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
entity.setBusiness(smsSendDTO.getBatchCode());
//保存短信接收日志
receiveLogMapper.insert(entity);
}
}
3.5 TCP接口
基于Netty进行网络编程,为短信接收服务提供TCP接口,应用系统可以通过TCP调用此接口来和短信接收服务对接。
涉及到的类:

-
Netty服务启动类:用于启动Netty服务
-
通道初始化器:主要目的是为程序员提供一个简单的工具,用于在某个Channel注册到EventLoop后,对这个Channel执行一些初始化操作,例如可以添加用户自定义的服务端处理器
-
服务端处理器:具体执行处理逻辑,例如读取消息
导入的初始工程中主体代码已经完成,只需要实现服务端处理器的具体处理逻辑即可(NettyServerHandler的channelRead0方法):
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {
log.info("接收请求开始:======= 接收报文:" + msg);
String respMsg = "success";
try {
//解析报文
SmsParamsDTO smsParamsDTO = parseMessage(msg);
if (null == smsParamsDTO) {
log.info("报文解析失败");
return;
}
//调用Service将消息保存到消息缓冲区
SpringUtils.getBean(SmsSendServiceImpl.class).send(smsParamsDTO);
} catch (Exception e) {
respMsg = e.getMessage();
}
log.info("返回报文 ========== " + respMsg);
ctx.writeAndFlush(respMsg + "\n");//这个地方必须加上"\n",不然客户端接收不到消息
}
可以使用telnet作为Netty客户端来测试Netty服务,报文如下:
{"accessKeyId": "7fea0419ea7c435887f996cfecda5a3a","mobile": "13812345678","params": {"code":"123456"},"signature": "DXQM_000000001","template": "DXMB_000000001","timestamp": "","sendTime":"2020-12-31 10:00"}
3.6 SDK
3.6.1 说明
SDK 是 Software Development Kit 的缩写,即软件开发工具包。SDK被开发出来是为了减少程序员工作量的,比如公司开发出某种软件的某一功能,把它封装成SDK,提供给其他公司和个人使用。
本小节需要开发短信接收服务SDK,通过SDK可以使应用系统更加方便的调用短信接收服务。
通过SDK方式调用短信接收服务,本质上还是调用的短信接收服务提供的HTTP接口(Controller),只不过是调用的过程在SDK中进行了封装。
项目结构:

3.6.2 实现
导入的初始工程中主体代码已经完成,只需要实现业务处理类的具体逻辑即可(SmsSendServiceImpl的send方法):
/**
* 通过HttpClient发送post请求,请求短信接收服务HTTP接口
* @param baseParamsDTO
* @param url
* @return
*/
private R send(BaseParamsDTO baseParamsDTO,String url){
//设置accessKeyId
baseParamsDTO.setAccessKeyId(accessKeyId);
if (auth) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(accessKeyId) || StringUtils.isBlank(accessKeySecret)) {
R.fail("accessKey 不能为空");
}
baseParamsDTO.setTimestamp(String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
baseParamsDTO.setEncryption(SmsEncryptionUtils.encode(baseParamsDTO.getEncryption(), baseParamsDTO.getAccessKeyId(), accessKeySecret));
}
if (StringUtils.isBlank(domain)) {
R.fail("domain 不能为空");
}
//HTTP客户端
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//Post请求对象
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(url);
//设置请求头
post.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8");
//构造请求体
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity(JSON.toJSONString(baseParamsDTO), "UTF-8");
//设置请求体
post.setEntity(stringEntity);
try {
//发送请求
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(post);
//获得响应信息
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
//解析响应状态码
if (200 == response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) {
log.info("httpRequest access success, StatusCode is:{}", response.getStatusLine()
.getStatusCode());
String responseContent = EntityUtils.toString(entity);
log.info("responseContent is :" + responseContent);
return JSON.parseObject(responseContent, R.class);
} else {
log.error("httpRequest access fail ,StatusCode is:{}", response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode());
return R.fail("status is " + response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error :", e);
return R.fail(e.getMessage());
} finally {
post.releaseConnection();
}
}
SDK开发完成后,为了方便其他应用使用,通常会将SDK打成jar包上传到远程maven仓库,在应用系统中直接通过maven坐标导入SDK即可使用。
如下是将SDK上传到Nexus后的效果:

3.6.3 测试
第一步:引入SDK的maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>pd-sms-sdk</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
第二步:编写配置文件
# 服务端使用sdk配置信息
itheima:
sms:
auth: false
domain: http://localhost:8771
accessKeyId: 7fea0419ea7c435887f996cfecda5a3a
accessKeySecret: 842ce103df7b4117bb47c888cc528516
第三步:编写单元测试
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.sms.SmsManageApplication;
import com.itheima.sms.sms.dto.SmsParamsDTO;
import com.itheima.sms.sms.service.SmsSendService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SmsManageApplication.class)
public class SdkTest {
@Autowired
private SmsSendService smsSendService;
/**
* 通过SDK方式调用短信接收服务
*/
@Test
public void testSend(){
SmsParamsDTO dto = new SmsParamsDTO();
dto.setMobile("13812345678");
dto.setSignature("DXQM_000000001");
dto.setTemplate("DXMB_000000001");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","1234");
dto.setParams(map);
dto.setSendTime("2020-12-18 10:00");
dto.setTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() +"");
smsSendService.sendSms(dto);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号