3次dupack成为历史了
RACK (draft-ietf-tcpm-rack-01): it is a newer algorithm * (2017-) that checks timing instead of counting DUPACKs. * Essentially a packet is considered lost if it's not S/ACKed * after RTT + reordering_window, where both metrics are * dynamically measured and adjusted. This is implemented in * tcp_rack_mark_lost.
remove obsolete and unused RFC3517/RFC6675 loss recovery code
RACK-TLP loss detection has been enabled as the default loss detection algorithm for Linux TCP since 2018,
也就是移除rfc6675 rfc3517,也就是默认使用rack-tlp 作为默认的丢包算法
以前的3次dupack触发丢包重传进入历史了!!
最新内核代码:没有tcp_update_scoreboard 减少了很多懵逼的逻辑,当时必须读rfc文档才清晰一点。
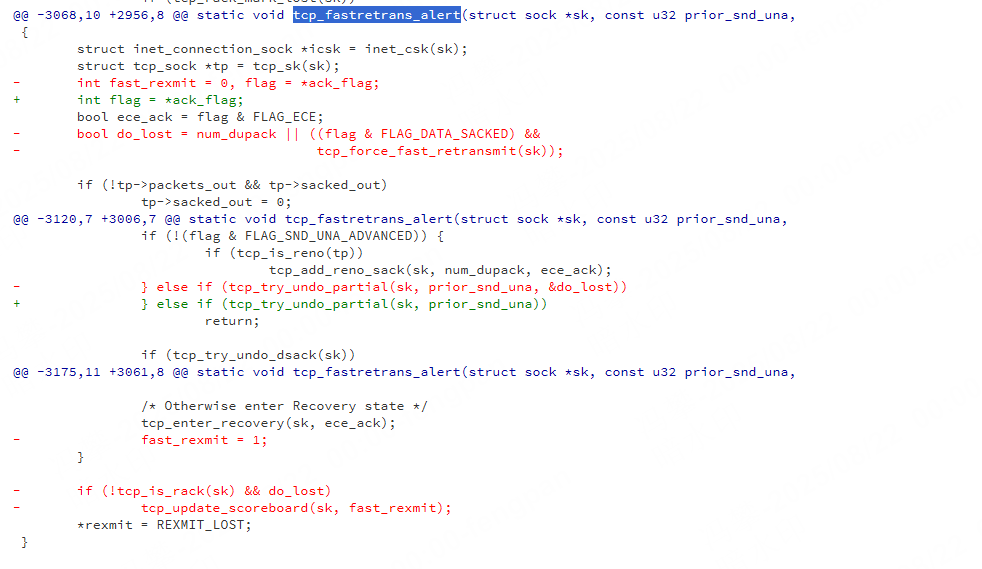
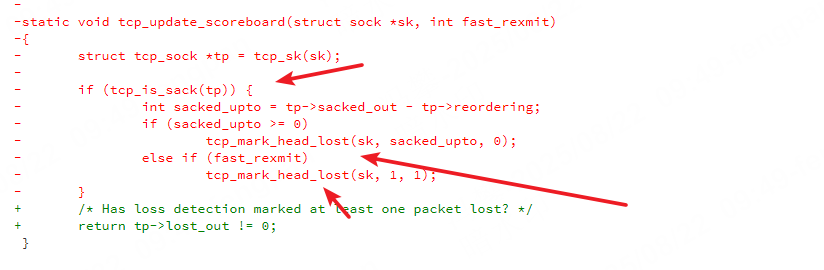
linux 5.10 内核代码如下
/* Linux NewReno/SACK/ECN state machine. * -------------------------------------- * * "Open" Normal state, no dubious events, fast path. * "Disorder" In all the respects it is "Open", * but requires a bit more attention. It is entered when * we see some SACKs or dupacks. It is split of "Open" * mainly to move some processing from fast path to slow one. * "CWR" CWND was reduced due to some Congestion Notification event. * It can be ECN, ICMP source quench, local device congestion. * "Recovery" CWND was reduced, we are fast-retransmitting. * "Loss" CWND was reduced due to RTO timeout or SACK reneging. * * tcp_fastretrans_alert() is entered: * - each incoming ACK, if state is not "Open" * - when arrived ACK is unusual, namely: * * SACK * * Duplicate ACK. * * ECN ECE. * * Counting packets in flight is pretty simple. * * in_flight = packets_out - left_out + retrans_out * * packets_out is SND.NXT-SND.UNA counted in packets. * * retrans_out is number of retransmitted segments. * * left_out is number of segments left network, but not ACKed yet. * * left_out = sacked_out + lost_out * * sacked_out: Packets, which arrived to receiver out of order * and hence not ACKed. With SACKs this number is simply * amount of SACKed data. Even without SACKs * it is easy to give pretty reliable estimate of this number, * counting duplicate ACKs. * * lost_out: Packets lost by network. TCP has no explicit * "loss notification" feedback from network (for now). * It means that this number can be only _guessed_. * Actually, it is the heuristics to predict lossage that * distinguishes different algorithms. * * F.e. after RTO, when all the queue is considered as lost, * lost_out = packets_out and in_flight = retrans_out. * * Essentially, we have now a few algorithms detecting * lost packets. * * If the receiver supports SACK: * * RFC6675/3517: It is the conventional algorithm. A packet is * considered lost if the number of higher sequence packets * SACKed is greater than or equal the DUPACK thoreshold * (reordering). This is implemented in tcp_mark_head_lost and * tcp_update_scoreboard. * * RACK (draft-ietf-tcpm-rack-01): it is a newer algorithm * (2017-) that checks timing instead of counting DUPACKs. * Essentially a packet is considered lost if it's not S/ACKed * after RTT + reordering_window, where both metrics are * dynamically measured and adjusted. This is implemented in * tcp_rack_mark_lost. * * If the receiver does not support SACK: * * NewReno (RFC6582): in Recovery we assume that one segment * is lost (classic Reno). While we are in Recovery and * a partial ACK arrives, we assume that one more packet * is lost (NewReno). This heuristics are the same in NewReno * and SACK. * * Really tricky (and requiring careful tuning) part of algorithm * is hidden in functions tcp_time_to_recover() and tcp_xmit_retransmit_queue(). * The first determines the moment _when_ we should reduce CWND and, * hence, slow down forward transmission. In fact, it determines the moment * when we decide that hole is caused by loss, rather than by a reorder. * * tcp_xmit_retransmit_queue() decides, _what_ we should retransmit to fill * holes, caused by lost packets. * * And the most logically complicated part of algorithm is undo * heuristics. We detect false retransmits due to both too early * fast retransmit (reordering) and underestimated RTO, analyzing * timestamps and D-SACKs. When we detect that some segments were * retransmitted by mistake and CWND reduction was wrong, we undo * window reduction and abort recovery phase. This logic is hidden * inside several functions named tcp_try_undo_<something>. */ /* This function decides, when we should leave Disordered state * and enter Recovery phase, reducing congestion window. * * Main question: may we further continue forward transmission * with the same cwnd? */ static bool tcp_time_to_recover(struct sock *sk, int flag) { struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); /* Trick#1: The loss is proven. */ if (tp->lost_out) return true; /* Not-A-Trick#2 : Classic rule... */ if (!tcp_is_rack(sk) && tcp_dupack_heuristics(tp) > tp->reordering) return true; return false; } /* Detect loss in event "A" above by marking head of queue up as lost. * For RFC3517 SACK, a segment is considered lost if it * has at least tp->reordering SACKed seqments above it; "packets" refers to * the maximum SACKed segments to pass before reaching this limit. */ static void tcp_mark_head_lost(struct sock *sk, int packets, int mark_head) { struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); struct sk_buff *skb; int cnt; /* Use SACK to deduce losses of new sequences sent during recovery */ const u32 loss_high = tp->snd_nxt; WARN_ON(packets > tp->packets_out); skb = tp->lost_skb_hint; if (skb) { /* Head already handled? */ //如果之前已经标记过丢失报文,取出保存的skb和丢包数量值 //如果仅标记一个报文(mark_head为真),并且保存的丢失报文开始序号在SND.UNA之后, //表明已经完成请求的一个丢包的标记 if (mark_head && after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq, tp->snd_una)) return; cnt = tp->lost_cnt_hint; } else { //否者由重传队列的首报文开始遍历 skb = tcp_rtx_queue_head(sk); cnt = 0; } skb_rbtree_walk_from(skb) { /* TODO: do this better */ /* this is not the most efficient way to do this... */ tp->lost_skb_hint = skb; tp->lost_cnt_hint = cnt; //由报文skb开始遍历,如果当前遍历报文的结束序号位于最高的丢包序号之后,结束遍历 if (after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq, loss_high)) break; if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->sacked & TCPCB_SACKED_ACKED) cnt += tcp_skb_pcount(skb); //如果当前遍历的SACK所确认报文数量达到要求的packets值===tp->sacked_out - tp->reordering;,退出遍历 //也就是目前认为有tp->sacked_out - tp->reordering 报文丢失 if (cnt > packets) break; if (!(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->sacked & TCPCB_LOST)) tcp_mark_skb_lost(sk, skb); /* tcp_skb_mark_lost,如果报文没有被标记过丢失(TCPCB_LOST),也没有被SACK确认(TCPCB_SACKED_ACKED), 将其设置TCPCB_LOST标志,并且更新lost_out丢包统计。函数tcp_verify_retransmit_hint用于更新retransmit_skb_hint 重传报文指针,其中记录的为首个应当重传的报文。 */ if (mark_head) break; } tcp_verify_left_out(tp); }
/* Process an event, which can update packets-in-flight not trivially. * Main goal of this function is to calculate new estimate for left_out, * taking into account both packets sitting in receiver's buffer and * packets lost by network. * * Besides that it updates the congestion state when packet loss or ECN * is detected. But it does not reduce the cwnd, it is done by the * congestion control later. * * It does _not_ decide what to send, it is made in function * tcp_xmit_retransmit_queue(). */ static void tcp_fastretrans_alert(struct sock *sk, const u32 prior_snd_una, int num_dupack, int *ack_flag, int *rexmit) { struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk); struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); int fast_rexmit = 0, flag = *ack_flag; bool ece_ack = flag & FLAG_ECE; bool do_lost = num_dupack || ((flag & FLAG_DATA_SACKED) && tcp_force_fast_retransmit(sk));//tcp_force_fast_retransmit 返回 "空洞-乱序"的大小, 如果超过3 个 (默认) 就认为丢包。 // tp->reordering 表示 重复dupack 度量值 ; 默认为3 if (!tp->packets_out && tp->sacked_out) tp->sacked_out = 0; /* Now state machine starts. * A. ECE, hence prohibit cwnd undoing, the reduction is required. */ if (ece_ack) tp->prior_ssthresh = 0; /* B. In all the states check for reneging SACKs. 检查是否为虚假的SACK,即ACK是否确认已经被SACK的数据 如果接收到的 ACK 指向已记录的 SACK,这说明我们记录的 SACK 并没有反应接收方的真实状态。 也就是说接收方现在已经处于严重的拥塞状态或者在处理上有bug,那么我们接下来就要按照重传超时的方式去处理。 因为按照正常的逻辑流程,接受的 ACK不应该指向已记录的 SACK,而应指向 SACK 并未包含的, 这说明接收方由于拥塞已经把 SACK 部分接收的段已经丢弃或者处理上有 BUG, 我们必须需要重传*/ if (tcp_check_sack_reneging(sk, flag)) return; /* C. Check consistency of the current state. 查看是否从发送队列发出的包的数量是否不小于发出主机的包的数量 该函数的功能主要是判断 left_out 是否大于 packets_out, 当然,这是不可能的,因 为前者是已经发送离开主机的未被确认的段数,而后者是已经离开发送队列 (不一定离 开主机)但未确认的段数。故而,这里有一个WARN_ON,以便输出相应的警告信息*/ tcp_verify_left_out(tp); /* D. Check state exit conditions. State can be terminated * when high_seq is ACKed. */ if (icsk->icsk_ca_state == TCP_CA_Open) { WARN_ON(tp->retrans_out != 0); tp->retrans_stamp = 0; } else if (!before(tp->snd_una, tp->high_seq)) {//tp->snd_una >= tp->high_seq switch (icsk->icsk_ca_state) { case TCP_CA_CWR: /* CWR is to be held something *above* high_seq * is ACKed for CWR bit to reach receiver. */ if (tp->snd_una != tp->high_seq) { tcp_end_cwnd_reduction(sk); tcp_set_ca_state(sk, TCP_CA_Open); } break; case TCP_CA_Recovery: /*TCP_CA_Recovery拥塞状态接收到ACK报文, 其ack_seq序号确认了high_seq之前的所有报文(SND.UNA >= high_seq), high_seq记录了进入拥塞时的最大发送序号SND.NXT,故表明对端接收到了SND.NXT之前的所有报文, 未发生丢包,需要撤销拥塞状态*/ if (tcp_is_reno(tp)) tcp_reset_reno_sack(tp);//设置 sacked_out 为 0 if (tcp_try_undo_recovery(sk))//尝试从 Recovery 状态撤销 成功,就直接返回 return; tcp_end_cwnd_reduction(sk);;//结束拥塞窗口缩小 break; } } /* E. Process state. */ switch (icsk->icsk_ca_state) { case TCP_CA_Recovery: if (!(flag & FLAG_SND_UNA_ADVANCED)) { if (tcp_is_reno(tp)){//没有使用SACK //如果收到的ACK并没有使snd_una前进、是重复的ACK,并且没有使用SACK,则:sacked_out++,增加sacked数据包的个数。 tcp_add_reno_sack(sk, num_dupack, ece_ack); } } else { /*对于TCP_CA_Recovery拥塞状态,如果ACK报文没有确认全部的进入拥塞时SND.NXT(high_seq)之前的数据,仅确认了一部分(FLAG_SND_UNA_ADVANCED), 执行撤销函数tcp_try_undo_partial*/ /* 如果在接收到部分确认ACK的情况下,只要tcp_packet_delayed成立,原始报文就没有丢失而是被延时了; 那就表明可以退出recover状态了进入到open或者disorder 调整窗口;但是如果有重传操作,则退出,不调整窗口*/ if (tcp_try_undo_partial(sk, prior_snd_una))//接收到对原始报文的确认 return; /* Partial ACK arrived. Force fast retransmit. //返回 "空洞-乱序"的大小 如果超过3 个 (默认) 就认为丢包 // tp->reordering默认为3 */ do_lost = tcp_force_fast_retransmit(sk); } /*对于处在TCP_CA_Recovery拥塞状态的,ACK报文并没有推进SND.UNA序号 ,或者, 在partial-undo未执行的情况下,尝试进行DSACK相关的撤销操作,由函数tcp_try_undo_dsack完成。*/ if (tcp_try_undo_dsack(sk)) {//全部重传被DSACK确认, 即重传是不必要的,执行拥塞窗口恢复操作 tcp_try_keep_open(sk); return; } //如果处于TCP_CA_Recovery拥塞状态的套接口,未能施行拥塞撤销操作(报文确实已经丢失) tcp_identify_packet_loss(sk, ack_flag); break; case TCP_CA_Loss: /* 在TCP_CA_Loss状态的套接口,如果ACK报文推进了SND.UNA序号,尝试进行TCP_CA_Loss状态撤销, 由函数tcp_try_undo_loss完成。对于FRTO,如果S/ACK确认了并没有重传的报文(原始报文), 同样尝试进入撤销流程,因为此ACK报文表明RTO值设置的不够长(并非拥塞导致报文丢失), 过早进入了TCP_CA_Loss状态。*/ tcp_process_loss(sk, flag, num_dupack, rexmit); tcp_identify_packet_loss(sk, ack_flag); if (!(icsk->icsk_ca_state == TCP_CA_Open || (*ack_flag & FLAG_LOST_RETRANS))) return; /* Change state if cwnd is undone or retransmits are lost */ fallthrough; default: if (tcp_is_reno(tp)) { if (flag & FLAG_SND_UNA_ADVANCED) tcp_reset_reno_sack(tp); tcp_add_reno_sack(sk, num_dupack, ece_ack); } if (icsk->icsk_ca_state <= TCP_CA_Disorder) tcp_try_undo_dsack(sk); tcp_identify_packet_loss(sk, ack_flag); //确定能够离开 Disorder 状态,而进入 Recovery 状态。 //如果不进入 Recovery 状态,判断可否进入 OPen 状态。 if (!tcp_time_to_recover(sk, flag)) { tcp_try_to_open(sk, flag);//如果不进入 Recovery 状态,判断可否进入 OPen 状态。 //此时判断存在left_out =tp->sacked_out + tp->lost_out;数据或者被sack或者存在 retrans_out 数据;则设置为disorder状态 //否者进入open状态 return; } /* MTU probe failure: don't reduce cwnd */ if (icsk->icsk_ca_state < TCP_CA_CWR && icsk->icsk_mtup.probe_size && tp->snd_una == tp->mtu_probe.probe_seq_start) { tcp_mtup_probe_failed(sk); /* Restores the reduction we did in tcp_mtup_probe() */ tp->snd_cwnd++; tcp_simple_retransmit(sk); return; } /* Otherwise enter Recovery state */ //确定能够离开 Disorder or open 状态,而进入 Recovery 状态。 tcp_enter_recovery(sk, ece_ack); fast_rexmit = 1; } /*tcp_fastretrans_alert函数中对丢包(do_lost)的判断, 如果接收到dupack,或者对端SACK序号块确认的最高序号,超出SND.UNA加上乱序级别的值, 认为套接口发生了丢包。另外,对于TCP_CA_Recovery拥塞状态的套接口, 如果接收到的ACK报文(dupack)未能推进SND.UNA,并且Partial-Recovery未能实行, 对于Reno-TCP(无SACK)或者tcp_force_fast_retransmit为真,设置丢包变量do_lost。 */ if (!tcp_is_rack(sk) && do_lost)/* 更新记分牌,标志丢失和超时的数据包,增加lost_out */ tcp_update_scoreboard(sk, fast_rexmit); //对于未启用RACK算法的情况,如果判断发生丢包,使用函数tcp_update_scoreboard处理 *rexmit = REXMIT_LOST; }
http代理服务器(3-4-7层代理)-网络事件库公共组件、内核kernel驱动 摄像头驱动 tcpip网络协议栈、netfilter、bridge 好像看过!!!!
但行好事 莫问前程
--身高体重180的胖子



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号