刷题记录表
ARC211A
考虑这样一个性质就是在不考虑 \(5\) 的情况下,答案是什么,当且仅当只有一对 \(i\) 和 \(10 - i\) 都存在的,答案才会加 \(1\)。
考虑有 \(5\) 的情况就是不能有相邻的,这个也是好说的,然后感觉就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
int a[10];
void work(){
n = 9;
int tot = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
if(i != 5)
tot += a[i];
}
int ans = 0;
ans += max(0ll, a[5] - tot - 1);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 4; i++){
if(a[i] && a[10 - i]){
cnt ++;
}
else{
if(a[i] || a[10 - i]){
cnt = -1;
}
}
}
if(a[5]){
cnt = -1;
}
if(cnt == 1){
ans ++;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS--){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC211B
神秘构造,我们考虑答案一定 \(\le 1\) 先特判掉 \(x = y\) 可能等于 \(0\) 的情况,然后就这样构造:
正确性感觉很显然,然后就没了吧。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int x, y, z;
void work(){
x = read();
y = read();
z = read();
if(x == y){
cout << y << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= y; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
cout << z << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= z; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
cout << z << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= z; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
return ;
}
cout << y << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= y - x; i++){
cout << '1' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
cout << z << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= z; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
cout << y + z << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= z; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
cout << '0' << ' ';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= y - x; i++){
cout << '1' << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = 1;
while(TCS--){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC211C
我们考虑一个事情就是我们肯定不会出现一次消掉有大于等于两个的极长连续段。
之后考虑每一个相邻连续段就是考察他旁边的两个点,然后贪心的看目前能决策的是不是全局最大值,然后就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
string s;
struct Data{
int l, r;
};
vector<Data> dat;
int sum[N];
int totmx = 0;
void work(){
n = read();
cin >> s;
s = ' ' + s + '#';
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
}
int last = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++){
if(s[i] == '#'){
if(i != 1 && s[i - 1] != '#'){
dat.push_back({last + 1, i - 1});
}
last = i;
}
}
int idl = 0, idr = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(s[i] == '.'){
idl = i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
if(s[i] == '.'){
idr = i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = idl; i <= idr; i++){
totmx = max(totmx, a[i]);
}
int tot = 0;
for(auto y: dat){
int maxx = 0;
for(int i = y.l; i <= y.r; i++){
maxx = max(maxx, a[i]);
}
for(int i = y.l; i <= y.r; i++){
sum[tot] += (a[i] == maxx);
}
tot ++;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < dat.size() - 1; i++){
int maxx = 0;
for(int j = dat[i].l; j <= dat[i + 1].r; j++){
maxx = max(maxx, a[j]);
}
int flag = (maxx == totmx);
ans += sum[i] * sum[i + 1] * flag;
// cerr << sum[i] * sum[i + 1] << ' ';
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = 1;
while(TCS--){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC211D
考虑什么时候不合法,一定是断开某条割边后 \(1, 2\) 在同一连通块,然后我们直接大力 \(dfs\) 每次断掉 \(dfs\) 树上的边就是对的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int>e[N], v[N];
int id[N];
bool flag[N * 3];
int ans[N][2];
bool vis[N][2];
void dfs(int now, int fa, int op){
ans[now][op] = fa;
vis[now][op] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < e[now].size(); i++){
int y = e[now][i], z = v[now][i];
if(vis[y][op]) continue;
if(flag[z]){
continue;
}
flag[z] = 1;
dfs(y, now, op);
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
v[x].push_back(i);
v[y].push_back(i + m);
}
memset(ans, -1, sizeof ans);
dfs(1, 0, 0);
dfs(2, 0, 1);
bool flag = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
flag |= (ans[i][0] == -1);
flag |= (ans[i][1] == -1);
}
if(flag){
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
cout << "Yes\n";
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(ans[i][0]){
cout << ans[i][0] << ' ';
}
if(ans[i][1]){
cout << ans[i][1] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
CF521D
我们考虑到只有乘法是好说的,现在考虑加入加法该怎么办,发现加法可以转化为乘法,赋值操作又可以看作是加法,然后就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int t, n, m;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int maxx[N];
int id[N];
int to[N];
struct Data{
double x;
int id;
};
vector<Data> e[N];
vector<Data> dat;
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
t = read();
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){
a[i] = read();
maxx[i] = a[i];
id[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int op = read();
to[i] = op;
if(op == 1){
int x = read();
int y = read();
if(y > maxx[x]){
maxx[x] = max(maxx[x], y);
id[x] = i;
}
}
if(op == 2){
int x = read();
e[x].push_back({(double)read(), i});
}
if(op == 3){
int x = read();
dat.push_back({(double)read(), i});
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){
if(id[i]){
e[i].push_back({(double)(maxx[i] - a[i]), id[i]});
}
sort(e[i].begin(), e[i].end(), [](Data x, Data y){
return x.x > y.x;
});
int sum = a[i];
for(auto y: e[i]){
dat.push_back({(sum + y.x) / sum , y.id});
sum += y.x;
}
}
sort(dat.begin(), dat.end(), [](Data x, Data y){
return x.x > y.x;
});
int tp = min(m, (int)dat.size());
cout << tp << '\n';
sort(dat.begin(), dat.begin() + tp, [](Data x, Data y){
return to[x.id] < to[y.id];
});
for(int i = 0; i < tp; i++){
cout << dat[i].id << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
CF505E
神仙题,我们考虑二分答案,但是直接做非常不好做,于是我们考虑反着做,用个优先队列来维护每次的最近的可能会减到 \(0\) 的竹子,然后给他拔高 \(p\),最后看能否全部到达 \(h_i\),太神秘了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m, t, p;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], a[N];
int cnt[N];
struct Data{
int x, y;
friend bool operator < (Data x, Data y){
return x.x > y.x;
}
};
bool check(int x){
priority_queue<Data> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cnt[i] = 0;
if(x - a[i] * m < h[i]){
q.push({x / a[i], i});
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= t; j++){
if(!q.size()){
break;
}
int id = q.top().y;
if(q.top().x < i) return 0;
q.pop();
cnt[id] ++;
if(x + cnt[id] * p - a[id] * m < h[id]){
q.push({(x + cnt[id] * p) / a[id], id});
}
}
}
if(q.size()){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
t = read();
p = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
h[i] = read();
a[i] = read();
}
int l = 0, r = 1e18;
int ans = 1e18;
while(l + 1 < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(mid)){
ans = min(ans, mid);
r = mid;
}
else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++){
if(check(i)){
ans = min(ans, i);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
ARC208A
这不就是 【模板】nim游戏 吗,直接判断 \(AND\) 和 \(XOR\) 是否相等就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
void work(){
n = read();
int sor = 0, sox = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
sor |= a[i];
sox ^= a[i];
}
if(sor == sox){
cout << "Bob\n";
}
else{
cout << "Alice\n";
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS--){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC208B
考虑确定第一个之后咋做,肯定是每次倍增,然后我们二分最小的可以充当第一个数的数值就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, k;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
bool check(int x){
int lst = x;
int now = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
now += lst - 1;
lst = lst * 2 - 1;
if(now >= k) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void work(){
n = read();
k = read();
int l = 1, r = 1e18;
int ans = 0;
while(l + 1 < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(mid)){
r = mid;
ans = mid;
}
else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++){
if(check(i)){
ans = i;
break;
}
}
int lst = ans;
int now = 0;
cout << lst << ' ';
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
now += lst - 1;
if(now >= k){
now -= lst - 1;
lst = lst + k - now;
now = k;
}
else
lst = lst * 2 - 1;
cout << lst << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC208C
考虑把取模转化为相减,即要求:
考虑 \(t = 0\) 这个是好做的, \(t = 1\) 就把异或拆成相加减去并,然后我们考虑证明如果 \(t = 0,1\) 无解,就一定无解。
考虑转化一下,有 \(x + tn = (n \oplus c) \ge n + c\),就有 \(c \ge x + (t - 1) n \ge 2x\),而我们知道如果 \(c \ge 2x\),那么 \(t = 0\) 一定有解,然后就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int x, c;
void work(){
c = read();
x = read();
int tp = (c ^ x);
if(x < tp){
cout << tp << '\n';
return ;
}
if(x > c || (c - x) & 1){
cout << -1 << '\n';
return ;
}
tp = (c - x) / 2;
if((tp & c) == tp){
cout << tp + (1ll << 34) << '\n';
}
else{
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC206A
唐蛋题,秒了,只需要规定在哪里计算就行。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N];
int cnt[N];
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
}
int ans = 1;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
if(a[i] != a[i - 1]){
ans += n - i - cnt[a[i]];
}
cnt[a[i]] ++;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
ARC206B
每个颜色跑个 lis 做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int p[N], c[N];
struct Segment{
int l, r;
int dat;
}seg[N * 4];
void upd(int p){
seg[p].dat = max(seg[p * 2].dat, seg[p * 2 + 1].dat);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r){
seg[p].l = l;
seg[p].r = r;
seg[p].dat = 0;
if(l == r){
return ;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p * 2, l, mid);
build(p * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r);
upd(p);
}
void clear(int p, int x){
seg[p].dat = 0;
if(seg[p].l == seg[p].r) {
seg[p].dat = 0;
return ;
}
int mid = (seg[p].l + seg[p].r) >> 1;
if(x <= mid){
clear(p * 2, x);
}
else{
clear(p * 2 + 1, x);
}
upd(p);
}
void change(int p, int x, int v){
if(seg[p].l == seg[p].r) {
seg[p].dat = max(seg[p].dat, v);
return ;
}
int mid = (seg[p].l + seg[p].r) >> 1;
if(x <= mid){
change(p * 2, x, v);
}
else{
change(p * 2 + 1, x, v);
}
upd(p);
}
int ask(int p, int l, int r){
if(seg[p].l >= l && seg[p].r <= r){
return seg[p].dat;
}
int mid = (seg[p].l + seg[p].r) >> 1;
int ans = 0;
if(l <= mid){
ans = max(ans, ask(p * 2, l, r));
}
if(r > mid){
ans = max(ans, ask(p * 2 + 1, l, r));
}
return ans;
}
vector<int>col[N];
int dp[N];
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p[i] = read();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
col[read()].push_back(i);
}
build(1, 1, n);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int ed = 0;
// cerr << seg[1].dat << '\n';
int mx = 0;
for(auto y: col[i]){
dp[y] = ask(1, 1, p[y]) + 1;
change(1, p[y], dp[y]);
ed = y;
mx = max(mx, dp[y]);
}
// cerr << ed << ' ' << dp[ed] << '\n';
ans += i * (col[i].size() - mx);
for(auto y: col[i]){
clear(1, p[y]);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
ARC207B
神秘构造题,我们考虑观察样例,可以发现 \(i\) 和 \(n - i + 1\) 是无法到达的,然后我们考虑构造一个二分图,将 \(i \le n / 2\) 的划分到左边,剩下的在右边,然后连边就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 210;
struct Data{
int x, y;
};
vector<Data> ans;
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
if(n <= 5){
cout << -1 << '\n';
return 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++){
for(int j = n / 2 + 1; j <= n; j++){
if(i + j != n / 2 + n / 2 + 1){
ans.push_back({i, j});
}
}
}
cout << ans.size() << '\n';
for(auto y : ans){
cout << y.x << ' ' << y.y << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
ARC207C
考虑一个贪心就是每次暴力往后跑,直到能分成一段为止,但是会有问题就是,可能有个东西放前面会更优秀,比如:
7
546 35 261 30 583 864 911
对于这个数据,最优秀的是将 \(1-2,3-5,6,7\),要是直接做就会是 \(1,2-5,6-7\)。
然后我们考虑 \(dp\),考虑一个事情就是我们可以二分右端点来转移,但是我写假了,所以这里还有个做法就是每个有用的转移点是均摊 \(O(\log V)\) 的,所以暴力就是对的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int dp[N], lst[N];
int st[N][30];
int pre[N];
int ask(int l, int r){
if(l > r) return 0;
int step = pre[r - l + 1];
return st[l][step] | st[r - (1ll << step) + 1][step];
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
pre[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
pre[i] = pre[i >> 1] + 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
st[i][0] = a[i];
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 20; j++){
for(int i = 1; i + (1ll << j) - 1 <= n; i++){
st[i][j] = (st[i][j - 1] | st[i + (1ll << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
dp[0] = 0;
lst[0] = 0;
int id = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = i; j >= 1; j--){
if(ask(j, i - 1) == ask(j, i)){
break;
}
if(lst[j - 1] <= ask(j, i)){
id = max(j - 1, id);
}
}
// cerr << i << ' ' << id << '\n';
lst[i] = ask(id + 1, i);
dp[i] = dp[id] + 1;
// cerr << "#" << i << ' ' << dp[i] << ' ' << id << '\n';
}
cout << dp[n];
return 0;
}
CF2173E
考虑一个事情就是我们可以显然 \(i\) 和 \(n - i\) 一起归位,然后我们计算他的期望,先让 \(i\) 归位的次数为 \(2\) 次,而让 \(n - i\) 与 \(i\) 一起归位的次数可以画图:
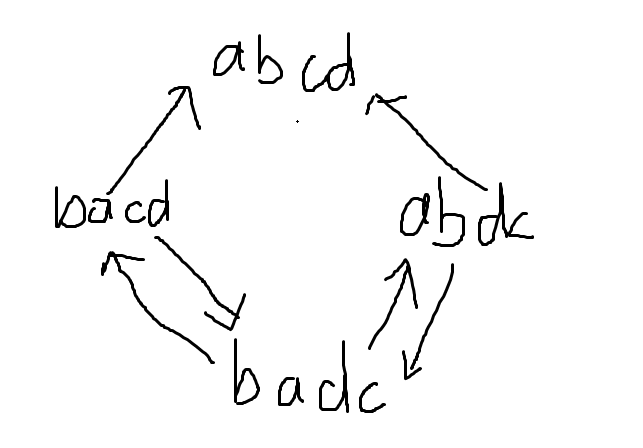
发现从 \(abdc\) 到 \(abcd\) 的次数为 \(3\),平均一下就是 \(2.5\),所以直接做就行。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 4010;
int a[N];
int pos[N];
void get_swap(int x, int y){
while(1){
cout << "? " << x << ' ' << y << endl;
int stx = read(), sty = read();
int tp = a[stx];
a[stx] = a[sty];
a[sty] = tp;
pos[a[stx]] = stx;
pos[a[sty]] = sty;
if((x == stx && y == sty) || (x == sty && y == stx)){
return ;
}
}
}
void work(){
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
for(int l = 1; l <= n / 2; l++){
int r = n - l + 1;
while(pos[l] != l){
get_swap(l, pos[l]);
}
while(pos[l] != l || pos[r] != r){
if(pos[l] != l){
get_swap(l, pos[l]);
}
else{
get_swap(r, pos[r]);
}
}
}
cout << "!" << endl;
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS--){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC203A
简单题,推推式子就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
void work(){
n = read();
m = read();
cout << (m + 1) / 2 + (m - (m + 1) / 2) * (n - 1) << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC203B
考虑一个事情就是一定可以通过 \(00 \to 0\) 来做。
所以不合法的情况当且仅当 \(suma \neq sumb\),或 \(suma = 1\) 且 有一个 \(1\) 是在开头或结尾。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N], b[N];
void work(){
n = read();
int suma = 0, sumb = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
suma += a[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
b[i] = read();
sumb += b[i];
}
if(suma != sumb){
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
if(suma == 1 && sumb == 1){
if(a[1] != b[1] || a[n] != b[n]){
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
}
cout << "Yes\n";
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC203C
分类讨论一下,最重要的就是 \(k = n + m\)
首先我们考虑 \(len = n + m - 2\) 的,减去重复的。
然后考虑 \(len = n + m\) 的,写写式子就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m, t;
const int N = 5e5 + 10, MOD = 998244353;
int fac[N], inv[N];
int quick_pow(int a, int b){
if(b == 0) return 1;
if(b & 1){
return a * quick_pow(a, b - 1) % MOD;
}
else{
int tmp = quick_pow(a, b / 2);
return tmp * tmp % MOD;
}
}
int C(int n, int m){
if(n < m) return 0;
return fac[n] * inv[m] % MOD * inv[n - m] % MOD;
}
void work(){
n = read();
m = read();
t = read();
if(t < n + m - 2){
cout << 0 << '\n';
return ;
}
if(t == n + m - 2){
cout << C(n + m - 2, n - 1) << '\n';
return ;
}
if(t == n + m - 1){
cout << C(n + m - 2, n - 1) * (2 * (n - 1) % MOD * (m - 1) % MOD) % MOD << '\n';
return ;
}
int lst = (2 * (n - 1) * (m - 1)) % MOD;
int tot = C(n + m - 2, n - 1) * (lst) % MOD * (lst - 1) % MOD * quick_pow(2, MOD - 2) % MOD;
int cov = C(n + m - 4, n - 2) * (n + m - 3) % MOD;
int tot1 = C(n + m - 2, m + 1) * (m - 1) % MOD;
int tot2 = C(n + m - 2, n + 1) * (n - 1) % MOD;
tot2 += tot1;
tot2 %= MOD;
tot -= cov;
tot += tot2;
tot += MOD;
tot %= MOD;
cout << tot << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
fac[0] = inv[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % MOD;
inv[i] = quick_pow(fac[i], MOD - 2);
}
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
CF521E
考虑跑出来 dfs树,假如说一条树边被非树边覆盖了两次及以上一定可以构造出来:
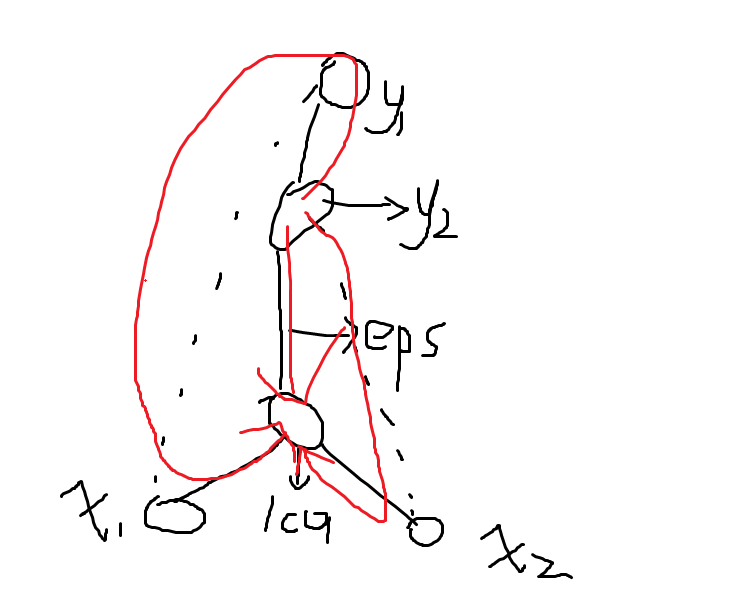
否则一定不行。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int>e[N];
struct Edge{
int x, y;
friend bool operator < (Edge x, Edge y){
return (x.x != y.x) ? (x.x < y.x) : (x.y < y.y);
}
};
vector<int> path;
bool vis[N], ins[N];
int dep[N];
int fa[N][30];
int ex[N], ey[N];
int LCA(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] > dep[y]){
swap(x, y);
}
int tmp = dep[y] - dep[x];
for(int i = 1; i <= tmp; i++){
y = fa[y][0];
}
if(x == y) {
return x;
}
while(1){
if(fa[x][0] == fa[y][0]){
return fa[x][0];
}
x = fa[x][0];
y = fa[y][0];
}
}
void add(int x, int y){
while(x != y){
path.push_back(x);
x = fa[x][0];
}
path.push_back(y);
}
void get(){
cout << path.size() << ' ';
for(auto y: path){
cout << y << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
path.clear();
}
void print(int x_1, int y_1, int x_2, int y_2){
if(dep[y_1] > dep[y_2]){
swap(x_1, x_2);
swap(y_1, y_2);
}
int z = LCA(x_1, x_2);
// cerr << "$#$#@$$@\n";
cout << "YES\n";
add(z, y_2);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
get();
add(y_2, y_1);
add(x_1, z);
get();
// cerr << "$#$@$#\n";
path.push_back(y_2);
add(x_2, z);
get();
exit(0);
}
void dfs(int now, int rf){
vis[now] = ins[now] = 1;
fa[now][0] = rf;
dep[now] = dep[rf] + 1;
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == rf) continue;
if(vis[y]) {
if(ins[y]){
for(int i = now; i != y; i = fa[i][0]){
if(ex[i]){
print(ex[i], ey[i], now, y);
}
else{
ex[i] = now;
ey[i] = y;
}
}
}
continue;
}
dfs(y, now);
}
ins[now] = 0;
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(!vis[i])
dfs(i, 0);
cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
CF526F
考虑按找 \(x\) 排序,那么就相当于要求满足要求的区间 \(l ,r\) 个数,其中有:
化简之后有 \(\max - \min + l - r = 0\)
考虑这个东西不会大于 \(0\),于是我们直接上线段树然后枚举右端点来做。
当右端点往右移动时,有 \(r \to r + 1\),\(\max,\min\) 的变化是用个单调栈就是好做的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
struct Data{
int x, y;
friend bool operator < (Data x, Data y){
return x.x < y.x;
}
}a[N];
//转换题意
//相当于要求 max - min = r - l
//max - min + l - r = 0;
//每次先把 +l 做了,
//再把 -r 做了,
//max,min 用个随便一个数据结构是不是随便做啊
struct Segment{
int l, r;
int dat;
int sum;
int laz;
}seg[N * 4];
void upd(int p){
seg[p].dat = min(seg[p * 2].dat, seg[p * 2 + 1].dat);
seg[p].sum = seg[p * 2].sum * (seg[p * 2].dat == seg[p].dat) + seg[p * 2 + 1].sum * (seg[p * 2 + 1].dat == seg[p].dat);
}
void spread(int p){
seg[p * 2].dat += seg[p].laz;
seg[p * 2].laz += seg[p].laz;
seg[p * 2 + 1].dat += seg[p].laz;
seg[p * 2 + 1].laz += seg[p].laz;
seg[p].laz = 0;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r){
seg[p].l = l;
seg[p].r = r;
if(l == r){
seg[p].dat = l;
seg[p].sum = 1;
return ;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p * 2, l, mid);
build(p * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r);
upd(p);
}
void change(int p, int l, int r, int v){
if(seg[p].l >= l && seg[p].r <= r){
seg[p].laz += v;
seg[p].dat += v;
return ;
}
spread(p);
int mid = (seg[p].l + seg[p].r) >> 1;
if(l <= mid){
change(p * 2, l, r, v);
}
if(r > mid){
change(p * 2 + 1, l, r, v);
}
upd(p);
}
struct Temp{
int id, fr;
};
stack<Temp> minn, maxx;
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = {read(), read()};
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
build(1, 1, n);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
change(1, 1, n, -1);
int lst = i - 1;
while(minn.size() && a[i].y < a[minn.top().id].y){
change(1, minn.top().fr + 1, lst, a[minn.top().id].y - a[i].y);
lst = minn.top().fr;
minn.pop();
}
minn.push({i, lst});
lst = i - 1;
while(maxx.size() && a[i].y > a[maxx.top().id].y){
change(1, maxx.top().fr + 1, lst, a[i].y - a[maxx.top().id].y);
lst = maxx.top().fr;
maxx.pop();
}
maxx.push({i, lst});
ans += seg[1].sum;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
CF547D
考虑给在同一行和同一列的亮亮配对,然后连边跑二分图染色即可。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int dat[N][2];
int col[N];
vector<int>e[N];
void dfs(int now, int tmp){
col[now] = tmp;
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(!col[y]){
dfs(y, 3 - tmp);
}
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
if(dat[x][0]){
e[dat[x][0]].push_back(i);
e[i].push_back(dat[x][0]);
dat[x][0] = 0;
}
else{
dat[x][0] = i;
}
if(dat[y][1]){
e[dat[y][1]].push_back(i);
e[i].push_back(dat[y][1]);
dat[y][1] = 0;
}
else{
dat[y][1] = i;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!col[i]){
dfs(i, 1);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(col[i] == 1){
cout << "b";
}
else{
cout << "r";
}
}
return 0;
}
CF547E
考虑只有 \(O(\sqrt n)\) 种长度,于是离线下来直接大力哈希就行了,用个桶存一下,然后就有:
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp> //关联容器,必加
#include<ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp> //哈希表
#include<ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp> //平衡树
#include<ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp> //字典树
#include<ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp> //优先队列
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io {
class In {
public:
template<typename T>
inline In &operator>>(T &x) {
x=0; bool f=0; char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9') f|=(c=='-'),c=getchar();
while(c>='0'&&c<='9') x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();
if(c=='.') {
c=getchar(); double dot=0.1;
while(c>='0'&&c<='9') x+=(c-'0')*dot,dot*=0.1,c=getchar();
} return (f?x=-x:x),*this;
}
inline In &operator>>(char &x) {while(isspace(x=getchar())); return *this;}
inline In &operator>>(char *x) {
char c=getchar(); while(isspace(c)) c=getchar(); while(!isspace(c)&&~c) *(x++)=c,c=getchar();
return *x=0,*this;
}
inline In &operator>>(string &x) {
char c=getchar(); x.clear();
while(isspace(c)) c=getchar(); while(!isspace(c)&&~c) x.push_back(c),c=getchar();
return *this;
}
inline In &operator>>(In &in) { return in;}
};
class Out {
private:
char buf[35]; short dot=6,top=0;
public:
template<typename T>
inline Out &operator<<(T x) {
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;
do { buf[++top]=x%10,x/=10;} while(x);
while(top) putchar(buf[top--]|'0'); return *this;
}
inline Out &operator<<(char c) {return putchar(c),*this;}
inline Out &operator<<(string x) {for(auto c:x) putchar(c); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(char *x) {while(*x) putchar(*(x++)); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(const char *x) {while(*x) putchar(*(x++)); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(double x) {snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"%.*lf",dot,x); return (*this)<<buf;}
inline Out &operator<<(Out &out) {return out;}
inline Out &setdot(const int n) {return dot=n,*this;}
};
In fin;
Out fout;
inline Out &setdot(const int n,Out& out=fout) {return fout.setdot(n),out;}
inline In &getline(char *x,In& in=fin) {
char c=getchar();
while(!(c==' '||!isspace(c))) c=getchar(); while(c==' '||!isspace(c)) (*x++)=c,c=getchar();
return *x=0,in;
}
inline In &getline(string &x,In& in=fin) {
char c=getchar(); x.clear();
while(!(c==' '||!isspace(c))) c=getchar(); while(c==' '||!isspace(c)) x.push_back(c),c=getchar();
return in;
}
}
using namespace io;
inline int read(){
int x; fin >> x; return x;
}
int tot;
__gnu_pbds::gp_hash_table<int, int> mp[2];
int n, q;
const int N = 2e5 + 10, P = 12347, MOD = 1000000007;
int pw[N];
void prework(){
pw[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
pw[i] = pw[i - 1] * P % MOD;
}
}
int rem[N];
int a[N];
string s[N];
vector<int> hsh[N];
int ans[N / 2 * 5];
struct Data{
int x, id;
int pos;
friend bool operator < (Data x, Data y){
return x.pos < y.pos;
}
};
vector<Data> st[450], ed[450];
inline int geth(int l, int r, int id){
return (hsh[id][r] - hsh[id][l - 1] * pw[r - l + 1] % MOD + MOD) % MOD;
}
int rhsh[N];
void work(int id){
if(st[id].size() == 0) return ;
int len = rem[id];
int spos = 0, epos = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(; spos < st[id].size(); spos++){
if(st[id][spos].pos != i){
break;
}
ans[st[id][spos].id] -= mp[1][rhsh[st[id][spos].x]];
}
for(int j = 1; j + len - 1 <= a[i]; j++){
mp[1][geth(j, j + len - 1, i)] ++;
}
for(; epos < ed[id].size(); epos++){
if(ed[id][epos].pos != i){
break;
}
ans[ed[id][epos].id] += mp[1][rhsh[ed[id][epos].x]];
}
}
mp[1].clear();
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
prework();
n = read();
q = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
fin >> s[i];
int len = s[i].size();
a[i] = len;
s[i] = ' ' + s[i];
if(!mp[0][len]){
mp[0][len] = ++tot;
rem[tot] = len;
}
for(int j = 1; j <= len; j++){
rhsh[i] = rhsh[i] * P + s[i][j] - 'a';
rhsh[i] %= MOD;
}
hsh[i].resize(len + 2);
for(int j = 1; j <= len; j++){
hsh[i][j] = hsh[i][j - 1] * P + s[i][j] - 'a';
hsh[i][j] %= MOD;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){
int l = read(), r = read(), x = read();
st[mp[0][a[x]]].push_back({x, i, l});
ed[mp[0][a[x]]].push_back({x, i, r});
}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++){
sort(st[i].begin(), st[i].end());
sort(ed[i].begin(), ed[i].end());
}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++){
work(i);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){
fout << ans[i] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
CF555E
发现跑一个 tarjan 跑出边双之后,直接大力在树上差分就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m, q;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int>ne[N], id[N], e[N];
int dfn[N], low[N];
stack<int>st;
int col[N];
int cnt = 0;
void dfs(int now, int fa){
dfn[now] = low[now] = ++(*dfn);
st.push(now);
for(int i = 0; i < ne[now].size(); i++){
int y = ne[now][i], z = id[now][i];
if(z == (fa ^ 1)) continue;
if(!dfn[y]){
dfs(y, z);
low[now] = min(low[now], low[y]);
}
else{
low[now] = min(low[now], dfn[y]);
}
}
// cerr << now << ' ' << dfn[now] << ' ' << low[now] << '\n';
if(low[now] == dfn[now]){
cnt ++;
while(st.top() != now){
col[st.top()] = cnt;
st.pop();
}
st.pop();
col[now] = cnt;
}
}
int fa[N][30];
int dep[N];
bool vis[N];
void dfs_tr(int now, int ff){
fa[now][0] = ff;
// cerr << now << ' ' << ff << '\n';
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++){
fa[now][i] = fa[fa[now][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
dep[now] = dep[ff] + 1;
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs_tr(y, now);
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]){
swap(x, y);
}
int tmp = dep[x] - dep[y];
int now = 0;
while(tmp){
if(tmp & 1){
x = fa[x][now];
}
tmp >>= 1;
now ++;
}
if(x == y) return x;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--){
if(fa[x][i] == fa[y][i]) continue;
x = fa[x][i];
y = fa[y][i];
}
return fa[x][0];
}
int siz[N][2];
void dfs_siz(int now, int ff){
vis[now] = 1;
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs_siz(y, now);
siz[now][1] += siz[y][1];
siz[now][0] += siz[y][0];
}
}
struct DSU{
int fa[N];
void init(int x){
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
fa[i] = i;
}
}
int get(int x){
return (fa[x] == x) ? (x) : (fa[x] = get(fa[x]));
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = get(x), fy = get(y);
if(fx == fy) return ;
fa[fx] = fy;
}
}ok;
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
q = read();
ok.init(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
ok.merge(x, y);
ne[x].push_back(y);
id[x].push_back(i * 2);
ne[y].push_back(x);
id[y].push_back(i * 2 + 1);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!dfn[i]){
dfs(i, 0);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(auto y: ne[i]){
if(col[i] != col[y]){
e[col[i]].push_back(col[y]);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
if(!dep[i]){
dfs_tr(i, 0);
}
}
// cerr << cnt << '\n';
while(q--){
int x = read(), y = read();
if(ok.get(x) != ok.get(y)){
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
int xx = col[x], yy = col[y];
int zz = LCA(xx, yy);
// cerr << xx << ' ' << yy << ' ' << zz << '\n';
siz[xx][0] ++;
siz[yy][1] ++;
siz[zz][0] --;
siz[zz][1] --;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
if(!vis[i]){
dfs_siz(i, 0);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
if(siz[i][0] && siz[i][1]){
// cerr << << '\n';
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
}
cout << "Yes\n";
return 0;
}
P5203
考虑存在这样一条路径的条件是什么,发现就是两条非树边在树上对应的路径有交,那么接下来就只要求这些的就行了。
先考虑给每条路径距离其 lca 最近的点 +1,那么一个朴素的想法就是直接大力前缀和,然后去重,可能有以下几种可能:
- 在同一个点加上了好几次,对于他们内部的需要确定一个顺序,所以每次就先加上然后在减去目前的点权。
- 在同一组上加了好几次,同样需要去重。
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f=1,t=0;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){t=t*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return t*f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x<0){putchar('-');x=-x;}
if(x>=10){write(x/10);}
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int>e[N];
int dep[N];
int fa[N][30];
void dfs(int now, int ff){
dep[now] = dep[ff] + 1;
fa[now][0] = ff;
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++){
fa[now][i] = fa[fa[now][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs(y, now);
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]){
swap(x, y);
}
int tmp = dep[x] - dep[y];
int now = 0;
while(tmp){
if(tmp & 1){
x = fa[x][now];
}
tmp >>= 1;
now ++;
}
if(x == y) return x;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--){
if(fa[x][i] != fa[y][i]){
x = fa[x][i];
y = fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
}
int x[N], y[N], z[N];
int getlst(int x, int y){
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--){
if(dep[fa[x][i]] <= dep[y]){
continue;
}
x = fa[x][i];
}
return x;
}
int siz[N];
map<pair<int, int>, int> mp;
void dfs_siz(int now, int ff){
siz[now] += siz[ff];
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs_siz(y, now);
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for(int i = n; i <= m; i++){
x[i - n + 1] = read();
y[i - n + 1] = read();
z[i - n + 1] = LCA(x[i - n + 1], y[i - n + 1]);
}
int tmp = m - n + 1;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= tmp; i++){
int tpx = getlst(x[i], z[i]), tpy = getlst(y[i], z[i]);
if(x[i] != z[i]){
siz[tpx] ++;
ans -= siz[tpx];
}
if(y[i] != z[i]){
siz[tpy] ++;
ans -= siz[tpy];
}
if(x[i] != z[i] && y[i] != z[i]){
ans -= mp[{min(tpx, tpy), max(tpx, tpy)}];
mp[{min(tpx, tpy), max(tpx, tpy)}] ++;
}
}
dfs_siz(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= tmp; i++){
ans += siz[x[i]] + siz[y[i]] - 2 * siz[z[i]];
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P5204
考虑一个事情就是我们可以这样将问题通过每次上升或下降来划分成好多段,然后就可以分开 dp,dp 要解决这样一个问题:没有相邻的长度为 \(m\) 的,最小值不是对应数值的方案数,这个是好 dp 的。
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f=1,t=0;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){t=t*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return t*f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x<0){putchar('-');x=-x;}
if(x>=10){write(x/10);}
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, Ainf = 1e9, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int a[N];
int dp[N];
int quick_pow(int a, int b){
if(!b){
return 1;
}
if(b & 1){
return a * quick_pow(a, b - 1) % MOD;
}
else{
int tmp = quick_pow(a, b / 2);
return tmp * tmp % MOD;
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n - m + 1; i++){
a[i] = read();
}
int ans = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n - m + 1; i++){
int l = i, r = i;
while(a[r + 1] == a[l]){
r ++;
}
int tp = r - l + 1 + m - 1;
if(l != 1 && a[l - 1] > a[l]) tp -= m;
if(r != n - m + 1 && a[r + 1] > a[r]) tp -= m;
int tx = Ainf - a[i];
dp[0] = 1;
// cerr << tp << '\n';
dp[1] = 1;
for(int j = 2; j <= tp + 1; j++){
dp[j] = (tx + 1) * dp[j - 1] % MOD;
if(j >= m + 1){
dp[j] -= dp[j - m - 1] * quick_pow(tx, m) % MOD;
dp[j] += MOD;
dp[j] %= MOD;
}
}
ans *= dp[tp + 1];
// cerr << dp[tp] << '\n';
ans %= MOD;
i = r;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
P5243
直接 暴力dp 复杂度疑似就是 \(O(n ^ {2.5})\) 的,然后就过了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
const int N = 1510, M = 2510, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int quick_pow(int a, int b){
if(!b) return 1;
if(b & 1){
return a * quick_pow(a, b - 1) % MOD;
}
else{
int tmp = quick_pow(a, b / 2);
return tmp * tmp % MOD;
}
}
int fac[N];
int n, m, tx, ty;
vector<int>e[N], v[N];
int tot;
int tag[N];
void dfs_tag(int now, int ff, int tg){
tag[now] = tg;
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs_tag(y, now, tg);
}
}
int tlg[N][M];
int siz[N][M];
void dfs_dis(int now, int ff, int dep){
if(ff != 0){
tlg[tag[now]][min(dep, ty)] += dep;
tlg[tag[now]][min(dep, ty)] %= MOD;
siz[tag[now]][min(dep, ty)] += 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < e[now].size(); i++){
int y = e[now][i], z = v[now][i];
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs_dis(y, now, dep + z);
}
}
int dp[M][2], tmp[M][2];
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
tx = read();
ty = read();
fac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % MOD;
// cerr << fac[i] << '\n';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = read(), y = read(), z = read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
v[x].push_back(z);
v[y].push_back(z);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!tag[i]){
dfs_tag(i, 0, ++*tag);
}
}
// cerr << *tag << '\n';
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
dfs_dis(i, 0, 0);
}
int bg = (n - m) * tx;
bg = min(bg, ty);
dp[bg][0] = 1;
dp[bg][1] = (n - m) * tx;
for(int i = 1; i <= n - m; i++){
for(int j = bg; j <= ty; j++){
tmp[j][0] = dp[j][0];
tmp[j][1] = dp[j][1];
dp[j][0] = 0;
dp[j][1] = 0;
}
for(int j = 0; j <= ty; j++){
if(!siz[i][j]) continue;
for(int k = bg; k <= ty; k++){
if(!tmp[k][0]) continue;
dp[min(j + k, ty)][0] += tmp[k][0] * siz[i][j] % MOD;
dp[min(j + k, ty)][0] %= MOD;
dp[min(j + k, ty)][1] += (tmp[k][0] * tlg[i][j] % MOD + tmp[k][1] * siz[i][j] % MOD) % MOD;
dp[min(j + k, ty)][1] %= MOD;
}
}
// cerr << dp[ty][0] << ' ' << dp[ty][1] << '\n';
}
cout << dp[ty][1] * fac[n - m - 1] % MOD * quick_pow(2, MOD - 2) % MOD << '\n';
return 0;
}
P5244
神仙题,考虑先排序,然后按照 lis 划分为若干层,每层里在排一下序,转移的过程肯定就是从下面一层转移上来,然后我们尝试挖掘性质,打表发现这玩意要是没有必须包含前一个的限制居然是有决策单调递减的性质的,然后考虑每次可以转移来的是一个区间,然后上线段树做决策单调性就行了,总复杂度为 \(O(n \log^2 n)\)。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define ll long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
struct Poin{
int x, y;
int id;
}poin[N];
int qx[N], qy[N];
ll get_val(int x, int y){
if((poin[x].x - poin[y].x) * 1ll * (poin[x].y - poin[y].y) <= 0){
cerr << "## " << x << ' ' << y << ' ' << (poin[x].x - poin[y].x) * 1ll * (poin[x].y - poin[y].y) << '\n';
exit(0);
}
return (poin[x].x - poin[y].x) * 1ll * (poin[x].y - poin[y].y);
}
int lis[N];
int id[N];
ll dp[N];
ll trudp[N];
struct Segment{
int l, r;
vector<int>ask;
}seg[N * 4];
void build(int p, int l, int r){
seg[p].l = l;
seg[p].r = r;
seg[p].ask.clear();
if(l == r){
return ;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p * 2, l, mid);
build(p * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r);
}
void change(int p, int l, int r, int x){
if(l > r) return ;
if(seg[p].l >= l && seg[p].r <= r){
seg[p].ask.push_back(x);
return ;
}
int mid = (seg[p].l + seg[p].r) >> 1;
if(l <= mid){
change(p * 2, l, r, x);
}
if(r > mid){
change(p * 2 + 1, l, r, x);
}
return ;
}
void get_ans(int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int qid){
if(l > r) return ;
if(ql > qr) return ;
if(l == r){
for(int i = ql; i <= qr; i++){
trudp[seg[qid].ask[i]] = min(trudp[l] + get_val(seg[qid].ask[i], l), trudp[seg[qid].ask[i]]);
}
return ;
}
int mid = (ql + qr) >> 1;
int rid = seg[qid].ask[mid];
int npos = 0;
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++){
if(dp[rid] > trudp[i] + get_val(i, rid)){
dp[rid] = trudp[i] + get_val(i, rid);
npos = i;
}
}
trudp[rid] = min(trudp[rid], dp[rid]);
dp[rid] = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
get_ans(l, npos, mid + 1, qr, qid);
get_ans(npos, r, ql, mid - 1, qid);
}
void preans(int p){
get_ans(seg[p].l, seg[p].r, 0, seg[p].ask.size() - 1, p);
if(seg[p].l == seg[p].r){
return ;
}
preans(p * 2);
preans(p * 2 + 1);
}
struct Bitr{
int tr[N * 5];
int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}
void change(int x, int v){
for(; x <= m; x += lowbit(x)){
tr[x] = max(tr[x], v);
}
}
int ask(int x){
int ans = 0;
for(; x; x -= lowbit(x)){
ans = max(tr[x], ans);
}
return ans;
}
}bt;
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
poin[i] = {read(), read()};
}
n ++ ;
poin[n] = {m, m};
sort(poin + 1, poin + 1 + n, [](Poin x, Poin y){
return x.x < y.x;
});
int maxx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
lis[i] = bt.ask(poin[i].y) + 1;
maxx = max(maxx, lis[i]);
bt.change(poin[i].y, lis[i]);
poin[i].id = i;
}
// cerr << maxx << '\n';
sort(poin + 1, poin + 1 + n, [](Poin x, Poin y){
return (lis[x.id] != lis[y.id]) ? (lis[x.id] < lis[y.id]) : (x.x < y.x);
});
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);
memset(trudp, 0x3f, sizeof trudp);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
qx[i] = poin[i].x;
qy[i] = poin[i].y;
// cerr << "Matrix " << qx[i] << ' ' << qy[i] << '\n';
}
int lsl = 1, lsr = 1;
sort(lis + 1, lis + 1 + n);
while(lis[lsr + 1] == 1){
lsr ++;
}
for(int i = lsl; i <= lsr; i++){
trudp[i] = poin[i].x * poin[i].y;
}
for(int i = 2; i <= maxx; i++){
int l = lsr + 1;
int r = l;
while(lis[r + 1] == i) {
r ++;
}
// cerr << l << ' ' << r << '\n';
build(1, lsl, lsr);
for(int j = l; j <= r; j++){
int ml = lsl, mr = lsr;
int ql = 0;
int qr = 0;
while(ml + 1 < mr){
int mid = (ml + mr) >> 1;
if(qx[mid] <= qx[j]){
ml = mid;
}
else{
mr = mid - 1;
}
}
for(int k = mr; k >= ml; k--){
if(qx[k] <= qx[j]){
qr = k;
break;
}
}
ml = lsl, mr = lsr;
while(ml + 1 < mr){
int mid = (ml + mr) >> 1;
if(qy[mid] <= qy[j]){
mr = mid;
}
else{
ml = mid + 1;
}
}
for(int k = ml; k <= mr; k++){
if(qy[k] <= qy[j]){
ql = k;
break;
}
}
// if(j == 240)
// cerr << "Quest " << ql << ' ' << qr << ' ' << j << '\n';
change(1, ql, qr, j);
}
preans(1);
lsl = l;
lsr = r;
}
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
// cerr << qx[i] << ' ' << qy[i] << ' ' << trudp[i] << '\n';
// }
cout << trudp[n];
return 0;
}
ARC198A
特判 \(1\) 然后直接输出偶数就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
void work(){
n = read();
if(n == 1){
cout << 1 << '\n';
cout << 1 << '\n';
return ;
}
cout << n / 2 << '\n';
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i += 2){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = 1;
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC198B
考虑满足条件的就合法:
- \(z > x\)
- \(y > x * 2\)
- \(2 | y\) 或者 \(z > 0\)
感觉挺幽默的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int x, y, z;
void work(){
x = read();
y = read();
z = read();
if(z > x){
cout << "No\n";
}
else if(y > x * 2){
cout << "No\n";
}
else if(y % 2 && z <= 0){
cout << "No\n";
}
else cout << "Yes\n";
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int TCS = read();
while(TCS --){
work();
}
return 0;
}
ARC198D
考虑并查集,然后我们考虑给一个路径两端点合并,然后考虑如何优化,可以直接判断如果合并过了那么就直接返回。
并查集过后答案就是好求的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io {
class In {
public:
template<typename T>
inline In &operator>>(T &x) {
x=0; bool f=0; char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9') f|=(c=='-'),c=getchar();
while(c>='0'&&c<='9') x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();
if(c=='.') {
c=getchar(); double dot=0.1;
while(c>='0'&&c<='9') x+=(c-'0')*dot,dot*=0.1,c=getchar();
} return (f?x=-x:x),*this;
}
inline In &operator>>(char &x) {while(isspace(x=getchar())); return *this;}
inline In &operator>>(char *x) {
char c=getchar(); while(isspace(c)) c=getchar(); while(!isspace(c)&&~c) *(x++)=c,c=getchar();
return *x=0,*this;
}
inline In &operator>>(string &x) {
char c=getchar(); x.clear();
while(isspace(c)) c=getchar(); while(!isspace(c)&&~c) x.push_back(c),c=getchar();
return *this;
}
inline In &operator>>(In &in) { return in;}
};
class Out {
private:
char buf[35]; short dot=6,top=0;
public:
template<typename T>
inline Out &operator<<(T x) {
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;
do { buf[++top]=x%10,x/=10;} while(x);
while(top) putchar(buf[top--]|'0'); return *this;
}
inline Out &operator<<(char c) {return putchar(c),*this;}
inline Out &operator<<(string x) {for(auto c:x) putchar(c); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(char *x) {while(*x) putchar(*(x++)); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(const char *x) {while(*x) putchar(*(x++)); return *this;}
inline Out &operator<<(double x) {snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"%.*lf",dot,x); return (*this)<<buf;}
inline Out &operator<<(Out &out) {return out;}
inline Out &setdot(const int n) {return dot=n,*this;}
};
In fin;
Out fout;
inline Out &setdot(const int n,Out& out=fout) {return fout.setdot(n),out;}
inline In &getline(char *x,In& in=fin) {
char c=getchar();
while(!(c==' '||!isspace(c))) c=getchar(); while(c==' '||!isspace(c)) (*x++)=c,c=getchar();
return *x=0,in;
}
inline In &getline(string &x,In& in=fin) {
char c=getchar(); x.clear();
while(!(c==' '||!isspace(c))) c=getchar(); while(c==' '||!isspace(c)) x.push_back(c),c=getchar();
return in;
}
}
using namespace io;
inline int read(){
int x; fin >> x; return x;
}
int n;
const int N = 3010;
int dep[N];
vector<int>e[N];
int fa[N][30];
void dfs(int now, int ff){
dep[now] = dep[ff] + 1;
fa[now][0] = ff;
for(int i = 1; i <= 12; i++){
fa[now][i] = fa[fa[now][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs(y, now);
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]){
swap(x, y);
}
int tmp = dep[x] - dep[y];
int now = 0;
while(tmp){
if(tmp & 1){
x = fa[x][now];
}
now ++ ;
tmp >>= 1;
}
if(x == y){
return x;
}
for(int i = 12; i >= 0; i--){
if(fa[x][i] != fa[y][i]){
x = fa[x][i];
y = fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
}
int getanc(int x, int anc){
for(int i = 12; i >= 0; i--){
if(dep[fa[x][i]] > dep[anc]){
x = fa[x][i];
}
}
return x;
}
bool flag[N][N];
char ch[N][N];
struct Dsu{
int fa[N];
void init(int x){
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
fa[i] = i;
}
}
int get(int x){
return (fa[x] == x) ? (x) : (fa[x] = get(fa[x]));
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = get(x), fy = get(y);
if(fx == fy) return ;
fa[fx] = fy;
}
}dsu;
void tag(int x, int y){
if(flag[x][y]) return ;
dsu.merge(x, y);
flag[x][y] = flag[y][x] = 1;
if(x == y) return ;
int z = LCA(x, y);
if(z != x && z != y){
tag(fa[x][0], fa[y][0]);
}
if(z == x){
tag(getanc(y, x), fa[y][0]);
}
if(z == y){
tag(getanc(x, y), fa[x][0]);
}
}
int col[N];
int dis[N][N];
struct Data{
int x, y;
};
int getm(int x, int y){
if(dis[x][y] != -1) return dis[x][y];
if(col[x] != col[y]){
return dis[x][y] = 0;
}
int z = LCA(x, y);
int res = 0;
if(z != x && z != y){
res = getm(fa[x][0], fa[y][0]);
}
if(z == x){
res = getm(getanc(y, x), fa[y][0]);
}
if(z == y){
res = getm(getanc(x, y), fa[x][0]);
}
return dis[x][y] = res;
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
dsu.init(n);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
flag[i][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
fin >> (ch[i] + 1);
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(ch[i][j] == '1'){
tag(i, j);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
col[i] = dsu.get(i);
}
memset(dis, -1, sizeof dis);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
dis[i][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(auto y: e[i]){
if(col[i] == col[y]){
dis[i][y] = 1;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
dis[i][j] = getm(i, j);
ans += dis[i][j];
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号