鸿蒙学习实战之路 - 瀑布流操作实现
鸿蒙学习实战之路 - 瀑布流操作实现
官方文档永远是你的好伙伴,请收藏!
华为开发者联盟 - 瀑布流最佳实践
华为开发者联盟 - WaterFlow 组件参考文档
关于本文
本文主要介绍在 HarmonyOS 中如何实现高性能、高体验的瀑布流布局,包含基础实现和高级优化技巧
- 本文并不能代替官方文档,所有内容基于官方文档+实践记录
- 所有代码示例都有详细注释,建议自己动手尝试
- 基本所有关键功能都会附上对应的文档链接,强烈建议你点看看看
概述
瀑布流(WaterFlow)布局是移动应用中常见的布局方式,用于展示高度不一的内容块,形成错落有致的视觉效果。在 HarmonyOS 中,我们可以使用 WaterFlow 组件快速实现瀑布流布局,但要实现高性能、流畅的瀑布流效果,还需要掌握一些优化技巧。
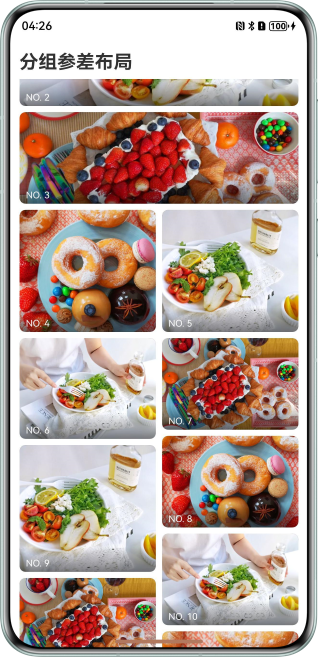
实现原理
关键技术
瀑布流布局主要通过以下核心技术实现:
- WaterFlow 组件 - 实现瀑布流的基础容器
- LazyForEach - 实现数据的懒加载,提升性能
- GridItem - 定义瀑布流中的每个内容项
- 异步加载 - 实现图片等资源的异步加载
- 状态管理 - 管理瀑布流的加载状态和数据
重要提醒!
实现高性能瀑布流需要注意:
- 内容项的高度要准确计算,避免布局抖动
- 图片资源需要懒加载,避免一次性加载过多资源
- 合理设置缓存策略,提升重复访问的性能
- 考虑大数据量下的性能优化和内存管理
开发流程
实现瀑布流布局的基本步骤:
- 创建 WaterFlow 组件作为布局容器
- 配置瀑布流参数(列数、间距等)
- 使用 LazyForEach 绑定数据源
- 实现内容项的布局和样式
- 添加异步加载和性能优化
基础瀑布流实现
场景描述
在应用中展示图片列表,每张图片高度不一,形成错落有致的瀑布流效果。
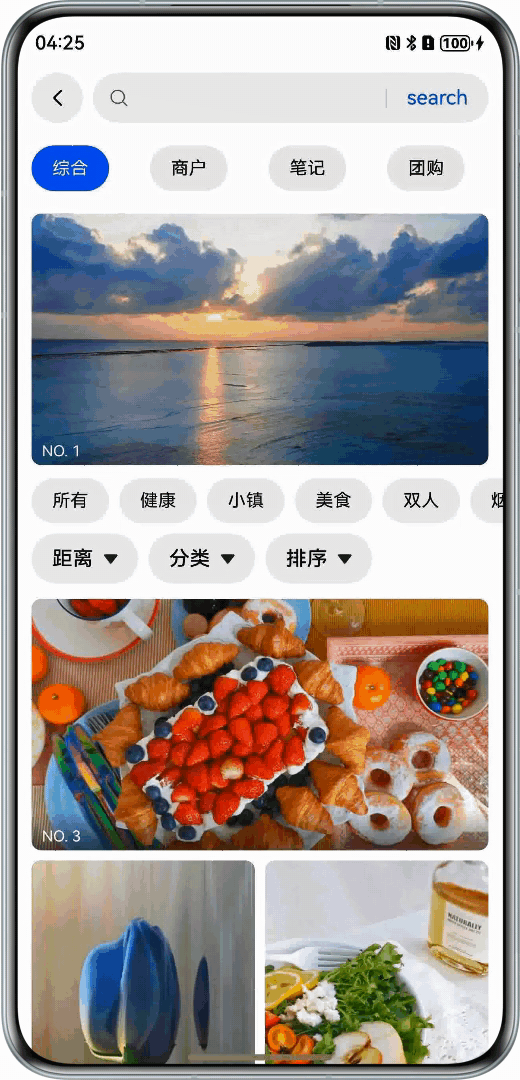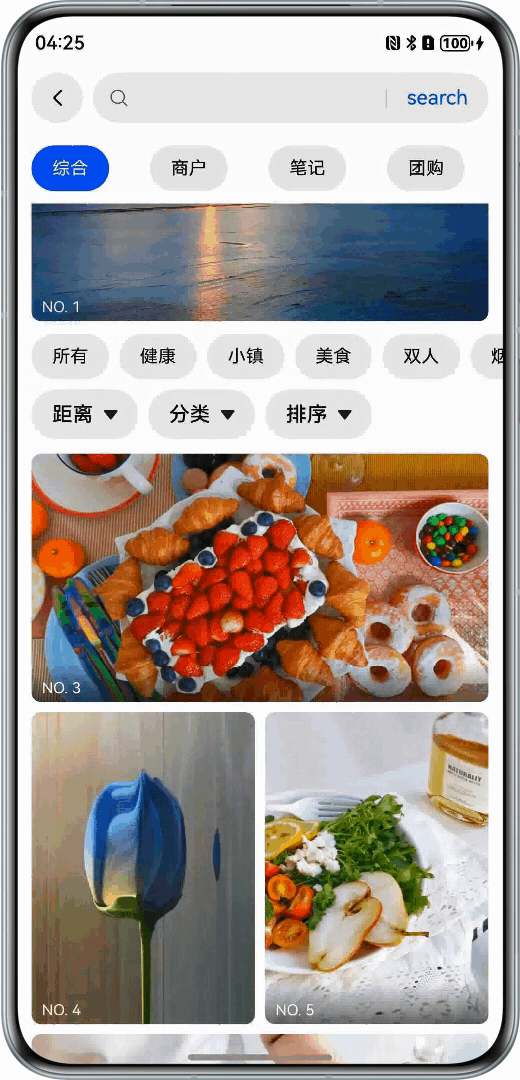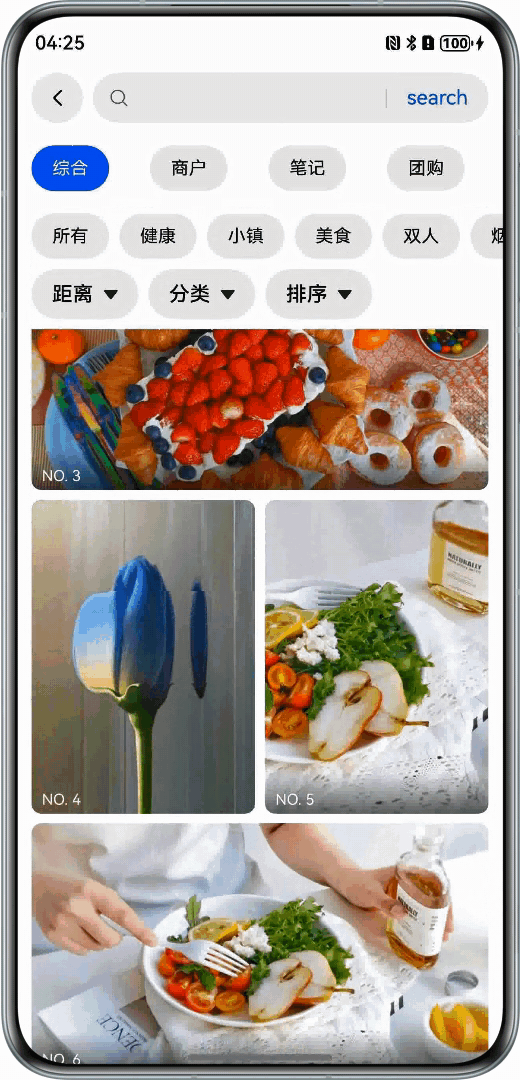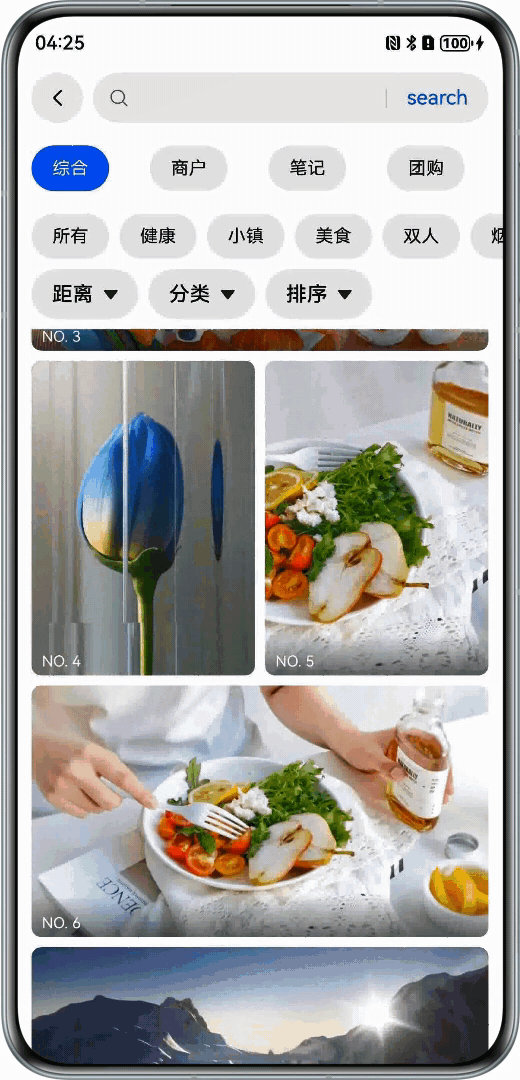
开发步骤
1. 创建基础的瀑布流布局
首先创建一个基本的 WaterFlow 组件作为瀑布流容器:
@Entry
@Component
struct BasicWaterFlowPage {
// 图片数据
@State images: ImageItem[] = [];
// 页面加载时初始化数据
aboutToAppear() {
this.initData();
}
// 初始化图片数据
initData() {
// 模拟图片数据
this.images = [
{ id: 1, url: 'https://example.com/image1.jpg', height: 300 },
{ id: 2, url: 'https://example.com/image2.jpg', height: 250 },
{ id: 3, url: 'https://example.com/image3.jpg', height: 350 },
{ id: 4, url: 'https://example.com/image4.jpg', height: 280 },
{ id: 5, url: 'https://example.com/image5.jpg', height: 320 },
{ id: 6, url: 'https://example.com/image6.jpg', height: 260 }
];
}
build() {
Column() {
// 瀑布流组件
WaterFlow() {
// 使用LazyForEach实现数据懒加载
LazyForEach(this.images, (item: ImageItem) => {
// 瀑布流中的每个item
GridItem() {
// 图片组件
Image(item.url)
.width('100%') // 宽度占满
.height(item.height) // 设置图片高度
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover) // 图片填充方式
.borderRadius(12) // 圆角处理
.margin(8) // 外边距
}
}, (item: ImageItem) => item.id.toString()) // 设置唯一key
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr') // 设置2列布局
.columnsGap(16) // 列间距
.rowsGap(16) // 行间距
.padding(16) // 内边距
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
// 图片数据模型
export interface ImageItem {
id: number; // 唯一标识
url: string; // 图片地址
height: number; // 图片高度
}
2. 添加加载状态和错误处理
为了提升用户体验,我们可以添加加载状态和错误处理:
@Entry
@Component
struct WaterFlowWithLoadingPage {
// 图片数据
@State images: ImageItem[] = [];
// 加载状态
@State isLoading: boolean = true;
// 错误信息
@State errorMessage: string = '';
// 页面加载时初始化数据
aboutToAppear() {
this.loadData();
}
// 加载数据
async loadData() {
try {
this.isLoading = true;
this.errorMessage = '';
// 模拟网络请求延迟
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500));
// 模拟图片数据
this.images = [
{ id: 1, url: 'https://example.com/image1.jpg', height: 300 },
{ id: 2, url: 'https://example.com/image2.jpg', height: 250 },
{ id: 3, url: 'https://example.com/image3.jpg', height: 350 },
{ id: 4, url: 'https://example.com/image4.jpg', height: 280 },
{ id: 5, url: 'https://example.com/image5.jpg', height: 320 },
{ id: 6, url: 'https://example.com/image6.jpg', height: 260 }
];
} catch (error) {
this.errorMessage = '加载失败,请稍后重试';
console.error('加载图片数据失败:', error);
} finally {
this.isLoading = false;
}
}
build() {
Column() {
// 加载状态显示
if (this.isLoading) {
Column() {
LoadingProgress() // 加载进度条
.color('#007DFF')
.size({ width: 40, height: 40 })
Text('加载中...') // 加载文本
.fontSize(14)
.color('#666666')
.margin({ top: 12 })
}
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
// 错误状态显示
else if (this.errorMessage) {
Column() {
Text('❌') // 错误图标
.fontSize(48)
Text(this.errorMessage) // 错误文本
.fontSize(14)
.color('#FF4D4F')
.margin({ top: 12 })
Button('重试') // 重试按钮
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ top: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
this.loadData(); // 重新加载数据
})
}
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
// 正常状态显示瀑布流
else {
WaterFlow() {
LazyForEach(this.images, (item: ImageItem) => {
GridItem() {
Image(item.url)
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius(12)
.margin(8)
}
}, (item: ImageItem) => item.id.toString())
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(16)
.rowsGap(16)
.padding(16)
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
高级瀑布流实现
场景描述
实现一个带有下拉刷新、上拉加载更多功能的瀑布流,支持图片懒加载和点击查看详情。
开发步骤
1. 添加下拉刷新功能
使用 Refresh 组件实现下拉刷新功能:
@Entry
@Component
struct WaterFlowWithRefreshPage {
// 图片数据
@State images: ImageItem[] = [];
// 加载状态
@State isLoading: boolean = true;
// 下拉刷新状态
@State refreshing: boolean = false;
// 当前页码
private currentPage: number = 1;
// 每页数量
private pageSize: number = 12;
// 页面加载时初始化数据
aboutToAppear() {
this.loadData();
}
// 加载数据
async loadData(isRefresh: boolean = false) {
try {
if (isRefresh) {
this.refreshing = true;
this.currentPage = 1;
} else {
this.isLoading = true;
}
// 模拟网络请求延迟
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500));
// 模拟新数据
const newData: ImageItem[] = Array.from({ length: this.pageSize }, (_, index) => ({
id: (this.currentPage - 1) * this.pageSize + index + 1,
url: `https://example.com/image${(this.currentPage - 1) * this.pageSize + index + 1}.jpg`,
height: Math.floor(Math.random() * 200) + 200 // 随机高度200-400
}));
// 更新数据
if (isRefresh) {
this.images = newData;
} else {
this.images = [...this.images, ...newData];
}
this.currentPage++;
} catch (error) {
console.error('加载图片数据失败:', error);
} finally {
this.isLoading = false;
this.refreshing = false;
}
}
build() {
Column() {
// 下拉刷新组件
Refresh({
refreshing: this.refreshing,
offset: 120,
friction: 100
})
{
WaterFlow() {
LazyForEach(this.images, (item: ImageItem) => {
GridItem() {
// 点击事件处理
GestureDetector() {
Image(item.url)
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius(12)
.margin(8)
}
.onClick(() => {
// 点击图片查看详情
console.log('查看图片详情:', item.id);
})
}
}, (item: ImageItem) => item.id.toString())
// 加载更多提示
if (!this.isLoading && this.images.length > 0) {
GridItem() {
Text('上拉加载更多')
.fontSize(14)
.color('#999999')
.padding(20)
}
.columnSpan(2) // 跨两列
}
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(16)
.rowsGap(16)
.padding(16)
// 滚动到底部触发加载更多
.onReachEnd(() => {
if (!this.isLoading) {
this.loadData();
}
})
}
.onRefresh(() => {
this.loadData(true); // 下拉刷新,重新加载第一页数据
})
// 底部加载指示器
if (this.isLoading && this.images.length > 0) {
Row() {
LoadingProgress()
.color('#007DFF')
.size({ width: 24, height: 24 })
Text('加载中...')
.fontSize(14)
.color('#666666')
.margin({ left: 8 })
}
.padding(20)
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
2. 实现图片懒加载和缓存
为了提升性能,我们可以实现图片的懒加载和缓存功能:
@Entry
@Component
struct WaterFlowWithLazyLoadPage {
// 图片数据
@State images: ImageItem[] = [];
// 加载状态
@State isLoading: boolean = true;
// 图片加载状态映射
@State imageLoadStatus: Record<number, 'loading' | 'loaded' | 'error'> = {};
// 页面加载时初始化数据
aboutToAppear() {
this.loadData();
}
// 加载数据
async loadData() {
try {
this.isLoading = true;
// 模拟网络请求延迟
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500));
// 模拟图片数据
this.images = Array.from({ length: 20 }, (_, index) => ({
id: index + 1,
url: `https://example.com/image${index + 1}.jpg`,
height: Math.floor(Math.random() * 200) + 200
}));
// 初始化图片加载状态
this.images.forEach(item => {
this.imageLoadStatus[item.id] = 'loading';
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('加载图片数据失败:', error);
} finally {
this.isLoading = false;
}
}
// 图片加载完成
onImageLoad(id: number) {
this.imageLoadStatus[id] = 'loaded';
}
// 图片加载失败
onImageError(id: number) {
this.imageLoadStatus[id] = 'error';
}
build() {
Column() {
if (this.isLoading) {
Column() {
LoadingProgress()
.color('#007DFF')
.size({ width: 40, height: 40 })
Text('加载中...')
.fontSize(14)
.color('#666666')
.margin({ top: 12 })
}
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
} else {
WaterFlow() {
LazyForEach(this.images, (item: ImageItem) => {
GridItem() {
Stack() {
// 图片加载中
if (this.imageLoadStatus[item.id] === 'loading') {
Row() {
LoadingProgress()
.color('#007DFF')
.size({ width: 24, height: 24 })
}
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(12)
.margin(8)
}
// 图片加载失败
else if (this.imageLoadStatus[item.id] === 'error') {
Row() {
Text('❌')
.fontSize(32)
}
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(12)
.margin(8)
}
// 图片加载完成
else {
Image(item.url)
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius(12)
.margin(8)
.onComplete(() => this.onImageLoad(item.id)) // 加载完成回调
.onError(() => this.onImageError(item.id)) // 加载失败回调
}
}
}
}, (item: ImageItem) => item.id.toString())
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(16)
.rowsGap(16)
.padding(16)
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
性能优化建议

1. 数据懒加载
使用 LazyForEach 替代 ForEach,实现数据的懒加载,避免一次性渲染过多内容项:
// 推荐使用
WaterFlow() {
LazyForEach(this.data, (item) => {
GridItem() {
// 内容项
}
}, (item) => item.id.toString())
}
// 不推荐使用(大数据量下性能差)
WaterFlow() {
ForEach(this.data, (item) => {
GridItem() {
// 内容项
}
}, (item) => item.id.toString())
}
2. 图片优化
- 图片懒加载:只加载可视区域内的图片
- 图片压缩:使用合适分辨率的图片,避免加载过大图片
- 图片缓存:实现图片缓存策略,减少重复请求
- 占位符:使用骨架屏或占位符提升用户体验
3. 布局优化
- 固定列数:避免动态修改列数导致布局重排
- 预计算高度:提前计算内容项高度,避免布局抖动
- 减少嵌套:减少组件嵌套层级,提升渲染性能
4. 内存优化
- 合理设置缓存大小:避免缓存过多数据导致内存溢出
- 及时释放资源:在组件销毁时释放图片等资源
- 避免内存泄漏:及时清理定时器和事件监听器
交互体验优化

1. 加载状态反馈
- 初始加载时显示加载动画
- 下拉刷新时显示刷新动画
- 上拉加载更多时显示加载指示器
- 加载失败时显示错误信息和重试按钮
2. 手势交互
- 支持下拉刷新
- 支持上拉加载更多
- 支持点击查看详情
- 支持长按操作
3. 视觉效果
- 添加适当的间距和圆角,提升视觉舒适度
- 使用渐入动画,提升页面活力
- 添加阴影效果,增强层次感
- 统一的色彩方案,提升品牌一致性
总结
本文介绍了在 HarmonyOS 中实现瀑布流布局的完整流程,从基础实现到高级优化,涵盖了以下内容:
- 基础瀑布流实现:使用 WaterFlow 组件创建基本的瀑布流布局
- 高级功能:添加下拉刷新、上拉加载更多、图片懒加载等功能
- 性能优化:数据懒加载、图片优化、布局优化、内存优化
- 交互体验:加载状态反馈、手势交互、视觉效果优化
通过本文的学习,你应该能够在 HarmonyOS 应用中实现高性能、流畅的瀑布流布局,为用户提供良好的视觉体验和交互体验。
如果你有任何问题或建议,欢迎留言讨论!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号